hammer falls off a roof top and strikes the ground with a certain kinetic energy. If it fell
from a roof twice as tall, how would its kinetic energy compare?
Answers
Answer:
If the starting GPE is doubled than it's KE would also double.
Related Questions
Consider the same system as before: a hockey puck with a mass of 0. 17 kg is traveling to the right along the ice at 15 m/s. It strikes a second hockey puck with a mass 0. 11 kg. The first hockey puck comes to rest after the collision. If conservation of momentum holds, what is the total final momentum of the system?.
Answers
When the first hockey puck comes to rest after the collision then the conservation of momentum holds and the total final momentum of the system is 23.18 m/s.
Applying the law of conservation of momentum,
we get,
m1v1i + m2v2i= m1v1f + m2v2f
0.17 (15) + 0.11 (0) = 0.17 (0) + (0-11) (V₂f)
0.17 x1500+ 0.11 V2f Vaf 0.17x15 0.11
V₁f =23.18 m/s
A collision between bodies in which the total kinetic energy of the bodies is conserved. Elastic collisions, such as the collision of a rubber ball on a hard surface, result in the reflection or "bouncing" of bodies away from each other.
In a perfectly elastic collision, no energy is turned into thermal energy internal to the bodies, and none is spent on permanently deforming the bodies or radiated away in some other fashion.
A collision between bodies in which the total kinetic energy of the bodies is not conserved. Inelastic collisions, such as the collision of two balls of clay, tend to result in the slowing and sometimes the sticking together of the colliding bodies.
To know more about conservation of momentum here,
https://brainly.com/question/17140635
#SPJ4
The system's total final momentum is 2.54 kg m/s m/s when the first hockey puck comes to rest following the collision, proving that momentum conservation persists.
Utilizing the principle of momentum conservation,
we get,
\(M_{1} V_{1}i +M_{2} V_{2}i =M_{_{1} } V_{1}f +M_{2} V_{2} f\)
0.17 (15) + 0.11 (0) = 0.17 (0) + (0.11) (V₂f)
\(V_{2}\)f =23.18 m/s
p = mv
p = 0.11*23.18 kg m/s
p = 2.54 kg m/s
a collision in which both bodies maintain their full internal kinetic energy. Elastic collisions cause bodies to reflect or "bounce" away from one another, like when a rubber ball strikes a hard surface.
When two perfectly elastic bodies collide, no energy is converted into internal heat energy and no energy is used to permanently distort the bodies.
Learn more about elastic collisions visit:
brainly.com/question/12941951
#SPJ4
A block on a horizontal surface of negligible friction is placed in contact with an ideal spring, as shown above. The block is moved to the left so that the spring is compressed a distance x from equilibrium and then released from rest. The block has kinetic energy k1 when it separates from the spring. When the spring is compressed a distance 2x and the block is released from rest, the kinetic energy of the block when it separates from the spring is:
Answers
Answer: 4K1
Explanation:
Invent a previously untried set of changes to make something interesting happen. Describe what you did, and what the effects were.
Answers
Answer:
Since gravitational force is inversely proportional to the square of the separation distance between the two interacting objects, more separation distance will result in weaker gravitational forces. So as two objects are separated from each other, the force of gravitational attraction between them also decreases.
6. Let u(x, y) = xy. (a) Show that u is harmonic. (b) Find a harmonic conjugate of u.
Answers
a. u is harmonic for let u(x, y) = xy because ∂²u/∂x² + ∂²u/∂y² = 0.
b. A harmonic conjugate of u is v = (x² - y²)/2.
To determine that u is harmonic, we need to verify whether u satisfies Laplace's equation or not. Laplace's equation is given by:
∂²u/∂x² + ∂²u/∂y² = 0
On differentiating u(x, y) = xy partially, we get,
∂u/∂x = y∂u/∂y = x
On differentiating partially again, we get,
∂²u/∂x² = 0∂²u/∂y² = 0
Therefore, ∂²u/∂x² + ∂²u/∂y² = 0
Thus, u is harmonic.
To find a harmonic conjugate of u, we need to find v(x, y) such that u + iv is analytic. In other words, v must satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann equations. The Cauchy-Riemann equations are given by:
∂u/∂x = ∂v/∂y∂u/∂y = -∂v/∂x
On substituting u = xy in the above equations, we get,
∂v/∂y = x∂v/∂x = -y
On integrating the above equations, we get
v = (x² - y²)/2 + C
Thus, a harmonic conjugate of u is v = (x² - y²)/2.
Learn more about harmonic conjugate: https://brainly.com/question/32598939
#SPJ11
Which planet experiences the greatest change between its actual day temperature and actual night temperature? A) Mercury. B) Venus. C) Earth. D) Mars
Answers
Mercury experiences greatest change between its actual day temperature and actual night temperature of any planet in our solar system. The correct answer is A .
During day, temperature on Mercury's surface can reach up to 430 degrees Celsius, due to its close proximity to sun and lack of a thick atmosphere to regulate temperatures. At night, however, surface temperature can plummet to -180 degrees Celsius, as planet's thin atmosphere is unable to retain heat. This temperature variation of over 600 degrees Celsius is largest of any planet in our solar system and is due to Mercury's slow rotation, which causes each day to last longer than two of its years, resulting in extreme temperature fluctuations. Correct answer is option: A.
To know more about Mercury experiences, here
brainly.com/question/11047112
#SPJ4
A ball of mass 0.15kg is kicked against a ridge vertical with horizontal velocity of 50m/s. If it rebounded with a horizontal velocity of 30m/s, calculate the impulse of the ball to the wall
Answers
So, the impulse of the ball to the wall is -12 N. It have same meaning to 12 N in opposite direction with its initial movement.
IntroductionHi ! In this ocassion, I will help you to solve the question about impulses. Impulse also relate to momentum, where the amount of impulse will cause the difference (indicated in units of direction) velocity when an object move. Impulses that have opposite direction to the original direction will have a negative value.
Formula UsedImpulse is the result of a change in momentum, so it can be expressed in this formula :
\(\sf{I = \Delta p}\)
\(\boxed{\sf{\bold{I = m (v' - v_0)}}}\)
With the following condition:
I = impulse (N.s)m = mass of the object (kg)\(\sf{v'}\) = final speed after collision (m/s)\(\sf{v_0}\) = initial speed before collision (m/s)Problem SolvingTips:We will use the starting point of the ball as a reference for the direction of ball's velocity. This is because what is being asked is the impulse of the ball to the wall not the impulse of the wall to the ball. But still, the value is the same.We know that :m = mass of the balls = 0.15 kg\(\sf{v'}\) = final speed of the balls = -30 m/s (30 m/s at the opposite direction from initial speed). \(\sf{v_0}\) = initial speed of the balls = 50 m/sWhat was asked ?I = impulse the ball to the wall = ... N.sProblem solving :\(\sf{I = m (v' - v_0)}\)
\(\sf{I = 0.15 (-30 - 50)}\)
\(\sf{I = 0.15 (-80)}\)
\(\boxed{\sf{I = -12 \: N.s}}\)
ConclusionSo, the impulse of the ball to the wall is -12 N. It have same meaning to 12 N in opposite direction with its initial movement.
At perihelion, the Earth is 96% of the Earth-sun distance at aphelion. Which of the following statements would be correct?
a-At aphelion, because the gravitational attraction is greater, the speed of the Earth is lower.
b-At aphelion, because the gravitational attraction is lower, the speed of the Earth is higher.
c-At perihelion, because the gravitational attraction is lower, the speed of the Earth is lower.
d-At perihelion, because the gravitational attraction is higher, the speed of the Earth is higher.
Answers
At aphelion, the Earth is 96% of the Earth-sun distance at aphelion which means that the correct statement is that at aphelion, because the gravitational attraction is lower, the speed of the Earth is higher and is denoted as option B.
What is Aphelion?
This is referred to as the farthest point in the orbit of a planet such as the earth from the sun.
In a a scenario where the Earth is 96% of the Earth-sun distance at aphelion, then it means that the orbit has almost been completed which means that a high amount of speed was involved in the process.
This is as a result of the gravitational attraction being lower which has an inverse relationship with the speed of the Earth which is why it was higher and is therefore the reason why option B was chosen.
Read more about Aphelion here https://brainly.com/question/913716
#SPJ1
what are fission write its type
Answers
Answer:
In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, nuclear fission is a nuclear reaction or a radioactive decay process in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller, lighter nuclei. ... Fission is a form of nuclear transmutation because the resulting fragments are not the same element as the original atom.
Explanation:
Plz mark brainliest thanks
A planet is in circular orbit around the Sun. Its distancefrom the Sun is four times the average distance of Earth from theSun. The period of this planet, in Earth years, is:_______.
A. 4
B. 8
C. 16
D. 64
E. 2.52
Answers
Answer:
B. 8 years
Explanation:
D = 1 a.u. - Distance from the Sun to the Earth in astronomical units (a.u.)
D₁ = 4 a.u - Distance from the Sun to the planet
T = 1 year - The period of the earth's revolution around the Sun
__________
T₁ - ? - The period of revolution of the planet around the Sun
Kepler's law
(T₁/T)² = (D₁/D)³
(T₁ / 1)² = (4 / 1)³
T₁² = 64
T₁ = √ 64 = 8 years
B. 8 years
The relationship between the planet's period and the Earth's period and cube root of the ratio between the planet's distance from the Sun and the Earth's distance from the Sun.
Kepler's third law is the theory applied to this puzzle.
Write the expression for the period of the planet first using Kepler's rule to take into account the period of the Earth, the distance from the Sun to the Earth, and the distance from the Sun to the planet.
To compute the period of the planet, finally, substitute the appropriate quantities. The relationship between the period and the separation between the Sun and the planet is provided by, in accordance with Kepler's third law: T² ∝ a³
T is the period in this case, and an is the separation between the planet and the Sun.
To know more about Kepler's third law, click on the link below:
https://brainly.com/question/6867220
#SPJ4
How does increasing the amount of charge on an object affect the electric force it exerts on another charged object?
The electric force increases because the amount of charge has an indirect relationship to the force.
The electric force increases because the amount of charge has a direct relationship to the force.
The electric force decreases because the amount of charge has an indirect relationship to the force.
The electric force decreases because the amount of charge has a direct relationship to the force.
Answers
Answer:
a
Explanation:
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Figure 4: Index Fossils, Scientists use index fossils to match rock layers. Interpret Diagrams: Label the layers to match the first area shown. Circle the fossil or fissils. What can you infer about the history of Location 4?

Answers
Answer:
kamalong with me to the butter fly and bee
Which nanotechnology product would most likely help the
electronics company?
biomaterials
carbon wires
quantum dots
OLEDs
Answers
Answer: OLEDs
Explanation:
The nanotechnology uses the surface of the carbon materials to generate the electricity. The evaporation of water on the surface of carbon materials helps in generation of electrical energy due to generation of thermal energy.
OLEDs can be defined as solid-state devices that comprises of organic molecules like carbon that will create electricity by exposing a surface for generation of thermal energy.
100 ml de una disolucion 0,5 M de sulfato de cobre II
Answers
Answer:
100 ml de una disolucion 05 M de sulfate de vivre
An object at rest on top of a shelf is likely to have:
A. No energy
B. Gravitational potential energy
C. Hydroelectric power
Answers
An object at rest on top of a shelf possesses gravitational potential energy. Gravitational potential energy is the energy an object possesses due to its position relative to the Earth's gravitational field. The correct option is B.
When an object is elevated above the ground, it has the potential to fall and convert that potential energy into kinetic energy.
In the given scenario, the object on the shelf is not in motion, but it is elevated above the ground due to its position on the shelf. Therefore, it possesses gravitational potential energy. The magnitude of the gravitational potential energy depends on the mass of the object, the acceleration due to gravity (usually denoted as "g"), and the height of the shelf.
While the object is at rest and not actively using or transforming its energy, it still retains the potential to release its gravitational potential energy if it were to fall from the shelf. The correct option is B.
To know more about Gravitational potential energy, refer here:
https://brainly.com/question/31024811#
#SPJ11
Answer these please.

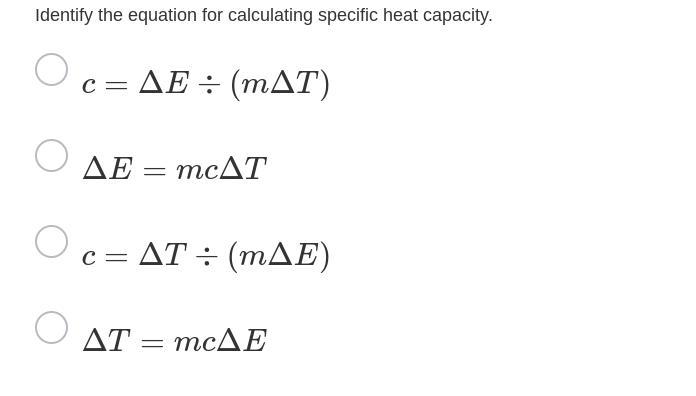

Answers
Explanation:
hope this helps you
..........

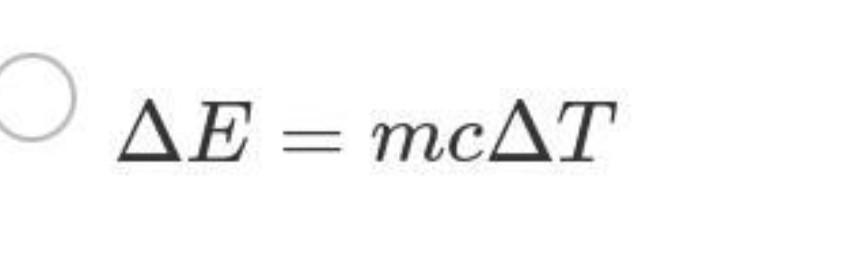
a marble launchers fires a marble into the air so that it reaches a height of 3.25 m determine the initial velocity of the marble
Answers
The velocity of the launched marble is 7.98 m/s. Using the formula by equation kinetic energy and potential energy.
What is potential energy?
Potential energy is a form of stored energy that is dependent on the relationship between different system components. When a spring is compressed or stretched, its potential energy increases. If a steel ball is raised above the ground as opposed to falling to the ground, it has more potential energy. It is capable of performing more work when raised.
What is velocity?The directional speed of an item in motion, as measured by a specific unit of time and observed from a certain point of reference, is what is referred to as velocity.
Calculations:
Total kinetic energy will get converted into potential energy
\(\frac{1}{2} m V^{2}\) = \(m g h\)
M = mass
V = initial velocity
h = maximum height
\(V = 2 g h^{0.5}\)
= \((2 * 9.8 * 3.25 )^{0.5}\) = 7.98 m/s.
To know more about velocity, check out:
https://brainly.com/question/80295
#SPJ1
A guitar sounds a "A" with a pitch of 440 Hz. What are the frequencies of the next three harmonics?
Answers
The harmonic frequencies would be 880 Hz, 1320 Hz, 1760 Hz, and 2200 Hz if the fundamental frequency was 440 Hz.
What is the wavelength of a sound wave in a particular medium with a frequency of 220 Hz and a speed of 440 m per second?The sound waves have a wavelength of 2m and travel at a speed of 440 m/s. Hence, the sound wave has a 2 m wavelength.
What wavelength does an air tone at 340 Hz have? What is the airborne ultrasonic wave's wavelength at 34000 Hz?340 m/s x 340 Hz x 1 m = 340 m/s, the formula for wavelength. A 34,000 hertz wave has a wavelength of 340 m/s, and its frequency is 0.01 m, or 1 cm.
To know more about harmonic frequencies visit:-
brainly.com/question/12320829
#SPJ1
A small CG flash lowers about 3 Coulombs of negative charge to ground in a period of, say, 100 milliseconds. Then the average current during this time is Group of answer choices a. 3 Amperes b. 30 Amperes c. 300 Amperes d. 3,000 Amperes
Answers
A small CG flash lowers about 3 Coulombs of negative charge to ground in a period of, say, 100 milliseconds. The average current during this time is 30 Amperes.
The rate at which charge flows through a circuit is called current. Charge is calculated in Coulombs (C), and time is calculated in seconds (s). Current is measured in Amperes (A), which is a measure of the number of Coulombs that pass by a certain point in one second.
The formula for calculating current (I) is as follows:I = Q / tWhere Q is the charge that passes a certain point and t is the time it takes for that charge to pass through to the given problem is as follows We can calculate the current during the 100 milliseconds using the given formula,I = Q / tI = 3 C / 0.1 sI = 30 AThus, the average current during this time is 30 Amperes.
To know more about negative charge visit :
https://brainly.com/question/2292900
#SPJ11
A half-wave rectifier is needed to supply 15-V de to a load that draws an average current of 250 mA. The peak-to-peak rip- ple is required to be 0.2 V or less. What is the minimum value allowed for the smooth- ing capacitance? If a full-wave rectifier is needed?
Answers
C_min = (I_avg * T) / V_ripple. If a full-wave rectifier is needed, the ripple voltage is typically reduced by half compared to a half-wave rectifier. Therefore, the same calculation can be used to determine the minimum smoothing capacitance for the full-wave rectifier.
but with a ripple voltage of half the value used in the half-wave rectifier calculation.Where C_min is the minimum required capacitance, I_avg is the average current, T is the time period of the waveform (in seconds), and V_ripple is the desired peak-to-peak ripple voltage.
In this case, I_avg = 250 mA (or 0.25 A) and V_ripple = 0.2 V. The time period T can be calculated as the reciprocal of the frequency of the AC input signal.
Once you have the time period T, you can substitute the values into the formula to determine the minimum required smoothing capacitance C_min.
Remember to convert all units to be consistent (e.g., A to mA and F to μF) when performing the calculation.
To know more about rectifier refer here:
https://brainly.com/question/25075033#
#SPJ11
What are Newton's 3 laws in simple terms?
Answers
Answer:
(1) Every object moves in a straight line unless acted upon by a force. There is no change in the state of motion unless there is an unbalanced force acting on it
(2) The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force exerted and inversely proportional to the object's mass.
F=m*a
(3) Every action has an equal and opposite reaction.
Which statement is not true?
A A south pole repels a north pole.
B A south pole repels a south pole.
C A north pole attracts a south pole.
D A north pole repels a north pole.
Answers
Answer:
A South pole repels a nort pole is not true
Explanation:
South pole attract north pole
Rank these wavelengths of light in order, according to their frequencies.
1. 0.8 km 2. 5 m 3. 0.02 nm 4. 460 nm 5. 7 cm 6. 3 μm
Answers
From low to high frequency, a wave's wavelength increases while its frequency decreases: 0.8 km, 5 m, 7 cm, 3 m, 460 nm, and 0.02 nm. The characteristic of a wave is known as its wavelength.
A wave's wavelength is the characteristic that determines how far identical locations between two succeeding waves are separated. The Greek letter lambda () is used to represent it. Thus, the wavelength is defined as the separation between one wave's crest or trough and the following wave.
The frequency of an event is its repetitions per unit of time. As a contrast to spatial frequency, it is also sometimes referred to as temporal frequency, and as a contrast to angular frequency, it is sometimes referred to as ordinary frequency.
Learn more about wavelength here
https://brainly.com/question/13533093
#SPJ4
How death rate helps in changing population
Answers
A body is under the action of two forces 7N and 10N.find the resultant of the two forces.ifThe two forces are parallel and act in the same directionThe two forces are inclined at an angle of 60°to each otherThe two forces are inclined at an angle of 160°The two forces act 90° to each other
Answers
To find the resultant of two forces, we can use vector addition. The magnitude and direction of the resultant depend on the given conditions. Let's calculate the resultants for each case:
When the two forces are parallel and act in the same direction: In this case, we can simply add the magnitudes of the forces. Resultant = 7 N + 10 N = 17 N. The resultant force is 17 N in the same direction as the two forces. When the two forces are inclined at an angle of 60° to each other: To find the resultant, we need to use vector addition. We can use the parallelogram method or the triangle method. Let's use the triangle method. Draw a triangle with sides representing the magnitudes of the forces. The angle between the two forces is given as 60°. Using the law of cosines, we can find the magnitude of the resultant: Resultant^2 = (7 N)^2 + (10 N)^2 - 2 * (7 N) * (10 N) * cos(60°) Resultant = sqrt(49 N^2 + 100 N^2 - 140 N^2 * cos(60°)) Resultant ≈ 15.3 N The resultant force is approximately 15.3 N. When the two forces are inclined at an angle of 160°: Similar to the previous case, we can use the triangle method. Resultant^2 = (7 N)^2 + (10 N)^2 - 2 * (7 N) * (10 N) * cos(160°) Resultant = sqrt(49 N^2 + 100 N^2 + 140 N^2 * cos(160°)) Resultant ≈ 3.5 N The resultant force is approximately 3.5 N. When the two forces act at 90° to each other: In this case, we can use the Pythagorean theorem to find the magnitude of the resultant. Resultant = sqrt((7 N)^2 + (10 N)^2) Resultant ≈ 12.2 N. The resultant force is approximately 12.2 N.
To learn more about forces, https://brainly.com/question/13191643
#SPJ11
An object with a potential energy of 981 J is placed at a height of 2m. What is the mass of the object?
Answers
Explanation:
Taking g=10m/s²
P.E =mgh
981J= 2×10×m
981J=20m
m. = 981J/20
m. = 49.05kg
If the gravity of the moon is 1/6 of Earth’s gravity, what is the mass of an object that has a weight of 115N on the moon?
Answers
Answer:
70.3 kg
Explanation:
The MASS will be the same on the moon as on earth....but the eight is different
gravity of moon = gravity of earth/6 = 9.81 / 6 m/s^2
F = ma
F/a = m = 115 N / ( 9.81/6 m/s^2) = 70.3 kg mass
Answer:
Explanation:
Given:
g = 9.8 m/s²
g₁ = g / 6 = 9.8 / 6 ≈ 1.6 m/s²
F = 115 N
____________
m - ?
m = F / g₁
m = 115 / 1,6 ≈ 71.9 kg
A rocket initially traveling straight up at a speed of 20. 0 m/s undergoes constant acceleration in the direction of travel to a speed of 30. 0 m/s over a distance of 40. 0 m. What is the magnitude of the rocket's acceleration?
0. 125
2. 50
6. 50
12. 5
Answers
The magnitude of the rocket's acceleration is 12.5 m/s².To find the magnitude of the rocket's acceleration, we can use the equation of motion: \(v^2 = u^2 + 2as\)
The above equation has v is the final velocity, u is the initial velocity, a is the acceleration, and s is the distance traveled. Rearranging the equation, we have \(a = (v^2 - u^2) / (2s)\).Given that the initial velocity (u) is 20.0 m/s, the final velocity (v) is 30.0 m/s, and the distance traveled (s) is 40.0 m, we can substitute these values into the equation:
a = (30.0² - 20.0²) / (2 * 40.0)
= (900 - 400) / 80
= 500 / 80
= 6.25 m/s².
Therefore, the magnitude of the rocket's acceleration is 6.25 m/s².
Learn more about equation of motion here:
https://brainly.com/question/29278163
#SPJ11
What is the difference between a unit and a variable?
Answers
Explanation:
a variable In algebra, a symbol (usually a letter) standing in for an unknown numerical value in an equation.
a unit In math, the word unit can be defined as the rightmost position in a number or the one's place
1. A 2-kg ball falls freely through a height of 3 m. Find its kinetic energy in joules when it hits the ground
2. A bullet moves with a velocity of 600 m/s and has gained a kinetic energy of 900 joules. Compute its mass.
3. An 8-hp crane lifts a 100-kg piece of junk metal in a time of 15 s. To what distance was the load lifted.
complete answer pls
Answers
1. 44.1 J is the kinetic energy in joules when it hits the ground
2.0.075 kg is its mass.
3.11.8 m is distance was the load lifted.
The kinetic energy of a freely falling object can be calculated using the formula KE = 1/2 * m * v^2, where m is the mass of the object and v is its velocity. At the moment of impact with the ground, the velocity of the 2-kg ball can be calculated.
using the formula v = sqrt(2 * g * h), where g is the acceleration due to gravity (9.8 m/s^2) and h is the height fallen. Substituting the values, we get KE = 1/2 * 2 kg * (sqrt(2 * 9.8 m/s^2 * 3 m))^2 = 44.1 J.
The kinetic energy of a moving object can be calculated using the formula KE = 1/2 * m * v^2. We can rearrange this formula to find the mass, m = 2 * KE / v^2. Substituting the given values, we get m = 2 * 900 J / (600 m/s)^2 = 0.075 kg.
The work done by the crane can be calculated using the formula W = F * d, where F is the force exerted by the crane and d is the distance the load is lifted. The force exerted can be calculated using the formula F = m * g, where m is the mass of the load and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
The work done can be calculated as W = m * g * d. We can rearrange this formula to find the distance lifted, d = W / (m * g). Substituting the given values, we get d = (8 hp * 746 W/hp * 15 s) / (100 kg * 9.8 m/s^2) = 11.8 m.
To know more about kinetic energy click on below link:
https://brainly.com/question/26472013#
#SPJ11
URGENT HELP PLS
1. Given a force-displacement curve as shown in the figure, what does the area of the region enclosed by the curve represent?
A. The force acting on the object
B. The displacement of the object
C. The magnitude of the coefficient of static friction
D. The work done on the object by the force

Answers
Explanation:
work done is equals to force into displacement in the direction of force
Ans: D