explain what happens within the structure of a molecule during an ultraviolet/visual spectroscopy experiment
Answers
The electromagnetic spectrum's shorter wavelength, higher energy radiation in the UV (200-400 nm) and visible (400-700 nm) ranges causes many organic molecules to go through electronic transitions, while interaction with infrared light causes molecules to go through vibrational transitions.
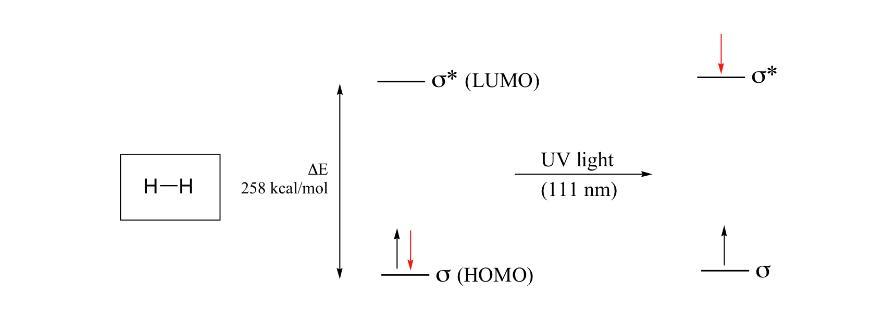
What is Electronic transitions?Electrons in atoms are located in atomic orbitals, as you might remember from CHE 103. In a molecule, electrons occupy molecular orbitas in a similar way. They are known as HOMO (Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital) and LUMO, respectively. A transition from HOMO to LUMO is possible for electrons in molecules.The molecule will absorb light of a wavelength with energy equal to the HOMO-LUMO energy gap, E, and use this energy to bump one of the HOMO's electrons to the LUMO. These electron transitions take place for some molecules in the UV-visible spectrum of the electromagnetic spectrum. Chromophores are molecules or portions of molecules that strongly absorb light in the UV-vis range. These electrical changes The majority of organic and biological chemists find that studying compounds with conjugated systems is where UV-vis spectroscopy is most helpful.The HOMO-LUMO energy gap shrinks in molecules with extended pi systems to the point where absorption occurs in the visible spectrum rather than the UV.With its system of 11 conjugated double bonds, beta-carotene absorbs light with wavelengths in the visible spectrum's blue region while allowing other visible wavelengths, primarily those in the red-yellow region, to pass through. Carrots have an orange color because of this.To Learn more about electronic transitions refer to:
https://brainly.com/question/29330696
#SPJ4
Related Questions
303.8 liters volume will be occupied by 217.0 grams of methane gas at STP.
True
False
Answers
Answer:
False
Explanation:
It will occupy 271.7
what mass (in grams) of NH4Cl is needed to prepare 350 mL of a 0.25 M ammonium chloride solution
Answers
Answer:
4.70 grams of NH4Cl is needed to prepare 350 mL of a 0.25 M ammonium chloride solution.
We need approximately 4.68 grams of NH4Cl to prepare a 0.25 M ammonium chloride solution with a volume of 350 mL.
To determine the mass of NH4Cl needed to prepare the solution, we us use the formula:
m=M x V x MM ... (i)
where,
m= mass in grams
M=molarity of solution
MM= molar mass of compound
V= volume in litres
The number of moles of NH4Cl needed can be calculated using:
Moles = Molarity x Volume ...(ii)
Moles = 0.25 mol/L x 0.350 L
Moles = 0.0875 mol
Hence we can replace M x V with number of moles in equation i.
The molar mass of NH4Cl is :
Molar mass of NH4Cl = (1 x 14.01 g/mol) + (4 x 1.01 g/mol) + (1 x 35.45 g/mol)
Molar mass of NH4Cl = 53.49 g/mol
We have all the variables
Putting them in equation i.
Hence,
Mass (g) = Moles x Molar mass
Mass (g) = 0.0875 mol x 53.49 g/mol
Mass (g) = 4.68 g
Therefore, you would need approximately 4.68 grams of NH4Cl to prepare a 0.25 M ammonium chloride solution with a volume of 350 mL.
To learn more about Stoichiometry,
https://brainly.com/question/16060223
a gas mixture being used to simulate the atmosphere of another planet consists of 359 mg of methane, 212 mg of argon, and 256 mg of nitrogen. the partial pressure of nitrogen at 308 k is 16 kpa. calculate the total pressure of the mixture. answer in units of kpa
Answers
The total pressure of the gas mixture is approximately 68.97 kPa.
To calculate the total pressure of the gas mixture, we need to consider the partial pressures of each component.
Given:
Mass of methane (CH4) = 359 mg
Mass of argon (Ar) = 212 mg
Mass of nitrogen (N2) = 256 mg
Partial pressure of nitrogen (N2) = 16 kPa
Step 1: Convert the masses of each component to moles using their respective molar masses:
Molar mass of methane (CH4) = 16.04 g/mol
Molar mass of argon (Ar) = 39.95 g/mol
Molar mass of nitrogen (N2) = 28.01 g/mol
Number of moles of methane (nCH4) = (359 mg / 1000) / (16.04 g/mol)
Number of moles of argon (nAr) = (212 mg / 1000) / (39.95 g/mol)
Number of moles of nitrogen (nN2) = (256 mg / 1000) / (28.01 g/mol)
Step 2: Calculate the mole fractions of each component:
Mole fraction of methane (χCH4) = nCH4 / (nCH4 + nAr + nN2)
Mole fraction of argon (χAr) = nAr / (nCH4 + nAr + nN2)
Mole fraction of nitrogen (χN2) = nN2 / (nCH4 + nAr + nN2)
Step 3: Calculate the partial pressures of each component:
Partial pressure of methane (PCH4) = χCH4 * Total pressure
Partial pressure of argon (PAr) = χAr * Total pressure
Partial pressure of nitrogen (PN2) = χN2 * Total pressure
Since the partial pressure of nitrogen is given as 16 kPa, we can substitute the values into the equation above to solve for the total pressure:
PN2 = χN2 * Total pressure
16 kPa = χN2 * Total pressure
Step 4: Solve for the total pressure (Total pressure = PN2 / χN2):
Total pressure = 16 kPa / χN2
Let's perform the calculations:
Step 1:
nCH4 = (359 mg / 1000) / (16.04 g/mol) ≈ 0.022 mol
nAr = (212 mg / 1000) / (39.95 g/mol) ≈ 0.0053 mol
nN2 = (256 mg / 1000) / (28.01 g/mol) ≈ 0.0091 mol
Step 2:
χCH4 = nCH4 / (nCH4 + nAr + nN2) ≈ 0.615
χAr = nAr / (nCH4 + nAr + nN2) ≈ 0.153
χN2 = nN2 / (nCH4 + nAr + nN2) ≈ 0.232
Step 3:
PCH4 = χCH4 * Total pressure
PAr = χAr * Total pressure
PN2 = χN2 * Total pressure
Step 4:
Total pressure = PN2 / χN2 = (16 kPa) / (0.232) ≈ 68.97 kPa
Therefore, the total pressure of the gas mixture is approximately 68.97 kPa.
Learn more about Total pressure from the link given below.
https://brainly.com/question/30668745
#SPJ4
Number of sodium atom(s) in salt (NaCl)
Answers
Answer:
NaCl consists of one atom each of sodium and chlorine. Hence, each molecule of NaCl has 2 atoms total.
Explanation:
Answer: There is only one atom of sodium in NACL
Explanation: But in total there two atoms because 1 sodium and 1 chlorine added all together
HOPE THIS HELPS!!!!
the benzoic acid/benzoate buffer ( ka = 6.5x10-5) has been measured to have a ph of 5.6. calculate the ratio of [c7h6o2] to [c7h5o2-]
Answers
the benzoic acid/benzoate buffer ( ka = 6.5x10-5) has been measured to have a ph of 5.6. calculate the ratio of [c7h6o2] to [c7h5o2-]:- the ratio of [C7H6O2] to [C7H5O2-] in the benzoic acid/benzoate buffer is 1:25.1.
Given the information, we need to calculate the ratio of benzoic acid ([C7H6O2]) to benzoate ([C7H5O2-]) in the buffer solution.
1. First, we'll use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation, which is:
pH = pKa + log ([A-]/[HA])
In this case, pH = 5.6 and pKa = -log(Ka) = -log(6.5 x 10^-5)
2. Calculate the pKa:
pKa = -log(6.5 x 10^-5) ≈ 4.19
3. Now, plug the pH and pKa values into the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation:
5.6 = 4.19 + log ([C7H5O2-]/[C7H6O2])
4. Solve for the ratio ([C7H5O2-]/[C7H6O2]):
5.6 - 4.19 = log ([C7H5O2-]/[C7H6O2])
1.41 = log ([C7H5O2-]/[C7H6O2])
5. Use the antilog to solve for the ratio:
[C7H5O2-]/[C7H6O2] = 10^1.41 ≈ 25.5
So, the ratio of [C7H5O2-] to [C7H6O2] in the buffer solution is approximately 25.5.
to learn more about benzoic acid click here:
brainly.com/question/24052816
#SPJ11
significant figures to 2.3 x 4.50
Answers
Answer:
10.35= 4 sig figs but change it to 2 since it's 2.3 is the lowest number
10.
hope this helps
have a good day :)
Explanation:
Could someone help me answer these questions with the answer and typed steps for how each answer was found? I asked this question previously but, I could not read the handwritten answer.
7. A 25 g soil sample was extracted with 75 mL of NH4OAc (pH 7.0), and the filtrate was analyzed
on an atomic absorption unit. The following results were obtained:
100 mg/L Ca2+, 45 mg/L Mg2+, 85.5 mg/L K+, 94.2 mg/L Al3+ and 8.0 mg/L H+.
a. What is the CEC in cmol(+)/kg for this sample?
b. What is the % B.S. for this soil?
c. What is the % acid saturation for this soil sample?
Answers
The CEC for this soil sample is 675.2 cmol(+)/kg.
The % Base Saturation for this soil sample is approximately 136.62%.
The % Acid Saturation for this soil sample is approximately 60.55%.
To calculate the CEC, % Base Saturation (B.S.), and % Acid Saturation for the given soil sample:
a. Calculation of CEC (Cation Exchange Capacity):
CEC is the sum of exchangeable cations in the soil. From the given results, we have:
CEC = Ca2+ + Mg2+ + K+ + Al3+
CEC = (100 mg/L + 45 mg/L + 85.5 mg/L + 94.2 mg/L) / (25 g / 1000)
CEC = 168.7 mg / (25 g / 1000)
CEC = 675.2 cmol(+)/kg
b. Calculation of % Base Saturation (B.S.):
% B.S. represents the percentage of CEC occupied by base cations. In this case, we consider Ca2+, Mg2+, and K+ as base cations. The formula to calculate % B.S. is:
% B.S. = (Ca2+ + Mg2+ + K+) / CEC * 100
% B.S. = (100 mg/L + 45 mg/L + 85.5 mg/L) / (168.7 cmol(+)/kg) * 100
% B.S. = 230.5 mg / (168.7 cmol(+)/kg) * 100
% B.S. = 136.62%
c. Calculation of % Acid Saturation:
% Acid Saturation represents the percentage of CEC occupied by acid cations, in this case, H+ and Al3+. The formula to calculate % Acid Saturation is:
% Acid Saturation = (H+ + Al3+) / CEC * 100
% Acid Saturation = (8.0 mg/L + 94.2 mg/L) / (168.7 cmol(+)/kg) * 100
% Acid Saturation = 102.2 mg / (168.7 cmol(+)/kg) * 100
% Acid Saturation = 60.55%
Please note that the given values were in milligrams per liter (mg/L), and the CEC and % Saturation values were calculated assuming a conversion from mg/L to cmol(+)/kg using the mass of the soil sample (25 g).
TO know more about CEC (Cation Exchange Capacity)
https://brainly.com/question/30689981
#SPJ11
2. What could you do to make sure the law of conservation of mass is shown?
Answers
Answer:
To ensure the law of conservation of mass is demonstrated, you can conduct an experiment that involves a chemical reaction where the total mass of the reactants is equal to the total mass of the products. Here's an example experiment showcasing this principle:
Materials needed:
- A balance or scale
- Two clear containers
- Baking soda (sodium bicarbonate)
- Vinegar (acetic acid)
- A balloon
Procedure:
1. Set up the balance or scale and make sure it is calibrated properly.
2. Place one of the clear containers on the balance and record its mass.
3. Add a measured amount of baking soda to the container and record the new total mass.
4. Attach the balloon to the mouth of the container without allowing any gas to escape.
5. Carefully pour a measured amount of vinegar into the balloon through the container's opening without mixing it with the baking soda.
6. Observe the reaction between the vinegar and baking soda. The reaction will produce carbon dioxide gas, which will inflate the balloon.
7. Once the reaction is complete and the balloon has stopped inflating, carefully remove it from the container.
8. Place the second clear container on the balance and record its mass.
9. Pour the contents of the balloon (carbon dioxide gas) into the second container.
10. Weigh the second container with the carbon dioxide gas and record the new total mass.
Observation and Conclusion:
By comparing the initial mass of the baking soda and the vinegar with the final mass of the carbon dioxide gas and the container, you will observe that the total mass of the reactants (baking soda and vinegar) is equal to the total mass of the products (carbon dioxide gas and container). This demonstrates the law of conservation of mass, which states that mass cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction, only rearranged.
By carefully measuring the masses before and after the reaction, you visually and quantitatively show that the total mass remains constant throughout the process. This experiment reinforces the fundamental principle of the law of conservation of mass, emphasizing that matter is conserved in chemical reactions, even when it undergoes changes in form or state.
Which of the following is/are considered alcohols?
a CH3OH
b CH3CH2OH
C CH3CH2CH2OH
d All of the above
Answers
Answer: THE ANSWER IS D
Explanation:
an alcohol is a hydrocarbon chain with an hydroxyl group (OH)
A, B, AND C ARE ALL ALCOHOLS, SO THE ANSWER IS D
If a substance has an enthalpy of condensation of -1. 46 kj/g and an enthalpy of sublimation of 4. 60 kj/g, what is its enthalpy of freezing in kj/g?
Answers
The enthalpy of freezing of the substance is 6.06 kj/g.
Enthalpy is a measure of the total heat content of a system, including its internal energy and the energy required to perform work. The enthalpy of a substance can change due to different physical or chemical processes, such as melting, boiling, or sublimation.
The enthalpy of freezing can be calculated using the enthalpy of condensation and enthalpy of sublimation as follows,
Enthalpy of freezing = Enthalpy of sublimation - Enthalpy of condensation
Enthalpy of freezing = 4.60 kj/g - (-1.46 kj/g)
Enthalpy of freezing = 4.60 kj/g + 1.46 kj/g
Enthalpy of freezing = 6.06 kj/g
To know more about the enthalpy, here
brainly.com/question/13996238
#SPJ4
Which of the following would support the theory that electrons are identical for all elements?
Answers
Answer:
what are the following?
When thinking about genetic engineering in agriculture, which type of issue has the most direct consequences?
O economical issues
O political issues
o social issues
O environmental issues
Answers
Answer:
environmental issues
Explanation:
Gasoline is a product of crude oil, compressed organic matter formed from accumulations of algae millions of years ago. Some places are now substituting ethanol in place of gasoline. Ethanol is formed by fermenting certain foods like corn with yeast, then extracting the alcohol that is given off. Which of these energy sources is nonrenewable?
Answers
Answer:
Gasoline/oil is not renewable
Write the correct abbreviation for each metric unit.
1) Kilogram __ 4) Milliliter __ 7) Kilometer __ 2) Meter 5) Millimeter __
8) Centimeter __ 3) Gram __ 6) Liter __ 9) Milligram __
Answers
The correct abbreviation for each metric unit is:
Kilogram - kg, Milliliter - ml, Kilometer- Km, Meter- m, Millimeter - mm, Centimeter - cm, Gram - g, Liter - L, and Milligram - mg.
What is the metric system?The metric system can be described as a system of measurement that succeeded the decimalized system based on the meter. Each of the fundamental dimensions can be expressed by a single base unit of measure.
For quantities derived from the base units of the system, units derived from the base units are used such as the square meter being the derived unit for the area, a quantity derived from length.
Metric units can be described as units based on the meter, gram, or second and decimal multiples or sub-multiples of these. The units of the International System of Units (SI). By extension, they involve units of electromagnetism from the CGS units and SI units systems.
Learn more about Metric units, here:
https://brainly.com/question/19483018
#SPJ1
What type of bond is Ca + Ar?
Answers
Hey there!
Well, “Ca” is ‘Calcium’ the atomic number of calcium is 20 on the periodic table & “Ar” is ‘Argon’ and atomic number of argon is 18. But with Argon being a noble gas and it’s outer electron shell being already full of electrons with non to spare or receive, and Calcium only having 2 valence electrons.
The chemical bond would most likely be nothing even in a hypothetical situation
Good luck on your assignment & enjoy your day!
~Amphitrite1040:)

Askin cell divides to make a new skin cell. Which component of cell theory does this best illustrate?
O All living things are made of cells.
O Cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things.
O All cells come from other cells.
O Cells are generated from nonliving materials.
Answers
Answer:
all cells come from other cells
HELP ASAP
Two isotopes of the FAKE element Sz have the following abundances;
Seabreezium-71 75%
Seabreezium - 76 25%
What is the average atomic mass?
(Limit your answer to the TENTHS place.)
Answers
Two isotopes of the FAKE element Sz, Average mass of Seabreezium is equal to 199.77625 amu.
Given that Two isotopes of of Sz is given as :
Seabreezium-71 75%
Seabreezium - 76 25%
Now,
Isotopes of Seabreezium is given as:
Seabreezium-271Seabreezium - 269Now,
1st isotope = 71 75% of 271
= 194.44amu
2nd isotope = 76 25% of 269
= 205.11 amu
Now,
Average Mass of Seabreezium = 205.11 + 194.44/2
Average Mass of Seabreezium = 199.77625 amu
Thus, from the above conclusion we can say that, Average mass of Seabreezium is equal to 199.77625 amu.
Learn more about Average Mass here :https://brainly.com/question/24186882
#SPJ13
d
C
r
f
Mol → Mol
MS
2Fe + 3Cl₂ → 2FeCl3
1. How many moles of chlorine are needed to produce 15.7 moles of FeCl3?
2. How many moles of iron are needed to react with 4.5 moles of chlorine?
Mol → Mass (grams)
2KCIO32KCI + 30₂
3. Calculate the mass of oxygen produced from the decomposition of 3.98 mol of
potassium chlorate.
4. How many grams of KCl are made if the reaction produces 7.2 mol of oxygen?
Mass (grams) → Mol
H₂ + Cl₂ → 2HCI
5. Calculate the number of moles of HCI made from 230. g of hydrogen.
6. If 5.8 g of hydrogen is used in the reaction, how many mol of chlorine are needed?
Mass (grams)→ Mass (grams)
2Ag + Cl₂ → 2AgCl
7. Calculate the mass of silver needed to react with chlorine to produce 84 g of silver
chloride.
8. How many grams of silver are needed to produce 6.8

Answers
Using the balanced chemical equation, 2Fe + 3Cl₂ → 2FeCl₃, we can see that 2 moles of Fe react with 3 moles of Cl₂ to produce 2 moles of FeCl₃.
Therefore, to produce 15.7 moles of FeCl₃, we need (15.7 mol FeCl₃) x (3 mol Cl₂ / 2 mol FeCl₃) = 23.55 moles of Cl₂.
Using the same balanced chemical equation, we can see that 2 moles of Fe react with 3 moles of Cl₂. Therefore, to react with 4.5 moles of Cl₂, we need (4.5 mol Cl₂) x (2 mol Fe / 3 mol Cl₂) = 3 moles of Fe.
Using the balanced chemical equation, 2KClO₃ → 2KCl + 3O₂, we can see that 2 moles of KClO₃ decompose to produce 3 moles of O₂. Therefore, to calculate the mass of O₂ produced from 3.98 mol of KClO₃, we need to convert the number of moles of KClO₃ to moles of O₂: (3.98 mol KClO₃) x (3 mol O₂ / 2 mol KClO₃) = 5.97 mol O₂.
Next, we can use the molar mass of O₂ to calculate the mass produced: (5.97 mol O₂) x (32.00 g/mol O₂) = 191.04 g O₂.
Using the same balanced chemical equation, we can see that 2 moles of KCl are produced for every 3 moles of O₂. Therefore, to produce 7.2 mol of O₂, we need (7.2 mol O₂) x (2 mol KCl / 3 mol O₂) = 4.8 mol KCl.
Next, we can use the molar mass of KCl to calculate the mass produced: (4.8 mol KCl) x (74.55 g/mol KCl) = 357.84 g KCl.
Using the balanced chemical equation, we can see that 1 mole of H₂ reacts with 1 mole of Cl₂ to produce 2 moles of HCl. Therefore, to calculate the number of moles of HCl produced from 230 g of H₂, we need to convert the mass of H₂ to moles: (230 g H₂) / (2.016 g/mol H₂) = 114.18 mol H₂.
Next, we can use the mole ratio to calculate the number of moles of HCl produced: (114.18 mol H₂) x (2 mol HCl / 1 mol H₂) = 228.36 mol HCl.
Using the same balanced chemical equation, we can see that 1 mole of H₂ reacts with 1 mole of Cl₂. Therefore, to react with 5.8 g of H₂, we need (5.8 g H₂) / (2.016 g/mol H₂) = 2.88 mol H₂.
Next, we can use the mole ratio to calculate the number of moles of Cl₂ needed: (2.88 mol H₂) x (1 mol Cl₂ / 1 mol H₂) = 2.88 mol Cl₂.
According to the balanced chemical equation, 2 moles of Ag react with 1 mole of Cl₂ to produce 2 moles of AgCl. Therefore, to produce 84 g of AgCl, we can calculate the number of moles of AgCl: (84 g) / (143.32 g/mol AgCl) = 0.5866 mol AgCl. From this, we can calculate the number of moles of Ag
To know more about molar mass, visit:
https://brainly.com/question/22997914
#SPJ1
BRAINLIEST AND FIVE STARS WITH A THANKS IF YOU ATLEAST ANSWER
Why are sedimentation ponds useful for reducing the affects of soil erosion?
A. They provide a place to raise fish that can be used to replace fish harmed by sedimentation.
B. They provide a water source that can be used for irrigation of crops.
C. They provide a place to collect soil sediment so that it doesn’t reach ponds, lakes and rivers.
D. They help transport soil sediments to rivers, ponds and lakes.
Answers
Answer:
I think D
Explanation:
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Sediment, as a physical pollutant, impacts receiving waters in the following principal ways: High levels of turbidity limit penetration of sunlight into the water column, thereby limiting or prohibiting growth of algae and rooted aquatic plants.
5. An aluminium kg. Determine a. 3 kg m-³ b. 12 kg m-³ cube of side 2 m has mass 24 the density of aluminium. c. 24 kg m-³ -3 d. 48 kg m-³
Answers
density = mass / volume
a. Density of aluminium = 3 kg/m³
We are given that the mass of the cube of aluminium is 24 kg. So, we can calculate its volume using the formula:
volume = mass / density
volume = 24 / 3
volume = 8 m³
Since the cube has a side length of 2 meters, its volume is given by:
volume = side³
8 = 2³
Therefore, the density of the cube is the same as the density of aluminium, which is 3 kg/m³.
b. Density of aluminium = 12 kg/m³
We are given that the mass of the cube of aluminium is 24 kg, and its side length is 2 meters. So, we can calculate its volume as:
volume = side³
volume = 2³
volume = 8 m³
Now we can use the formula to calculate the density:
density = mass / volume
density = 24 / 8
density = 3 kg/m³
The density of the cube is the same as the density of aluminium, which is 3 kg/m³.
c. Density of aluminium = 24 kg/m³
Using the same approach as before, we can calculate the volume of the cube:
volume = mass / density
volume = 24 / 24
volume = 1 m³
Since the side length of the cube is not given, we cannot calculate it directly. However, if we assume that the cube is a regular cube, then its volume is given by:
volume = side³
Therefore, we can calculate the side length as:
side = cube root of (volume)
side = cube root of (1)
side = 1 meter
So, if the cube is a regular cube with a side length of 1 meter, then its density is 24 kg/m³.
d. Density of aluminium = 48 kg/m³
Using the same approach as earlier:
volume = side³
volume = 24 / 48
volume = 0.5 m³
If we assume that the cube is a regular cube, then its volume is given by:
volume = side³
Therefore, we can calculate the side length as:
side = cube root of (0.5)
side = 0.79 meters
So, if the cube is a regular cube with a side length of 0.79 meters, then its density is 48 kg/m³.
which of these methods could are used to separate an insoluble solid and soluble solid
Answers
Answer:
To separate an insoluble solid from a soluble solid: Mixing the mixture with water, filtering out the insoluble solid, and then evaporating the water to isolate the soluble solid.
Explanation:
What is the rate law for the reaction A + B → C + D given the experimental data for four trials of initial rate?
Answers
Rate = k[A]^m[B]^n
Explanation:
To determine the rate law for the reaction A + B → C + D given the experimental data, follow these steps:
1. Write the general rate law expression: Rate = k[A]^m[B]^n, where k is the rate constant, m and n are the orders of reaction with respect to A and B, respectively.
2. Analyze the experimental data: In this case, the experimental data for four trials of initial rate is not provided. However, you can still follow the method explained below.
3. Compare two trials where the concentration of one reactant changes and the other remains constant. Observe the change in the initial rate.
4. Use the rate law expression to find the relationship between the change in concentration and the change in rate. This will give you the order of the reaction for each reactant.
5. Plug the orders for each reactant back into the general rate law expression.
The final rate law for the reaction A + B → C + D would be: Rate = k[A]^m[B]^n, with the values of m and n determined from the experimental data analysis.
To know more about Rate Law:
https://brainly.com/question/30884683?
#SPJ11
which of the following types of radiation causes the formation of damaging chemical bonds in dna?
Answers
The type of radiation that causes the formation of damaging chemical bonds in DNA is ionizing radiation. This type of radiation has enough energy to remove an electron from an atom or molecule, creating charged particles called ions.
These ions can then react with the atoms in DNA, forming chemical bonds that can cause damage such as breaks in the DNA strands or changes to the DNA sequence. This can lead to mutations, cell death, or even the development of cancer. It's important to limit exposure to ionizing radiation, which can come from sources such as X-rays, gamma rays, and radioactive materials.
The type of radiation that causes the formation of damaging chemical bonds in DNA is ionizing radiation. Ionizing radiation includes alpha particles, beta particles, gamma rays, and X-rays.
This type of radiation can remove tightly bound electrons from atoms, creating ions that can form harmful chemical bonds and lead to DNA damage, increasing the risk of mutations and potential health problems.
To know more about DNA, refer
https://brainly.com/question/21992450
#SPJ11
Complete the following table based on known properties of ionic and covalent compounds.

Answers
Answer:
structure of KF - ionic
Explanation:
Which of the following choices would have a negative entropy change? A. CaCO3(s)−>CaO(s)+CO2(g)
Answers
Answer: N2(g) + 3H2(g)- >2NH3(g) denotes a negative entropy change.
Explanation:
Entropy is defined as the extent of disorder in a system. The degree of entropy is more in a gas and less in a solid.
Here, 1st reaction produces ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen. We can see that four moles of gases produces 2 moles of gaseous product. So the degree of disorder in the system is decreasing. So the entropy is also decreasing.
Can someone unscramble OLINGI (I think the word as something to do with science :)
Answers
the best answer i came up with is oiling
:D
Answer:
B was also capitalized, I unscrambled it and the right word is boiling.
Explanation:
I did the test.
The mouth is a part of what organ system
Answers
Answer:
Digestive system
Explanation:
..........
Sodium and potassium ions are electrolytes. therefore, they dissolve _____ in water
Answers
Sodium and potassium ions are electrolytes, and they dissolve readily in water.
Electrolytes are substances that, when dissolved in water or other solvents, dissociate into ions and are capable of conducting electric current. They are typically composed of ions, such as positively charged cations (e.g., sodium, potassium, calcium) and negatively charged anions (e.g., chloride, bicarbonate, phosphate).
When these ions come into contact with water molecules, the positive sodium (Na⁺) or potassium (K⁺) ions are attracted to the negative pole of the water molecules (oxygen), while the negative chloride (Cl⁻) or sulfate (SO₄²⁻) ions are attracted to the positive pole of the water molecules (hydrogen).
This attraction causes the ions to become surrounded by water molecules, effectively dissolving them and forming a solution. The ability of sodium and potassium ions to dissociate in water and conduct electric current is what classifies them as electrolytes.
Learn more about Electrolytes, here:
https://brainly.com/question/32477009
#SPJ4
Plz help!!! How do I answer these??? :( I don’t get this at all!! Please help
Sorry meant to put under biology!

Answers
Answer:
1) 60°
2) 60°
3) 45°
4) E
5)90°
6) E
the diagram below represents 23 pairs of structures taken from the nucleus of a human body cell
Answers
If the diagram represents 23 pairs of structures taken from the nucleus of a human body cell then it is referring to the chromosomes of a human cell.
What are the chromosomes of a human cell?The chromosomes of a human cell are linear structures contained in the cell nucleus which are arranged into 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes that match during the cell division process.
Therefore, with this data, we can see that the chromosomes of a human cell are arranged into 23 linear structures that pair during cell division.
Learn more about the human chromosomes here:
https://brainly.com/question/13148765
#SPJ1