A very long, straight wire carries a constant current. The magnetic field a distance d from the wire and far from its ends varies with distance d according to
A) d^-3
B) d
C) d^2
D) d^-1
E) d^-2
Answers
A very long, straight wire carries a constant current. The magnetic field a distance d from the wire and far from its ends varies with distance d according to d^-1. The correct option is D.
This is because the magnetic field around a long straight wire carrying a constant current is directly proportional to the current and inversely proportional to the distance from the wire. This relationship is known as the Biot-Savart law. Mathematically, it can be written as B = (μ₀/4π) * (I/d), where B is the magnetic field, I is the current, d is the distance from the wire, and μ₀ is the magnetic constant.
When we rearrange the equation to isolate d, we get d = (μ₀/4π) * (I/B). Since I and μ₀ are constant, we can see that d is inversely proportional to B. This means that as the distance from the wire increases, the magnetic field strength decreases proportionally to the inverse of the distance.
Therefore, the correct answer is D) d^-1, which represents an inverse relationship between the magnetic field and the distance from the wire.
For more such questions on Magnetic field.
https://brainly.com/question/28449593#
#SPJ11
Related Questions
An engine raises 100kg of water through a height of 60m in 20secs.What is the power of the engine
Answers
P = mgh/t
p=power = ?
m=mass = 100kg
h=height = 60m
t=time = 20s
g=10m/s
p=mgh/t
p= (100 × 10 × 60) / 20
= (60000) / 20
=3000 W
What do you notice about the beam of light? Think about the direction and the speed of the waves.
Answers
The beam of light travels in a straight line, with electromagnetic waves oscillating transversely. The speed of light is constant, and the wavelength and frequency of light waves determine its color and other properties.
The beam of light consists of electromagnetic waves traveling in a straight line. These waves oscillate perpendicular to the direction of propagation, creating a transverse wave. Light waves travel at a constant speed in a vacuum, which is approximately 299,792 kilometers per second (or about 186,282 miles per second). This speed is often denoted as "c" and is a fundamental constant in physics.Light waves exhibit characteristics such as wavelength and frequency. Wavelength refers to the distance between successive wave crests or troughs, while frequency is the number of wave cycles passing through a point in one second. The speed of light is related to its wavelength and frequency through the equation c = λν, where c represents the speed, λ is the wavelength, and ν is the frequency.
Different colors of light are characterized by their wavelengths, with shorter wavelengths corresponding to higher frequencies and vice versa. For example, red light has a longer wavelength and lower frequency compared to blue light.
For more such questions on electromagnetic
https://brainly.com/question/24319848
#SPJ8
A runner achieves a velocity of 11.1 m/s, 9 sec after he begins. What is his acceleration? What distance did he cover?
Answers
Answer:
Explanation: velocity = distance/time
velocity (v) = 11.1m/s
time =9 sec
distance =velocity x time
distance = 11.1 x 9 =99.9m
Answer: Acceleration of the runner =1.23 m/s²
The distance covered by the runner will be 99.9 m
Explanation: Given,
Velocity=11.1 m/s²
Time= 9 seconds
Acceleration=?
Acceleration = Velocity/Time
Acceleration = 11.1 / 9
Acceleration = 1.23 m/s²
The distance covered by the runner= 11.1 m/s² × 9 seconds
The distance covered by the runner= 99.9 m
A damped harmonic oscillator, with a damping force proportional to its speed, is oscillating with an amplitude of 0.500 cm at When t
Answers
The solution to this equation depends on the specific values of m, c, and k. It can be solved analytically or numerically to determine the behavior of the oscillator over time.
The given question is incomplete and lacks the necessary information to provide a specific answer. It is unclear what information is provided about the damped harmonic oscillator. To answer the question accurately, I would need additional details, such as the equation of motion for the damped harmonic oscillator, the damping constant, and the initial conditions.
However, I can provide a general explanation of a damped harmonic oscillator. In a damped harmonic oscillator, the damping force is proportional to the velocity of the oscillator. This force opposes the motion of the oscillator, causing it to gradually lose energy and decrease in amplitude over time.
To analyze the behavior of a damped harmonic oscillator, we need to consider the equation of motion. Typically, the equation is expressed as:
\(m * d^2x/dt^2 + c * dx/dt + k * x = 0\)
where m is the mass of the oscillator, c is the damping constant, k is the spring constant, x is the displacement from the equilibrium position, and t is time.
The solution to this equation depends on the specific values of m, c, and k. It can be solved analytically or numerically to determine the behavior of the oscillator over time.
To know more about velocity visit:
brainly.com/question/30559316
#SPJ11
8. Noticing how much food is on your lunch
tray is a quantitative observation because
Answers
Answer:
you are making an observation that uses numbers.
Explanation:
Urgent! Which is not an example of work? Question 2 options: pushing a box across the floor picking up a box off the floor raising a barbell over your head trying to push a rock that never moves
Answers
Answer:
trying to push a rock that never moves
Explanation:
The diagram below shows a circuit
containing two lamps. What will
ammeter 3 read?

Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
Given:
E₁ = E₂ = E₃ = 1.5 V
I₁ = 2 A
I₂ = 0.5 A
_________
I₃ - ?
Current strength in the common circuit:
I₁ = 2 V
The lamps are connected in parallel.
I₁ = I₂ + I₃
Ammeter 3 read:
I₃ = I₁ - I₂ = 2V - 0.5V = 1.5 V
Answer:1.5
Explanation:
on a certain day the average air temperature was 30 degree celsius and the dew point is 8 degree celsius .if the stp of water vapour is 15.6mmHg at 30 degree celsius and 9.5mmHg of 8g.find the percentage relative density of the air
Answers
To find the percentage relative density of the air, we need to calculate the vapor pressure and the saturation vapor pressure at the given temperature.
Given:
Average air temperature = 30°C
Dew point = 8°C
STP of water vapor at 30°C = 15.6 mmHg
Vapor pressure at 8°C = 9.5 mmHg
The vapor pressure at the given temperature is 9.5 mmHg, and the saturation vapor pressure at the average air temperature of 30°C is 15.6 mmHg.
To calculate the percentage relative density of the air, we use the formula:
Percentage Relative Density = (Vapor Pressure / Saturation Vapor Pressure) * 100
Substituting the values:
Percentage Relative Density = (9.5 mmHg / 15.6 mmHg) * 100
Calculating the value:
Percentage Relative Density = 60.8974358974359%
Therefore, the percentage relative density of the air is approximately 60.90%.
Learn more about relative density here:
brainly.com/question/28858363
#SPJ11
I NEED HELP!!!!
The three areas of discipline are ________.
isolation
instruction
punishment
admonition
nurture
Answers
Answer:
Instruction, admonition, nurture
Explanation:
the practice of training people to obey rules or a code of behavior, using punishment to correct disobedience:how would the intensity of sunlight at earth's surface change if earth were 2 times farther from the sun than it is currently?
Answers
If earth were 2 times farther from the sun, the intensity will be decreased by a factor of 2.25.
Intensity is the power per unit area. it is a physical quantity. Brightness refers to how the human visual system perceives light and is not a physical quantity.
In direct sunlight, the measured lux can reach 130,000 40 when the sun is at the zenith (straight up). On most sunny days (without direct light), the illuminance is typically 10,000 to 25,000 lux. On cloudy days, the incident light can only reach 1000 lux, and at dusk, it is 10 lux 40.
we know that the intensity of sunlight at the earth's surface is given by
I = P/4πr²
P is the power radiated by the sun
r is the distance between the earth and the sun.
if the earth were 1.5 times farther away hence
I' = P/4π(1.5)r²
= 1/2.25 × (P/4πr²)
I' = 1/2.25
So, the intensity will be decreased by a factor of 2.25
here note that P remains constant and intensity is simply proportional to 1/r²
Hence, the intensity will be decreased by a factor of 2.25
Learn more about intensity here:-https://brainly.com/question/3917542
#SPJ4
Thirteen resistors are connected across points A and B as shown in the figure. If all the resistors are
accurate to 2 significant figures, what is the equivalent resistance between points A and B?
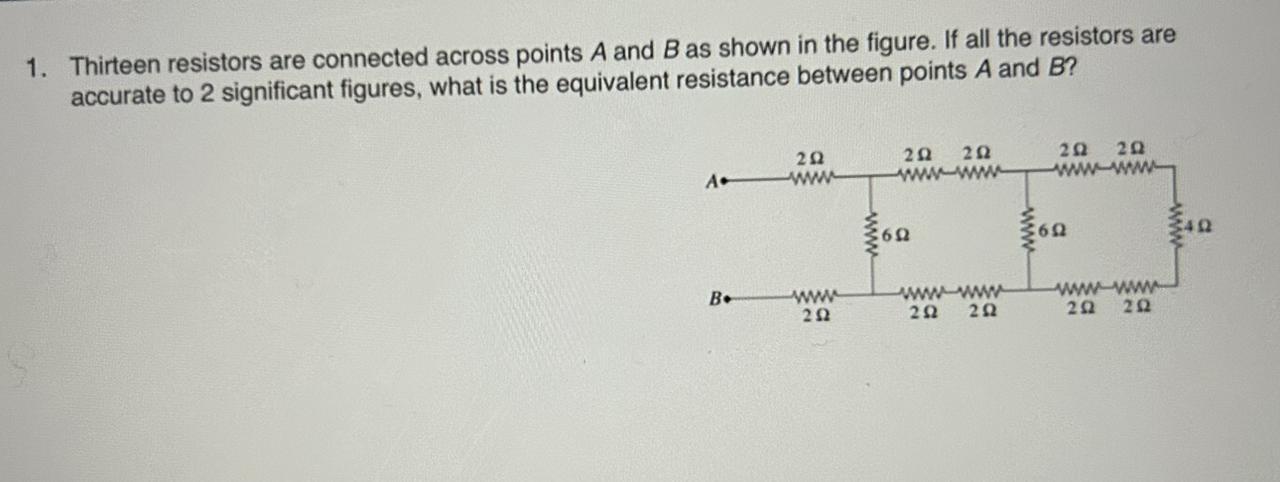
Answers
The equivalent resistance between points A and B in the diagram is 22 Ω
How do I determine the equivalent resistance?We shall begin by obtaining the equivalent resistance in parallel (i,e the three 6 Ω resistor). Details below:
Resistor 1 (R₁) = 6 ΩResistor 2 (R₂) = 6 ΩResistor 3 (R₃) = 6 ΩEquivalent resistance (Rₜ) = ?1/Rₜ = 1/R₁ + 1/R₂ + 1/R₃
1/Rₜ = 1/6 + 1/6 + 1/6
1/Rₜ = 3/6
1/Rₜ = 1/2
Rₜ = 2 Ω
Finally, we shall determine the equivalent resistance between A and B (i.e series arrangement). Details below:
Resistor 1 (R₁) = Resistor 2 (R₂) = ... = Resistor (R₁₁) = 2 ΩEquivalent resistance (R) =?R = R₁ + R₂ + R₃ + R₄ + R₅ + R₆ + R₇ + R₈ + R₉ + R₁₀ + R₁₁
R = 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2
R = 22Ω
Thus, we can conclude that the equivalent resistance is 22 Ω
Learn more about resistance:
https://brainly.com/question/13691672
#SPJ1
Compare and contrast angular momentum and linear momentum. Include two ways that they are alike and two ways that they are different. Be sure to discuss how mass affects both angular and linear momentum.
Answers
Angular momentum and linear momentum are two physical concepts that have some similarities and differences. They are both measures of motion, but they describe different types of motion.
Similarities:
Both angular and linear momentum are conserved in isolated systems, meaning that the total amount of momentum in a system remains constant unless acted upon by an external force.Both angular and linear momentum are vector quantities, meaning they have both magnitude and direction.Differences:
Angular momentum is a measure of an object's rotational motion, while linear momentum is a measure of an object's translational motion.Angular momentum depends on the object's mass and its distance from the axis of rotation, while linear momentum depends only on the object's mass and velocity.What is angular momentum and linear momentum?The term angular momentum and linear momentum are similar in that they are both conserved and vector quantities, but they differ in that angular momentum describes rotational motion and linear momentum describes translational motion.
In summary, angular momentum depends on both mass and distance from the axis of rotation, while linear momentum depends only on mass and velocity.
Learn more about angular momentum from
https://brainly.com/question/4126751
#SPJ1
Two 5.0-cm-diameter metal disks separated by a0.61-mm-thick piece of Pyrex glass are charged to a potential difference of 1300V . (Dielectric constant of the Pyrex glass is Pkpyrex=4.7.)
A) What is the surface charge density on the disks?
B) What is the surface charge density on the glass?
Answers
The surface charge density on the disks is, \(4.3910^{-5} C/m^2\). The surface charge density on the glass is, σ = \(-4.39\times 10^{-5} C/m^2\).
We can solve this problem using the capacitance equation for a parallel plate capacitor with a dielectric material between the plates:
C = εA/d
where C is the capacitance, ε is the permittivity of the dielectric material, A is the area of the plates, and d is the distance between the plates.
The potential difference V between the plates is related to the charge Q on the plates and the capacitance C by:
V = Q/C
The capacitance of the parallel plate capacitor is:
C = εA/d = \((4.78.85\times 10^{-12} \text{ F/m})\times \dfrac{\pi (0.025 m)^2}{0.00061 m}\)
\(= 4.22 \times 10^{-11} F\)
The charge on each plate is:
Q = CV
\(= (4.22\times 10^{-11} F)(1300 V)\\\\ = 5.48\times10^{-8} C\)
The surface charge density on each disk is:
\(\sigma = Q/A\\\\ = 2\dfrac{Q}{\pi r^2}\\\\ = \dfrac{2(5.4810^{-8} C)}{\pi (0.025 m)^2}\\\\ = 4.3910^{-5} C/m^2\)
The surface charge density on the Pyrex glass is equal and opposite to the surface charge density on the disks. This is because the total charge on the system must be conserved. Therefore, the surface charge density on the Pyrex glass is:
σ = \(-4.39\times 10^{-5} C/m^2\)
To know more about capacitor, here
brainly.com/question/31627158
#SPJ4
the maximum value of a short circuit current from line-to-neutral grounded
Answers
The maximum value of a short circuit current from line-to-neutral grounded will depend on various factors such as the voltage level of the electrical system.
The impedance of the circuit, the available fault current, and the protective devices that are in place to limit the current.In a typical residential or commercial electrical system in the United States, the maximum short circuit current from line-to-neutral grounded is typically around 10,000 to 20,000 amps for a 120/240 volt system. However, in larger industrial or utility systems with higher voltage levels, the short circuit current can be much higher and can exceed several hundred thousand amps.It is important to note that short circuit currents can cause significant damage to electrical equipment and can pose a serious safety hazard to people who come into contact with the electrical system.
To know more about electrical visit :
https://brainly.com/question/31668005
#SPJ11
to increase the range of the water, isabella places her thumb on the hose hole and partially covers it. assuming that the flow remains steady, what fraction f of the cross-sectional area of the hose hole does she have to cover to be able to spray her friend?
Answers
The fraction is f = 84.196 % which is equivalent to 84%
We know that the value of acceleration due to gravity is
g = 9.8m/s^2
y₀ = 1 m
x = 10 m
and the time taken is not given
thus time taken = t sec
A₀ = π 1.5²
Thus the equation becomes;
y = y₀ + ut + 1/2 gt²
⇒ 0 = y₀ - 1/2 gt²
⇒ t = \(\sqrt{\frac{2y.}{g} }\)
After substituting the values we get
⇒ t = 0.45152 seconds
Thus x = x₀ + vt
10 = 0 + 0.45152 v
On further solving we get
v = 22.14741 m/s
From continuity equation we get
Av = A₀v₀
On substituting the values we get
⇒ A = 1.11706 cm^2
Thus the fraction is given by
f = ( A₀ - A ) / A₀ X 100 %
After substituting the values we get
f = 84.196 % which is equivalent to 84%
To know more about continuity equation you may visit the link :
https://brainly.com/question/8226176
#SPJ4
If you move 50 meters in 10 seconds, what is your speed
Answers
Explanation:
My answer didn't save :(
5 meters per second
11.1845 miles per hour
Explanation:50/10=5
In experiment 1, a block of mass m is attached to the end of vertical spring of spring constant k0 with its free end at vertical position l0, as shown in figure 1. The mass of the spring is considered to be negligible. When the block is attached to the spring and is at rest at the block-spring’s equilibrium position, the spring is stretched so that its end is at a new position l1, as shown in figure 2. The block is then pulled down to a new vertical position l2 and then released from rest so that the block-spring system oscillates. Assume that the reference line for zero gravitational potential energy of the system is at the lowest point in the system’s vertical displacement from equilibrium. The experiment is assumed to be performed near earth’s surface. What is the magnitude of the change in potential energy of the block-spring system when it travels from its lowest vertical position to its highest vertical position?.
Answers
The magnitude of the change in potential energy of the block-spring system when it travels from its lowest vertical position to its highest vertical position is mg(l₁ + l₀ + x - l₂)
The gravitational potential energy of the block is given by mgh, where m is the mass of the block, g is the acceleration due to gravity and h is the height of the block from the reference line. Let us assume that the block moves from its lowest position, l₂ to its highest position, l₁ and that the elongation of the spring in this position is x.
The total length of the spring when it is elongated by x is given by (l₀ + x)
Therefore, the gravitational potential energy of the block when it is at its lowest position, l₂ is given by mgl₂
And, the gravitational potential energy of the block when it is at its highest position, l₁ is given by mg(l₁ + l₀ + x)
Therefore, the change in potential energy of the block-spring system when it travels from its lowest vertical position to its highest vertical position is given by:
mg(l₁ + l₀ + x) - mgl₂
= mg(l₁ + l₀ + x - l₂)
The magnitude of the change in potential energy of the block-spring system when it travels from its lowest vertical position to its highest vertical position is mg(l₁ + l₀ + x - l₂).
To know more about block-spring system, refer
https://brainly.com/question/14156520
#SPJ11
A long, horizontal wire Ab rests on the surface of a table and carries a current I. A horizontal wire CD is vertically above wire AB , and is free to slide up and down on the two vertical metal guides C and D ( as shown in Fig) .Wire CD is connected through the sliding contacts to another wire that also carries a current I , opposite in direction to the current in wire AB . The mass per unit length of the wire CD is λ. To what equilibrium height h will the wire CD rise. assuming that magnetic force on it is wholly due to current in wire AB ?
Answers
The equilibrium height to which the wire CD will rise is given by the expression h = μ₀I² / 2π λg
What is magnetic field ?A region in which the force of magnetism acts is known as the magnetic field, and it surrounds magnetic materials or a moving electric charge. Moving magnetic dipoles and electric charges produce a magnetic field, which acts as a force field on other nearby magnetic dipoles and moving charges.
Magnetic field at a distance h produced by a current carrying wire
B = μ₀I/ 2πh
Magnetic force due to the present current carrying wire can be calculated by the formula
F = B I L
And we also know that F = mg
On equating these mg = B I L
( μ₀I/ 2πh ) I = ( m/ I ) g = λg
thus we get the value of h as
h = μ₀I² / 2π λg
Thus, the equilibrium height to which the wire CD will rise is given by the expression h = μ₀I² / 2π λg .
To know more about magnetic field you may visit the link:
https://brainly.com/question/23096032
#SPJ4
7. Two bikes travelling in the same direction move at a speed of 30 km/hr. The bikes are separated by a distance of 5 km. What would the speed of the car travelling in the opposite direction be if it meets these bikes at an interval of 4 minutes?
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
Call the bike on the right A
Call the bike on the left B
The car begins it's time when it passes A
4 minutes later, it passes B.
But B has moved in 4 minutes and that is the key to the problem.
How far has B moved.
t = 4 minutes = 4/60 hours = 1/15 of an hour.
d = ?
rate = 30 km / hr
d = r * t
d = 30 km/hr * 1/15 hours = 2 km
The distance between the bikes is 5 km.
So the car has traveled 5 - 2 = 3 km
d = 3 km
r = ?
t = 4 minutes = 1/15 hour
r = d/t = 3/(1/15)= 3 / 0.066666666 = 45 km/hr.
The effort needed when a simple machine is used is best described by which of these statements?
Answers
Answer:
effort effort effort effort effort effort
26. How many covalent bonds does water have?
a.1 b.2 c.3 d.4 e.5
Answers
Answer:
(b) 2
Explanation:
base your answer to the question on the information given. a 1,000-kilogram car traveling with a velocity of 20 meters per second decelerates uniformly at -5.0 meters per second^2 until it comes to rest. what is the total distance the car travels as it decelerates to rest?
Answers
Answer:
40 meters
Explanation:
To solve this, we will use the motion formula \(v^{2} =u^{2} +2as\), where v is the final speed, u is the initial speed, a is the acceleration, and s is the distance. We know:
u= 20m/s
a= - 5m/s^2 (note the minus sign because we are decelerating)
v= 0m/s (our final speed will be 0 because we want to come to a stop)
Now plug in these values into the formula:
\(v^{2} =u^{2} +2as\)
\(0^{2} =20^{2} +2(-5)s\)
\(0 =400-10s\)
\(10s=400\)
\(s=40\\\)
A 25 W fluorescent light bulb emits 5.0 J of thermal energy each second. What is the efficiency of the fluorescent light? I just want an explanation.
Answers
Answer:
80%
Explanation:
what are metalloids?
Answers
Answer:
a type of chemical element whose properties are intermediate between those of metals and nonmetals.
what force caused the dust and particles to clump together?
Answers
The force that causes dust and particles to clump together is known as the cohesive force.
The force that causes dust and particles to clump together is known as the cohesive force. Cohesive forces are attractive forces between the molecules of the particles. These forces arise due to the presence of intermolecular forces such as Van der Waals forces, hydrogen bonds, and dipole-dipole interactions. When these cohesive forces are stronger than the forces keeping the particles apart, the particles come together and stick to each other, forming clumps or aggregates. In the case of the formation of larger objects, such as planets or moons, the gravitational force also plays a role in pulling together smaller clumps of material to form larger bodies.
But scientists have long been baffled by precisely how dust particles adhere to one another. Electrostatic forces would create clumps the size of pebbles, much to how dust bunnies develop under a couch.
for such more question on cohesive force
https://brainly.com/question/11885065
#SPJ4
Describe the tide requirements necessary to create a tidal power plant.
Answers
Answer:
La energía mareomotriz se produce gracias al movimiento generado por las mareas, esta energía es aprovechada por turbinas, las cuales a su vez mueven la mecánica de un alternador que genera energía eléctrica, finalmente este último esta conectado con una central en tierra que distribuye la energía hacia la comunidad.
Why are astronomers interested in building observatories capable of detecting neutrinos, cosmic rays, and gravitational waves?.
Answers
Astronomers are interested in building observatories capable of detecting neutrinos, cosmic rays, and gravitational waves because these are not forms of light, they can provide information about the objects that emit them that light cannot.
Astronomers study the heavens at X-ray wavelengths using satellites and earth-orbiting observatories. Because X-rays and gamma rays are absorbed high in the Earth's atmosphere, instruments to observe this radiation must be placed in orbit above the atmosphere.
Astronomy relies on electromagnetic radiation to help us see the universe. It allows us to see (visual light) on Earth. Pulsars, for example, emit X-rays but not visible light, which is how we know they exist. Neutrinos are also made up of energy, but they are made up of radioactive decay.
This enables scientists to measure them despite the fact that they can pass through almost anything without being noticed. Gravitational waves are disturbances caused by the curvature of space that expand at a specific rhythm or "force" that travels at the speed of time. Because they can all be measured without being light, they are ideal for being found in space to create more knowledge about the universe.
Learn to know more about astronomers at
https://brainly.com/question/1003405
#SPJ4
what does it mean mechanical advange is less than one?
Answers
Answer:
this happens when the input force is greater than the output force
HOPE IT HELPED YOU...
me·chan·i·cal ad·van·tage
noun
the ratio of the force produced by a machine to the force applied to it, used in assessing the performance of a machine.
A 16.0 kg child on roller skates, initially at rest, rolls 2.0 m down an incline at an angle of 20.0° with the horizontal. If there is no friction between incline and skates, what is the kinetic energy of the child at the bottom of the incline?
Answers
The kinetic energy of the child at the bottom of the incline is 106.62 J.
The given parameters:
Mass of the child, m = 16 kgLength of the incline, L = 2 mAngle of inclination, θ = 20⁰The vertical height of fall of the child from the top of the incline is calculated as;
\(sin(20) = \frac{h}{2} \\\\h = 2 \times sin(20)\\\\h = 0.68 \ m\)
The gravitational potential energy of the child at the top of the incline is calculated as;
\(P.E = mgh\\\\P.E = 16 \times 9.8 \times 0.68\\\\P.E = 106.62 \ J\)
Thus, based on the principle of conservation of mechanical energy, the kinetic energy of the child at the bottom of the incline is 106.62 J since no energy is lost to friction.
Learn more about conservation of mechanical energy here: https://brainly.com/question/332163
How much force would be needed to cause a 4.6kg object to accelerate at 9.2m/s/s? *
Answers
Answer:
42.32 NExplanation:
The force acting on an object given it's mass and acceleration can be found by using the formula
force = mass × acceleration
From the question we have
force = 4.6 × 9.2
We have the final answer as
42.32 NHope this helps you