A car jack with a mechanical advantage of 8 needs to produce an output force of 400 N to raise a car. What input force is required?
Please answer to your best ability and please don't steal my points.
Answers
Answer:
533 n
Explanation:
The required input force is 50 N to produce desire output.
What is mechanical advantage?The mechanical advantage of a tool, mechanical device, or machine system is a measure of force amplification. To achieve the desired amplification in output force, the device trades off input forces against movement. The law of the lever serves as a model for this.
Mechanisms are machine components that are designed to manage forces and movement in this manner.
We know that:
Mechanical advantage = input force /Output force
Hence, the required input force = Output force from the jack ÷ Mechanical advantage of the jack
= 400 N ÷ 8
= 50 N.
Therefore, The required input force is 50 N.
Learn more about mechanical advantage here:
https://brainly.com/question/16617083
#SPJ2
Related Questions
Braden has a list of materials that he is trying to classify as being able to conduct electricity or as not being able to conduct electricity well. Of the following objects, which of them conduct electricity?
a set of keys
soda cans
a wooden spoon
I only
I and III
I and II
II and III
Answers
The soda cans and hardwood spoons in objects II and III can be categorised as having good electrical conductivity and having poor electrical conductivity, respectively.
Which electrical conduit is the best?Pure silver is the best conductor of electricity, but unsurprisingly, it is not one of the metals that is used to transmit electricity most frequently. There are a few disadvantages to the widespread use of purified silver.
Which metal conducts energy the best?Silver, copper, and gold are the metals with the highest conductivity. For instance, copper is widely used in metal wiring and is extremely conductive. Brass, on the other hand, has copper in it, but the other components of its composition make it less conductive.
To know more about electrical conductivity visit:-
https://brainly.com/question/29773282
#SPJ1
A 0. 850 kg air-track glider moving at 1. 75 m/s bumps into a 1. 45 kg glider initially at rest. If the collision is elastic, find the total kinetic energy after collision. If the collision is completely inelastic, find the total kinetic energy after collision
Answers
The final velocity of the 1.45 kg glider after the collision is approximately 0.3017 m/s.
The momentum before the collision is equal to the momentum after the collision, assuming no external forces act on the system.
The momentum (p) of an object is given by the product of its mass (m) and velocity (v):
p = m * v
Before the collision, the total momentum of the system is:
\(p_{initial} = p_1_{initial} + p_2_{initial}\)
= \(m_1 * v_1 + m_2 * v_2\)
After the collision, the 0.25 kg glider comes to a stop, so its final velocity (\(v_1_{final\)) is 0 m/s. The final velocity of the 1.45 kg glider (\(v_2_{final\)) is what we need to calculate.
Using the principle of conservation of momentum, the total momentum after the collision is:
\(p_{final} = p_1_{final} +\) \(p_2_{final\)
= \(m_1\) * \(m_2_{final\) + \(m_2\) *\(v_2_{final\)
= 0.25 kg * 0 m/s + 1.45 kg * \(v_2_{final\)
Since momentum is conserved, we can equate the initial momentum to the final momentum:
\(p_{initial} = p_{final}\)
\(m_1 * v_1_{initial} + m_2 * v_2_{initial} = m_1 * v_1_{final} + m_2 * v_2_{final}\)
0.25 kg * 1.75 m/s + 1.45 kg * 0 m/s = 0.25 kg * 0 m/s + 1.45 kg * \(v_2_{final\)
0.4375 kg·m/s = 1.45 kg * \(v_2_{final\)
Simplifying the equation, we find:
\(v_2_{final\) = 0.4375 kg·m/s / 1.45 kg
\(v_2_{final\) ≈ 0.3017 m/s
Therefore, the final velocity of the 1.45 kg glider after the collision is approximately 0.3017 m/s.
To know more about final velocity, here
brainly.com/question/9163788
#SPJ4
--The complete Question is, A 0.25 kg air-track glider moving at 1.75 m/s bumps into a 1.45 kg glider initially at rest. After the collision, the 0.25 kg glider comes to a stop. What is the final velocity of the 1.45 kg glider?--
What is quantum, in your own words but be more detailed.
Answers
Answer: Quantum is really just an amount of any physical entity involved in an interaction.
Explanation:
Sally traveled from Albany to Syracuse on Saturday. The trip took 3.5 hours and she traveled at
an average rate of 62 mph. How many miles did Sally travel? (Don't forget units.)
Answers
Answer:
attached below
Explanation:

turn your front wheels toward the curb when you park your car __________.
Answers
When you park your car, turn your front wheels towards the curb.When parking on a hill or incline, it is important to turn your front wheels towards the curb to prevent the car from rolling down the hill in case the brakes fail.
This is known as "curb parking" and is recommended by most driving experts and government agencies. Turning the wheels towards the curb means that if the car starts to roll, it will hit the curb and stop, instead of rolling into traffic or causing an accident. The direction in which you turn the wheels depends on whether you are parking uphill or downhill. When parking uphill, turn the wheels towards the curb and when parking downhill, turn the wheels away from the curb. In addition to turning the wheels, it is also important to engage the parking brake and put the car in gear or park to further prevent any unintended movement of the vehicle.
To learn more about incline refer:
https://brainly.com/question/13403572
#SPJ11
Part 1 of "Birth of the Earth" (video clips 1 and 2)
1. Rusty Schweickart said that astronauts on the international space station (ISS) orbit the Earth every
hours.
2. Finding the conditions that led to Earth's formation around other stars could mean that
could be forming elsewhere in the universe.
3. How far do we have to rewind the clock to the beginning of our solar system?
years.
4. Our Earth started out as a
of
5. The same process that started our solar system formation is happening 7,000 light-years away in the
6. To compress the gas and dust into dense stars and planets, takes a supremely powerful event. What kind of
event?
miles per hour following a supernova.
7. Super-heated plasma blasts into space at
8. A host of different factors have to line up to get a planet just like the Earth. What 3 things does Professor
Krauss say you have to have?
The right
the right
and the right kind of
9.
is a powerful
systems. But specks of dust are far too small to pull on each other to form planets.
force. It shapes galaxies and solar
10. Launching a half ton canister at over 100 miles an hour gives the dust particles just
gravity.
11. The Germans think that the force that binds the dust particles together is
force.
seconds of zero
12. Turning dust balls into rocks takes a whole new process. A cosmic
13. Eventually the
(baby planets) get to the size of asteroids, kilometers across.
14. Baby Earth is now the size of a few city blocks. Big enough for a new force to take charge. That force is
15. So this formation process which was taking a long time to get to size where gravity kicks in, suddenly gets
kicked into overdrive and the
grows very rapidly.

Answers
Rusty Schweickart said that astronauts on the international space station (ISS) orbit the Earth every 90 minutes.
How to explain the questionsFinding the conditions that led to Earth's formation around other stars could mean that habitable planets could be forming elsewhere in the universe.
How far do we have to rewind the clock to the beginning of our solar system? About 4.6 billion years.
Our Earth started out as a ball of dust and gas.
The same process that started our solar system formation is happening 7,000 light-years away in the Orion Nebula.
To compress the gas and dust into dense stars and planets, takes a supremely powerful event, supernova explosion is needed.
Super-heated plasma blasts into space at millions of miles per hour following a supernova.
A host of different factors have to line up to get a planet just like the Earth. What 3 things does Professor Krauss say you have to have? The right size, the right distance from the sun, and the right kind of atmosphere.
Gravity is a powerful force. But specks of dust are far too small to pull on each other to form planets.
Launching a half ton canister at over 100 miles an hour gives the dust particles just enough gravity.
The Germans think that the force that binds the dust particles together is electrostatic force.
Turning dust balls into rocks takes a whole new process. A cosmic ray collision.
Eventually the planetesimals (baby planets) get to the size of asteroids, kilometers across.
Baby Earth is now the size of a few city blocks. Big enough for a new force to take charge. That force is gravity.
So this formation process which was taking a long time to get to size where gravity kicks in, suddenly gets kicked into overdrive and the protoplanet grows very rapidly.
Learn more about astronaut on
https://brainly.com/question/24204882
#SPJ1
List out of how animals and plants can cause weathering.
Plants
Answers
A spring with a spring constant 2.3 N/cm
is compressed 32 cm and released. The 9 kg
mass skids down the frictional incline of height
50 cm and inclined at a 15◦ angle.
The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s^2
The path is frictionless except for a distance of 0.6 m along the incline which has a
coefficient of friction of 0.5

Answers
The values into the acceleration equation, we get: a = (24.9 N - 44.1 N) / 9 kg = -2.3 m/s^2. Therefore, the mass is decelerating along the incline.
What is acceleration described as?The speed at which velocity varies with regard to time. Since acceleration has both a magnitude and a direction, it is a vector number.
Let's first determine the mass's potential energy at the summit of the incline:
PE = mgh = 9 kg * 9.8 m/s² * 0.5 m = 44.1 J
PE = (1/2)kx² = (1/2) * 2.3 N/cm * (32 cm / 100)²
= 11.8 J
KE = (1/2)mv²
The work done by friction is given by:
W = f * d * cosθ
Therefore, the kinetic energy of the mass just as it reaches the bottom of the incline is:
KE = PE(spring) - W(friction) = 11.8 J - 2.4 J = 9.4 J
Substituting the given values into the kinetic energy equation and solving for v, we get:
9.4 J = (1/2) * 9 kg * v²
v = √(9.4 J / (4.5 kg)) = 1.84 m/s
Finally, we can calculate the acceleration of the mass along the incline using the equation:
a = (f_net - f_friction) / m
f_friction = μ_k * m * g = 0.5 * 9 kg * 9.8 m/s²= 44.1 N
The net force acting on the mass along the incline is given by:
f_net = m * g * sinθ = 9 kg * 9.8 m/s² * sin(15°) = 24.9 N
Substituting the values into the acceleration equation, we get:
a = (24.9 N - 44.1 N) / 9 kg
= -2.3 m/s².
To know more about acceleration visit:-
https://brainly.com/question/12550364
#SPJ1
what is electric switch
Answers
Answer:
A device that is used to break an electric circuit is called electric switch
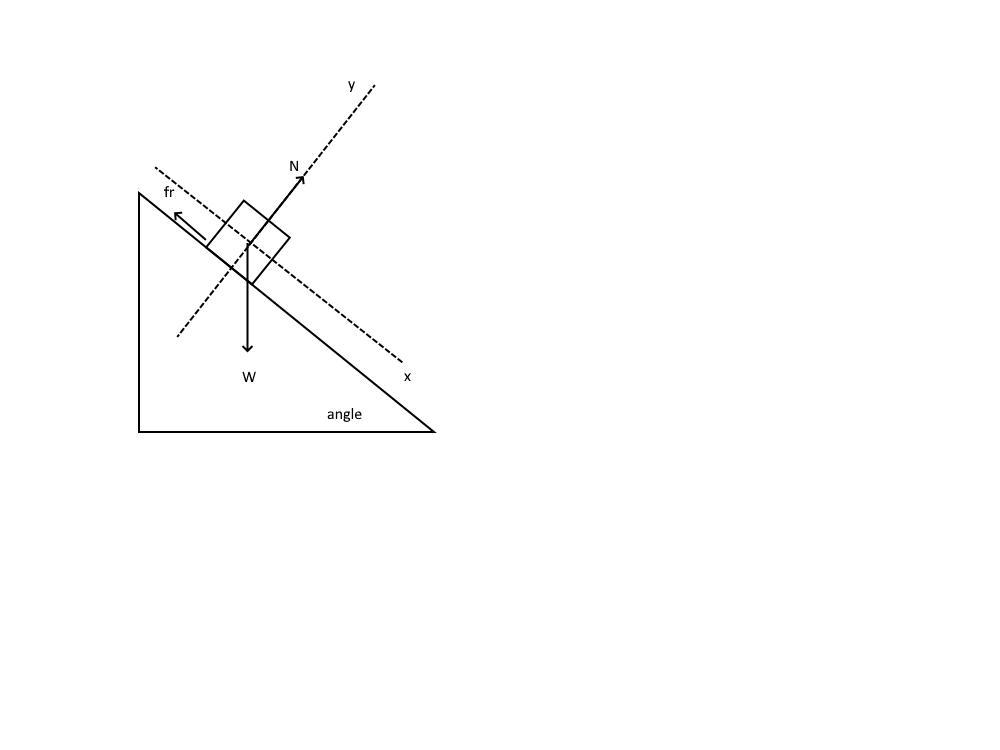
A student strikes a block at the bottom of a ramp, giving it an initial speed vo up the ramp, as shown at right. There is friction between the ramp and the block as it slides a distance x up the ramp and then slides back down. On the dots below, which represent the block as it is sliding up the ramp and down the ramp, draw and label
the forces (not components) exerted on the block. Represent each force by a distinct arrow starting on, and
pointing away from, the dot. The dashed lines are drawn at the same angle as the surface of the ramp.
Up the Ramp
Down the Ramp
Answers
Newton's second law allows to find the results for the free body diagram of the movements on the ramp are;
In the attachments we have the graphs of the forces for the case of raising and lowering the ramp.
Newton's second law indicates that the net force is proportional to the product of the body's mass and its acceleration.
A free-body diagram is a schema of the force where the details of the bodies are omitted.
Reference systems are coordinate systems with respect to which measurements and vector decompositions will be carried out.
In the attachments the part of going up the ramp the x axis is parallel and the positive direction in the direction of movement:
Raising the positive x-axis ramp up Going down the ramp positive x axis going ramp down.
The positive direction of the y-axis is perpendicular to the ramp.
We can see that the force of the weight and the normal remain fixed in any of the movements, but the friction force that opposes the movement changes direction.
In conclusion using Newton's second law we can find the results for the free body diagram of the movements on the ramp are;
In the attachments we have the graphs of the forces for the case of raising and lowering the ramp.Learn more here: brainly.com/question/8522449

Make the following conversion:
A) 60∘C into F
B)70∘C into K
C) 303∘K into C
D) 140∘F into C
If you don't know what I mean by C, F, K and ∘ it meaning is:
C- Celsius
F- Fahrenheit
K- kelvin
∘- degree sign
Answers
Answer:
Kelvin to Celsius: C = K - 273 (C = K - 273.15 if you want to
if the universe is 13.8 billion years old, how can we see 46 billion light years away
Answers
if the universe is 13.8 billion years old, how can we see 46 billion light years away because space has also been expanding?
When total distance to distant cosmic objects like galaxies is taken into account, their measurement is referred to as cosmological distance. This distance accounts for universe's ongoing expansion. Space itself stretches as a result of the universe's expansion, causing two things' distances to grow even when they are not physically moving apart.
One may observe objects that are currently positioned farther distant than the age of the universe thanks to this stretching of space. For a very long time, light emanating from these far-off objects has been travelling through space. Light has essentially travelled a greater distance than the actual physical distance between us and the object because of the universe's expansion during that time.
Read more about universe on:
https://brainly.com/question/28365362
#SPJ4
error using save must be a string scalar or character vector.
Answers
The "Error using save must be a string scalar or character vector" message indicates that the input argument for the save function is not a valid string.
The save function is used to save variables in a MATLAB workspace to a file. The error message "Error using save must be a string scalar or character vector" typically occurs when the input argument for the save function is not a valid string. This means that the filename argument that is passed to the save function should be a character array or string scalar. If the filename argument is not a string, MATLAB will generate the error message.
To resolve this error, you should ensure that the filename argument is a valid string. If you are passing a variable that contains the filename, you should ensure that it is a character array or string scalar before passing it to the save function. One way to do this is by using the char or string functions to convert the variable to a string. Alternatively, you can specify the filename directly as a string when calling the save function. It is also important to ensure that the filename does not contain any special characters or invalid characters that are not allowed in filenames.
To learn more about string refer:
https://brainly.com/question/27832355
#SPJ11
If you weigh 38 kilograms on your bathroom scale, your weight in space will be ________.
38 kilograms
more than 38 kilograms
less than 38 kilograms
38 kilograms minus your clothes
Answers
Answer:
Less than 36kilo's
Explanation:
The print on the package of 100-watt Wave Electric light bubs states that these bulbs have an average life of 750 hours. Also assume that the lives of all such bulbs have a normal distribution with standard deviation of 50 hours. How many bulbs in a consignment of 700 could be expected to have a life of 710 to 830 hours? 0.7333 0.1571 513 955 110
Answers
Option c is correct. Approximately 513 bulbs in the consignment can be expected to have a life between 710 and 830 hours.
For solving this problem, need to calculate the z-scores for the given range of bulb lives and then use these z-scores to find the corresponding probabilities from the standard normal distribution table.
The z-score can be calculated using the formula:
z = (x - μ) / σ,
where x is the value, interested in, μ is the mean, and σ is the standard deviation. In this case, the mean (μ) is 750 hours and the standard deviation (σ) is 50 hours.
For a life of 710 hours:
z = (710 - 750) / 50 = -0.8
For a life of 830 hours:
z = (830 - 750) / 50 = 1.6
Next, look up the probabilities associated with these z-scores in the standard normal distribution table. The probability associated with a z-score of -0.8 is 0.2119, and the probability associated with a z-score of 1.6 is 0.9452.
For finding the number of bulbs expected to have a life between 710 and 830 hours, calculate the difference between these probabilities:
0.9452 - 0.2119 = 0.7333
Therefore, approximately 0.7333 * 700 = 513 bulbs in the consignment can be expected to have a life between 710 and 830 hours.
Learn more about bulbs here:
https://brainly.com/question/30880419
#SPJ11
i) ii) iii) 12 V What is the total resistance of the circuit? 1+1 30+20. - A 26 30 600 What is the current reading of the ammeter? 600=12 What is the power of the 30 ohm resistor? 144 = 48 30 P = √² 12² - 144 R 30 iv) Explain what is meant by the term e.m.f of the battery. 20. Ω > 30. Ω
Answers
The answer for (iv) is;
E.M.F of the battery refers to the chemical energy in the battery that is being converted into electrical energy for the flow of electrons to carry current in a circuit.
Paco was driving his scooter west with an initial velocity of 4 m/s. He accelerates at 0. 5 m/s2 for 30 seconds. What is his final velocity? 2 m/s 8 m/s 19 m/s 60 m/s.
Answers
Answer:
Final velocity = 19 m/s
Explanation:
Initial velocity (u) = 4 m/s
Acceleration (a) = 0.5 m/s²
Time (t) = 30 s
Final velocity (v) = ?
In this question, you must use the formula:
v = u + at
Substitute the values into the formula.
v = 4 + (0.5 × 30)
v = 4 + 15
v = 19 m/s
The Figure 6A-2 Stüve diagram includes lines representing the adiabatic processes of dry (unsaturated) and saturated air. Click on Figure 6A-2 to print or draw on it digitally. Figure 6A-2. Vertical atmospheric (Stüve) chart with adiabats. On the Stüve diagram, the solid, straight green lines from upper left to the lower right represent the dry adiabatic lapse rate: the temperature change of an unsaturated air parcel undergoing vertical motion in the atmosphere. The dashed, curved blue lines from upper left to lower right represent the temperature change of saturated air undergoing vertical motion, the saturated adiabatic lapse rate. Locate an air parcel with a temperature of 17
∘
C and a pressure of 1000mb by placing a dot on the chart on the 1000mb horizontal line where 17
∘
C would occur. 7. If this air rises as unsaturated (dry) air from 1000mb, determine its temperature at 500mb by following the solid, straight green dry adiabatic lapse rate line from the starting point, up to 500mb. At 500mb, the temperature of the unsaturated air parcel is about
∘
C. a. −5 b. −35 c. −45 8. If this air rises as saturated air from 1000mb, determine its temperature at 500mb by following the dashed, curved blue saturated adiabatic lapse rate line passing from the starting point up to 500mb. At 500mb, the saturated air parcel's temperature is approximately
∘
C. a. −15 b. −25 c. −35 9. At 500mb, the temperature of the unsaturated air parcel is the temperature of the saturated air parcel. a. lower than b. the same as c. higher than 10. This comparison demonstrates that rising unsaturated, clear air cools than rising saturated, cloudy air over the same pressure change. a. less b. more
Answers
When an air parcel rises from 1000mb to 500mb, unsaturated air cools to around -35°C, while saturated air cools to approximately -25°C.
On the Stüve diagram, the solid, straight green lines represent the dry adiabatic lapse rate, which indicates the temperature change of an unsaturated air parcel undergoing vertical motion in the atmosphere. The dashed, curved blue lines represent the temperature change of saturated air undergoing vertical motion, known as the saturated adiabatic lapse rate.
To determine the temperature of the air parcel at 500mb when it rises as unsaturated air, we follow the solid, straight green dry adiabatic lapse rate line from the starting point (17°C, 1000mb) up to 500mb. Following this line, we find that at 500mb, the temperature of the unsaturated air parcel is approximately -35°C.
On the other hand, if the air parcel rises as saturated air, we follow the dashed, curved blue saturated adiabatic lapse rate line from the starting point (17°C, 1000mb) up to 500mb. By following this line, we determine that at 500mb, the temperature of the saturated air parcel is approximately -25°C.
Comparing the temperatures of the unsaturated and saturated air parcels at 500mb, we find that the temperature of the unsaturated air parcel (-35°C) is lower than the temperature of the saturated air parcel (-25°C). Therefore, at 500mb, the temperature of the unsaturated air parcel is lower than the temperature of the saturated air parcel.
This comparison demonstrates that rising unsaturated, clear air cools more than rising saturated, cloudy air over the same pressure change.
To learn more about unsaturated air click here:
brainly.com/question/30457844
#SPJ11
If you know the answer please answer the following question down in the picture below.

Answers
Please help thank you!

Answers
Answer:
mass, weight
Explanation:
mass is constant, and weight is dependant on your location
Answer:
I think d
Explanation:
because distance j
has to be the last one that's the only one with distance
A rectangular container of base 50 cm by 30 cm is filled with water to a
depth of 5 cm. How much is the pressure exerted at the base?
(Take pw= 1000 kg/m and g =10 m/s?)
Answers
Answer:
please find attached pdf
Explanation:
Given values are:
Height,
5 cm or, 0.05 mBase of container,
50 cmThe pressure exerted will be:
→ \(P = hdg\)
By substituting the values, we get
\(= 0.05\times 1000\times 10\)
\(= 500 \ Nm\)
Thus the above answer is correct.
Learn more about pressure here:
https://brainly.com/question/26018692
Which of the following forms matter?
A. Proteins
B.atoms
C.cells
D. DNA
Answers
Answer:b) atoms
Explanation:which are in turn made up of protons, neutrons and electrons
Answer:
B. Hope it helped brainiest plz
Explanation:
B. is that answer
A car speeds over a hill past point A, as shown in the figure. What is the maximum speed the car can have at point A such that its tires will not leave the track? Round to one decimal place and include units. Image:

Answers
Answer:
see explanations below
Explanation:
At the point when the car leaves the track, the reaction on the road is zero, meaning that the centrifugal force equals the gravitation force, namely
mv^2/r = mg
Solve for v in SI units
v^2 = gr = 9.81 m/s^2 * 14.2 m = 139.302 m^2/s^2
v = sqrt(139.302) = 11.8 m/s
Answer: at 11.8 m/s (26.4 mph) car will leave the track.
what is the probable origin of the dark colored features in this image of the surface of mars? it is about 20 km across.
Answers
The probable origin of the dark colored features in the surface of mars for about 20 kilometers across are dunes shaped by the wind.
Explanation:
Dunes are familiar features on Earth and they also occur on Mars, Venus, and Saturn's moon, Titan. What all these bodies have in common is an atmosphere, plus substantial amounts of loose sand-size particles. Of all the extraterrestrial dunes scientists know about, those on Mars are the most closely studied.
A dune is a heap of sand piled up and shaped by the wind. (Underwater dunes exist on Earth, but we can ignore these in regard to today's Mars.) The word "dune" implies a substantial size — at least several meters (yards) high. But small ripples of sand only a few centimeters (inches) high are made in the same way from the same materials. The difference lies mainly in the supply of particles and how much time the wind has had to work on them.
To learn more
https://brainly.com/question/7410453
3. Someone said, "The goal of the railroad is not to have a
better Operating Ratio, it’s to make more money." Explain how it’s
possible to make more money with a worse Operating Ratio?
Answers
While a better Operating Ratio generally indicates higher efficiency and profitability, there are circumstances where focusing on other strategic initiatives, such as infrastructure investments or pricing strategies, can result in increased revenue and ultimately lead to higher profits, even with a temporarily worse Operating Ratio.
While it may seem counterintuitive, it is indeed possible to make more money with a worse Operating Ratio in certain situations. The Operating Ratio is a financial metric used in the railroad industry to measure the efficiency of operations, calculated by dividing operating expenses by operating revenue and expressing it as a percentage. A lower Operating Ratio indicates better cost control and higher profitability.
However, there are scenarios where focusing solely on achieving a better Operating Ratio may not necessarily maximize profits. For instance, a railroad company might strategically invest in infrastructure upgrades or equipment purchases that temporarily increase operating expenses but lead to long-term revenue growth. These investments can be essential for expanding capacity, improving service quality, and attracting more customers, ultimately generating higher overall revenue despite a temporary increase in operating expenses.
Additionally, a railroad may adopt pricing strategies to maximize revenue, even if it negatively impacts the Operating Ratio. This could involve offering discounted rates or incentives to secure long-term contracts with high-volume customers, resulting in lower operating revenue per unit but ensuring a steady and predictable stream of business.
Learn more about Operating Ratio here:
brainly.com/question/24077007
#SPJ11
What must happens within earth for a volcano to form
Answers
Answer:
Volcanoes on Earth form from rising magma. ... Magma also rises when these tectonic plates move toward each other. When this happens, part of Earth's crust can be forced deep into its interior. The high heat and pressure cause the crust to melt and rise as magma.
An object of mass 1.5 kg is moving forwards along the floor against an applied force of
40.0 N [backwards]. If the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.25, determine the
acceleration of the object.
Answers
Answer:
The acceleration of the object is -29.12 m/s².
Explanation:
The acceleration of the object can be calculated by Newton's second law:
\( \Sigma F = ma \)
\( - F - F_{\mu} = ma \)
\( - F - \mu mg = ma \)
Where:
F: is the applied force = 40.0 N
μ: is the coefficient of kinetic friction = 0.25
m: is the mass of the object = 1.5 kg
g: is the acceleration due to gravity = 9.81 m/s²
a: is the acceleration =?
\( a = \frac{- F - \mu mg}{m} = \frac{-40.0 N - 0.25*1.5 kg*9.81 m/s^{2}}{1.5 kg} = -29.12 m/s^{2} \)
The minus sign is because means that the object is decelerating due to the applied force and the friction.
Therefore, the acceleration of the object is -29.12 m/s².
I hope it helps you!
Need help ASAP!!! Need graphs drawn and the answers to the question on top of each table

Answers
Answer:
1) 8s
2).8cm/s/s
3)3.5?
Explanation:
not sure about answer 3 FYI
Jason hits a volleyball so that it moves with an initial velocity of 6.0 m/s
straight upward. If the volleyball starts from 2.0 m above the floor,
how long will it be in the air before it strikes the floor?
Answers
Answer:
Approximately \(1.5\; {\rm s}\).
(Assumptions: \(g = 9.81\; {\rm m\cdot s^{-2}}\); air resistance on the volleyball is negligible.)
Explanation:
Under the assumptions, acceleration of the volleyball would be \(a = (-g) = (-9.81)\; {\rm m\cdot s^{-2}}\) during the entire flight. (This value is negative since the ball is accelerating downwards- toward the ground.)
By the time the volleyball hits the ground, the volleyball would be at a position \(2.0\; {\rm m}\) below where it was launched. In other words, the (vertical) displacement of the volleyball during the entire flight would be \(x = (-2.0)\; {\rm m}\). (Negative since the ball is below where it was launched.)
Apply the SUVAT equation \((v^{2} - u^{2}) = 2\, a\, x\) to find the velocity of the volleyball right before hitting the ground. In this equation:
\(v\) is the velocity of the volleyball right before hitting the ground,\(u = 6.0\; {\rm m\cdot s^{-1}}\) is the initial velocity of the volleyball,\(a = (-9.81)\; {\rm m\cdot s^{-2}}\) is the acceleration of the volleyball, and\(x = (-2.0)\; {\rm m\cdot s^{-1}}\) is the displacement of the volleyball during the flight.Rearrange this equation and solve for the velocity right before landing, \(v\). Note that because \(v\!\) is raised to the power of \(2\) in \((v^{2} - u^{2}) = 2\, a\, x\), both \(v = \sqrt{u^{2} + 2\, a\, x}\) and \(v = -\sqrt{u^{2} + 2\, a\, x}\) could satisfy this equation. However, \(v\!\!\) needs to be negative since the volleyball would be travelling downwards before reaching the ground.
Therefore, right before reaching the ground, velocity of the volleyball would be:
\(\begin{aligned} v &= -\sqrt{u^{2} + 2\, a\, x \\ &= -\sqrt{(6.0)^{2} + 2\, (-9.81)\, (-2.0)} \; {\rm m\cdot s^{-1}} \\ &\approx (-8.67)\; {\rm m\cdot s^{-1}}\end{aligned}\).
In other words, velocity of this volleyball has changed from \(u = 6.0\; {\rm m\cdot s^{-1}}\) (upwards) to \(v \approx (-8.67)\; {\rm m\cdot s^{-1}}\) (downwards) during this flight. Divide the change in the velocity \((v - u)\) by the rate of change in velocity \(a = (-9.81)\; {\rm m \cdot s^{-2}}\) to find the duration of this flight:
\(\begin{aligned}t &= \frac{v - u}{a} \\ &\approx \frac{(-8.67) - 6.0}{(-9.81)}\; {\rm s} \\ &\approx 1.5\; {\rm s}\end{aligned}\).
A prairie dog runs 60 meters west, and then 80 meters northwest.
Find the components in the horizontal and vertical direction.
Find the magnitude of the resultant vector, correct units, the angle, and the direction words (e.g. south of east, north of west, etc.).
Answers
23 km when x1+ x2 = 0.87/10. is the main answer.
The size of a vector in the x-direction is expressed by its x-component, also known as its horizontal component. The size of a vector in the y-direction is represented by its y-component, also known as its vertical component. A projectile's trajectory is determined by velocity in two dimensions. The projectile's x and y components each represent its horizontal and vertical motion, respectively. Meters are the units used to indicate both horizontal and vertical distances (m).
A+B=A= (x1+x 2) i+20 jx1+x2/20
=tan60 = 0.5/0.87.
A=x1 i+10 j.
B=x2 i+10 j.
A+ B = (.87/10) 2 + 20 /2
= 23 km when x1+ x2 = 0.87/10.
Learn more about Component here-
https://brainly.com/question/27893112
#SPJ9