PLEASE HELP ME!!
Fill in the blanks with the coefficients to balance this chemical equation:

Answers
The balanced chemical equation is 2 AlI₃ + 3 HgCl₂\(\rightarrow\) 2 AlCl₃ + 3 HgI₂ for the given chemical reaction.
What is chemical equation?
Chemical equation is a symbolic representation of a chemical reaction which is written in the form of symbols and chemical formulas.The reactants are present on the left hand side while the products are present on the right hand side.
A plus sign is present between reactants and products if they are more than one in any case and an arrow is present pointing towards the product side which indicates the direction of the reaction .There are coefficients present next to the chemical symbols and formulas .
The first chemical equation was put forth by Jean Beguin in 1615.By making use of chemical equations the direction of reaction ,state of reactants and products can be stated. In the chemical equations even the temperature to be maintained and catalyst can be mentioned.
Learn more about chemical equation,here:
https://brainly.com/question/28294176
#SPJ1
Related Questions
Can someone please help me with science.

Answers
Answer:
I think it is D or A
Explanation:
I have not done this in a long time, so sorry if wrong.
The conductance of a wire varies directly as the square of the wire's diameter and inversely as its
length. Fifty meters of wire with diameter 2 mm has conductance 0.12 mho (unit of conductance).
If a wire of the same material has length 75 m and diameter 2.5 mm, what is its conductance?
Answers
Since it varies directly with the square of the wire's diameter and inversely with wire length, the conductance of a wire is 0.15 mho.
Does a wire's electrical resistance change inversely with its square of diameter and directly with its length?A wire's electrical resistance varies inversely as the square of its diameter and directly as its length. A wire with a diameter of 1/4 inch and a length of 200 inches has a 20 ohm resistance.
Let L be the wire's length, d its diameter, and C its conductance be the parameters.
Based on the facts provided, we can:
C ∝ d² (conductance varies directly as the square of the diameter)
C ∝ 1/L (conductance varies inversely as the length)
Combining these two proportionalities, we get: C ∝ d²/L
This connection can be used to find a solution to the issue. Using the numbers for the 50 m wire, we can first calculate the proportionality constant as follows:
C = k(d²/L)
0.12 = k(2²/50)
k = 0.12*50/4 = 1.5
So, using this value of k, we can determine the conductance of a 75 m wire with a 2.5 mm diameter:
C = k(d²/L)
C = 1.5*(2.5²/75)
C = 0.15 mho
To know more about resistance visit:-
https://brainly.com/question/30799966
#SPJ1
An appliance is in a room repeatedly making the same sound all day. As the room heats up from 25 degrees Celsius to 35 degrees Celsius, what changes?
A. The sound wave's velocity decreases
B. The sound wave's frequency decreases
C. The sound wave's frequency increases
D. The sound wave's velocity increases
Answers
An appliance is in a room repeatedly making the same sound all day. As the room heats up from 25 degrees Celsius to 35 degrees Celsius is
B) The sound wave's frequency decreases
As the temperature of the room increments, the speed of sound waves within the discussed increments.
In any case, the recurrence of the sound wave created by the machine remains steady. This implies that the wavelength of the sound wave changes as the speed of the wave changes.
Agreeing with the wave condition, the speed of a wave is rise to its recurrence increased by its wavelength.
Subsequently, in the event that the speed of the wave increments and the recurrence remains steady, the wavelength must diminish. This results in a diminish within the recurrence of the sound wave, making it lower pitched.
To know more about frequency refer to this :
https://brainly.com/question/254161
#SPJ1
Answer:
Its A the other person is wrong
Explanation:
SPEAR is a storage ring at the Stanford Linear Accelerator which has a circulating beam of electrons that are moving at nearly the speed of light (2.998 108 m/s). If a similar ring is about 80.0 m in diameter and has a 0.59 A beam, how many electrons are in the beam
Answers
Answer:
n = 3.1x10¹²
Explanation:
To find the number of electrons we need to find first the charge (q):
\( I = \frac{q}{\Delta t} \rightarrow q = I*\Delta t \) (1)
Where:
I: is the electric current = 0.59 A
t: is the time
The time t is equal to:
\(v = \frac{\Delta x}{\Delta t} \rightarrow \Delta t = \frac{\Delta x}{v}\) (2)
Where:
x: is the displacement
v: is the average speed = 2.998x10⁸ m/s
The displacement is equal to the perimeter of the circumference:
\( \Delta x = 2\pi*r = \pi*d \) (3)
Where d is the diameter = 80.0 m
By entering equations (2) and (3) into (1) we have:
\(q = I*\Delta t = I*\frac{\Delta x}{v} = \frac{I\pi d}{v} = \frac{0.59 A*\pi*80.0 m}{2.99 \cdot 10^{8} m/s} = 4.96 \cdot 10^{-7} C\)
Now, the number of electrons (n) is given by:
\( n = \frac{q}{e} \)
Where e is the electron's charge = 1.6x10⁻¹⁹ C
\( n = \frac{q}{e} = \frac{4.96 \cdot 10^{-7} C}{1.6 \cdot 10^{-19} C} = 3.1 \cdot 10^{12} \)
Therefore, the number of electrons in the beam is 3.1x10¹².
I hope it helps you!
What is the "price" that you pay for using less force?
Answers
What is the “price” that you pay for using less force? The price that you pay for using less force is having to do more work.
.....................................
dont ask this is what i looked up and found
The "price" that you pay for using less force is:
The object would not moveForce is defined as the energy which is required to move or change the velocity of an object.
There are different types of force which includes:
Gravitational forceApplied forceFrictional force, etcAs a result of this, if there is less force exerted on an object, then the "price" which would be paid for this is that the object would not move.
Read more here:
https://brainly.com/question/24557735
A motorcyclist sees a branch in the road and it hits the brakes slowing down at -6.42 m/s 2 if it takes and 2.85 seconds. What is the starting velocity?
Answers
Answer:the answer is 18.297m/s
Explanation:

Objects x and y are connected by a string of negligible mass and suspended vertically over a pulley of negligible mass, creating an atwood’s machine, as shown in the figure. The objects are initially at rest, and the mass of object y is greater than the mass of object x. As object y falls, how does the gravitational potential energy of the object x-object y-earth system change? all frictional forces are considered to be negligible.
Answers
We have that the gravitational potential energy effect on the system is mathematically given as
The gravitational potential energy decreases because the center of mass of Object X and Object Y moves downward.Option C
From the question we are told
The objects are initially at rest, and the mass of object y is greater than the mass of object x. As object y falls, how does the gravitational potential energy of the object x-object y-earth system change? all frictional forces are considered to be negligible.Centre of massDue to reduce in top of Y, doable strength will limit and due to amplify in peak of X, achievable power will increase.
Now, PE = mgh.
Generally the equation for the Velocity of centre of mass is mathematically given as
\(V =\frac{ m1v1 + m2v2}{ m1 + m2}\\\\Therefore \\\\V =\frac{ (m1 - m2) v}{ m1 + m2}\)
Hence, V is positive as m1 > m2
Therefore
centre of mass of system moves downwards.The conclusion
The gravitational potential energy decreases because the center of mass of Object X and Object Y moves downward.
Option C
For more information on gravitation visit
https://brainly.com/question/16517842
Complete QuestionObjects X and Y are connected by a string of negligible mass and suspended vertically over a pulley of negligible mass, creating an Atwood’s machine, as shown in the figure.
The objects are initially at rest, and the mass of Object Y is greater than the mass of Object X. As Object Y falls, how does the gravitational potential energy of the Object Y-Object Y-Earth system change? All frictional forces are considered to be negligible.
a
The gravitational potential energy increases because the center of mass of Object X and Object Y moves upward.
b
The gravitational potential energy increases because the center of mass of Object X and Object Y moves downward.
c
The gravitational potential energy decreases because the center of mass of Object X and Object Y moves downward.
d
The gravitational potential energy decreases because the center of mass of Object X and Object Y moves upward.
Imagine you are an astronomer who recently discovered a new planet orbiting a distant star.
Which set of characteristics would you use to classify this planet as an inner or terrestrial planet? Check all that apply.
D dense and solid
D- very large
O thick atmosphere containing hydrogen and helium
D lacking a solid surface
D located near a star
Answers
Answer:
I think its dense and solid and located near a star.
Explanation:
Hope this helps, good luck.
23. As the frequency of a wave increases, the period of the wave
Answers
Answer: decreases
Explanation: As frequency increases the period of a wave decreases because they have an inverse relationship. The equation for wave period (T) is the inverse of the frequency (f). So, as frequency increases, the value for period will decrease accordingly.
What is the estimated volume of the table tennis ball?
cm3
What is the estimated volume of the golf ball?
cm3
Answers
Answer:
The estimated volume of a standard table tennis ball is approximately 2.7 cm³.
The estimated volume of a standard golf ball is approximately 41.6 cm³.
Explanation:
How many grams of aluminum sulfate must be dissolved in 650. mL of water to make 84.0% (m/v) aluminum sulfate solution?
Answers
3415.2 grams
Explanation
to solve this we can use a rule of three
Step 1
Let
water= 100-84%= 16%
so,
\(\text{ 16 \%=650 mL}\)for the water , 1 mL = 1 gram , so
\(\text{ 16\% =650 grams}\)now, let represents the mass of the aluminiu, so
\(\text{ 84 \%= x}\)a) the ratio is the same, so we have a proportion
\(\frac{16}{650}=\frac{84}{x}\)Step 2
finally, solve for x
\(\begin{gathered} \frac{16}{650}=\frac{84}{x} \\ \text{cross multiply } \\ 16\cdot x=84\cdot650 \\ 16x=54600 \\ \text{divide both sides by 16} \\ \frac{16x}{16}=\frac{54600}{16} \\ x=3412.5 \end{gathered}\)so, the mass of the aluminum is
3415.2 grams
establishing a potential difference the deflection plates in an oscilloscope are 10 cm by 2 cm with a gap distance of 1 mm. a 100 volt potential difference is suddenly applied to the initially uncharged plates through a 925 ohm resistor in series with the deflection plates. how long does it take for the potential difference between the deflection plates to reach 60 volts? s what will the electric potential difference across the capacitor be a long time after the circuit is connected? v what will the electric potential difference across the resistor be a long time after the circuit is connected?
Answers
a) It takes approximately 1.3 x 10^-7 seconds for the potential difference between the deflection plates to reach 60 volts.
b) At very long times after the circuit is connected, the potential difference across the capacitor will be equal to the potential difference across the voltage source, which is 100 volts.
c) Similarly, at very long times after the circuit is connected, the potential difference across the resistor will be 0 volts, since there will be no voltage drop across it.
a) To determine the time it takes for the potential difference between the deflection plates to reach 60 volts, we need to use the equation for the charging of a capacitor through a resistor
Vc = Vf(1 - e^(-t/RC))
where Vc is the potential difference across the capacitor, Vf is the final potential difference (100V), t is time, R is the resistance (925 ohms), and C is the capacitance of the deflection plates. The capacitance can be calculated using
C = εA/d
where ε is the permittivity of free space (8.85 x 10^-12 F/m), A is the area of the deflection plates (10 cm x 2 cm = 0.02 m^2), and d is the distance between the plates (1 mm = 0.001 m).
Plugging in the values, we get
C = (8.85 x 10^-12 F/m)(0.02 m^2)/(0.001 m) = 0.177 x 10^-9 F
Now we can solve for t
60V = 100V(1 - e^(-t/(925 x 0.177 x 10^-9)))
0.4 = e^(-t/3.28 x 10^-7)
ln(0.4) = -t/3.28 x 10^-7
t = -ln(0.4) x 3.28 x 10^-7
t ≈ 1.3 x 10^-7 seconds
Therefore, it takes approximately 1.3 x 10^-7 seconds for the potential difference between the deflection plates to reach 60 volts.
b) At very long times after the circuit is connected, the capacitor will be fully charged and no current will be flowing through the circuit. Therefore, the potential difference across the capacitor will be equal to the potential difference across the voltage source, which is 100 volts.
c) Similarly, at very long times after the circuit is connected, the capacitor will be fully charged and no current will be flowing through the circuit. Therefore, the potential difference across the resistor will be 0 volts, since there will be no voltage drop across it.
Learn more about capacitor here
brainly.com/question/22850143
#SPJ4
How much net force is required make a 10 kg box accelerate at a rate of 5 m/s2?
O2N
0 50 N
0 15 N
0 100 N
Answers
F = (10)(5)
F = 50
Answer: 50 N
if a ball is thrown straight upward with an initial velocity of feet per second, its height above the ground, in feet, can be written as , where denotes the time in seconds that the ball has been airborne. what was the average rate of change of the height of the ball over the first seconds?
Answers
The height above the ground in feet of the ball can be represented by the equation h = ut+1/2at², where u in the initial speed in feet per second, the average rate of change of height in first few second will also be given by the same equation.
The ball thrown upward with an initial speed of u feet per second will attain a height of h feet.
Now, we know, from the equation of motion,
S = ut + 1/2at²
This can be rewritten for the height purpose,
h = ut + 1/2at²
Where,
h is the height in feet,
t is time in seconds,
u is the initial speed in feet per seconds,
a is the acceleration of the ball.
The average rate of change of height will also be given by the same equation. We just have to know that for how much amount of time we need to find the change rate.
To know more about equation of motion, visit,
https://brainly.com/question/25951773#:~:text=Expert%2DVerified%20Answer&text=Motion%3A%20This%20can%20be%20defined,.....%20Equation%201
#SPJ4
I need the answer now
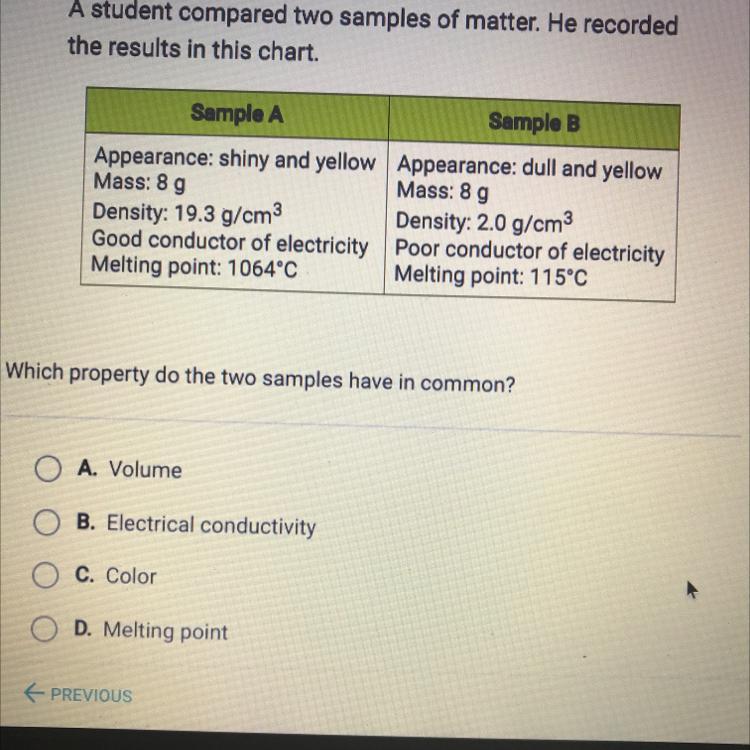
Answers
Answer:
It's C) color
Explanation:
--------
A box is at rest on a table. What can you say about the forces acting on the box?
The upward _____and the downward______are balanced.
applied force
frictional force
normal force
drag force
gravitational force
tension
Answers
Answer:
gravitational force
Explanation:
Two forces of 60N and 50N are acting at an angle of 30° to one another. (a) Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and the angle it makes with the larger force. (b) What is the equilirant vector for this situation?
Answers
(a) The magnitude of the resultant force is approximately 74.1N, and it makes an angle of approximately 35.5° with the larger force.
(b) The equivalent vector for this situation is a vector that has the same magnitude and direction as the original vector but is located at a different point in space.
What are the values for the magnitude, angle and equilirant vector of the resultant force?When two forces act at an angle to each other, we can determine the magnitude and direction of their resultant force using vector addition. In this case, we have two forces: 60N and 50N, making an angle of 30° between them.
To find the magnitude of the resultant force, we use the law of cosines. The formula is given by:
Resultant force magnitude = √(60^2 + 50^2 - 2 * 60 * 50 * cos(30°))
= √(3600 + 2500 - 6000 * 0.866)
≈ √(6100 - 5196)
≈ √904
≈ 30.1N
To determine the angle the resultant force makes with the larger force, we can use the law of sines. The formula is given by:
sin(θ) / 60N = sin(150°) / 30.1N
sin(θ) = (60N * sin(150°)) / 30.1N
θ ≈ arcsin(2 * sin(150°))
θ ≈ arcsin(2 * 0.5)
θ ≈ arcsin(1)
θ ≈ 90°
Therefore, the magnitude of the resultant force is approximately 30.1N, and it makes an angle of approximately 90° with the larger force.
To understand the equivalent vector, let's consider an example. Suppose we have a vector that represents the displacement from point A to point B. This vector has a specific magnitude and direction.
Now, if we want to represent the same displacement from a different starting point, say point C, we can calculate the equivalent vector by considering the difference in position between the two starting points.
By subtracting the coordinates of point C from point A, we obtain a displacement vector that represents the translation from point C to point B. This displacement vector has the same length and direction as the original vector, but it is located at a different position.
Learn more about resultant force
brainly.com/question/22260425
#SPJ11
How do control rods in a nuclear power plant help to prevent the nuclear fission reaction from getting out of control?
Answers
Answer:
By absorbing neutrons, the control rod prevents further neutron fission. Control rods are an important safety system for nuclear reactors. Their rapid action and prompt reaction to the reactor are irreplaceable. Control rods are used to maintain the desired state of fission reactions in a nuclear reactor (i.e. subcritical state, critical state, power changes). They form a key component of the Emergency shutdown system (SCRAM).
The node of the control rods block.
Control rod assembly for the VVER reactor. Absorber – boron carbide
Control rods are typically cluster assemblies of control rods (PWRs) inserted into guide sleeves inside a nuclear fuel assembly. The shell protects the absorbing material (e.g. boron carbide granules), usually made of stainless steel. They are grouped into groups (rows), and movements
Explanation:
The power factor PF of an ac circuit determines the a. frequency of the power waveform. b. ratio between inductive and capacitive reactive power in a circuit. c. ratio between the number of resistive components and the number of reactive components in a circuit. d. ratio between the active power and the apparent power of the circuit. 2. Complete the following sentence: The reactive power Q
1
in an ideal inductor a. lags the reactive power Q
C
in a capacitor by 180
∘
. b. leads the reactive power
Q
c
in a capacitor by 90
∘
. c. leads the reactive power Q
C
in a capacitor by 180
∘
. d. lags the reactive power Q
C
in a capacitor by 90
∘
. 3. What are the problems of a low power factor in an industrial application?
Answers
1. The power factor (PF) of an AC circuit determines the: d. ratio between the active power and the apparent power of the circuit.
2. The reactive power Q in an ideal inductor: a. lags the reactive power Qc in a capacitor by 180°.
3. The problems of a low power factor in an industrial application are power losses, Overloading, Penalties from utilities etc.
The power factor (PF) is a measure of how effectively a circuit converts electrical power into useful work. It is the ratio between the active power (measured in watts) and the apparent power (measured in volt-amperes) of the circuit. A power factor of 1 indicates that all the electrical power supplied to the circuit is converted into useful work. A power factor less than 1 indicates that some of the electrical power is being wasted.
Reactive power is the power exchanged between inductive and capacitive components in an AC circuit. In an ideal inductor, the reactive power lags behind the reactive power in a capacitor by 180°. This means that when the reactive power in the capacitor is at its maximum, the reactive power in the inductor is at its minimum, and vice versa. This phase difference is caused by the storage and release of energy in the magnetic field of the inductor.
A low power factor in an industrial application can lead to several problems:
Increased power losses: A low power factor means that more current is required to deliver the same amount of power, leading to increased resistive losses in the circuit. This results in higher energy consumption and increased costs.Overloading of equipment: Low power factor causes increased current flow, which can overload transformers, generators, and other equipment in the power distribution system. This can lead to equipment failure and reduced overall system reliability.Inefficient use of electrical power: With a low power factor, a significant portion of the supplied electrical power is wasted as reactive power. This results in inefficient use of electrical power and reduced system efficiency.Penalties from utilities: Some utilities impose penalties or charges for having a low power factor. These penalties are designed to encourage users to improve their power factor and reduce the strain on the power distribution system.To address these problems, industrial applications often use power factor correction techniques such as installing capacitors or synchronous condensers to offset the reactive power and improve the power factor. This helps reduce energy losses, improve equipment efficiency, and avoid penalties from utilities.
To know more about electrical power, visit:
https://brainly.com/question/33340158
#SPJ11
if the glider oscillates back and forth on the air-track, at what point in the motion is the acceleration zero? where is the velocity maximum? show with a drawing.
Answers
If the glider oscillates back and forth on the air-track, at what point in the motion is the acceleration zero when the glider reaches the extreme points of its motion, i.e., at the endpoints of the oscillation.
In the motion of a glider oscillating back and forth on an air-track, the acceleration is zero when the glider reaches the extreme points of its motion, i.e., at the endpoints of the oscillation. These points are called the turning points or the points of maximum displacement.
On the other hand, the velocity is maximum at the center of the motion, which is the midpoint between the two turning points. At this point, the glider changes its direction of motion and its velocity reaches its maximum value.
Here's a simplified diagram illustrating the motion of the glider:
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
---+-------+---
Turning Turning
Point Point
At the turning points, the acceleration is zero (the glider momentarily stops before changing its direction), while at the midpoint between the turning points, the velocity is maximum (the glider is moving at its highest speed).
Note that this diagram represents a one-dimensional motion, where the glider moves back and forth along a straight line. In reality, the glider's motion may involve more complex trajectories, but the concept of acceleration being zero at the turning points and maximum velocity at the midpoint still holds true.
To learn more about acceleration visit: https://brainly.com/question/460763
#SPJ11
What's the free body diagram for:
Mr. Seifert needs to push a cardboard box down the hallway for Ms. Wang. The box has a mass of 40 kg and he is pushing it with an acceleration of 2 m/s/s. Because the cardboard does not slide easily, there is a friction force of 25 Newtons acting on the box to the LEFT. How much force is Mr. Seifert applying to the box to move it forward to the RIGHT?
Answers
(a) The free body diagram for representing all the forces acting on an object.
(b) The force Mr. Seifert is applying to the box to move it forward to the RIGHT is 105 N.
What is free body diagram?
A free body diagram is a graphical illustration of all the forces acting on an object.
The force applied by Mr Seifert is calculated by applying Newton's second law of motion as follows;
F - Ff = ma
where;
F is the applied forceFf is the force of frictionm is the mass of the cardboarda is the acceleration of the cardboardThe given parameters include;
mass of the cardboard = 40 kg
force of friction = 25 N
acceleration of the cardboard = 2 m/s²
The force applied by Mr Seifert is calculated as follows;
F = Ff + ma
F = 25 N + (40 kg x 2 m/s²)
F = 105 N
Learn more about applied force here: https://brainly.com/question/14428983
#SPJ1
What volume of 2. 00 M HCl in liters is needed to react completely (with nothing left over) with 0. 500 L of 0. 500 M Na2CO3
Answers
To react completely with 0.500 L of volume of 0.500 M Na2CO3, you would need 0.250 L of 2.00 M HCl.
Write down the balanced chemical equation for the reaction between HCl and Na2CO3:
2 HCl + Na2CO3 → 2 NaCl + H2O + CO2
Determine the stoichiometry of the reaction:
From the balanced equation, we can see that 2 moles of HCl react with 1 mole of Na2CO3.
Calculate the number of moles of Na2CO3:
Given that the volume of Na2CO3 solution is 0.500 L and the concentration is 0.500 M, we can use the formula:
Moles = Concentration × Volume
Moles of Na2CO3 = 0.500 M × 0.500 L = 0.250 moles
Use the stoichiometry to determine the number of moles of HCl needed:
According to the stoichiometry of the balanced equation, 1 mole of Na2CO3 reacts with 2 moles of HCl.
Therefore, to react with 0.250 moles of Na2CO3, we would need 2 × 0.250 = 0.500 moles of HCl.
Convert moles of HCl to volume:
Given that the concentration of HCl is 2.00 M, we can use the formula:
Volume = Moles / Concentration
Volume of HCl = 0.500 moles / 2.00 M = 0.250 L
Convert the volume to liters:
The final answer is 0.250 liters of 2.00 M HCl are needed to react completely with 0.500 L of 0.500 M Na2CO3.
For more such questions on volume, click on:
https://brainly.com/question/29796637
#SPJ8
The can be obtained by using the balanced chemical equation: Na2CO3 + 2 HCl → 2 NaCl + H2O + CO2 Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction.
Na2CO3 + 2 HCl → 2 NaCl + H2O + CO2
Calculate the number of moles of Na2CO3. Using the formula n = c × V, where n is the number of moles, c is the concentration, and V is the volume, we get:
n = c × V
= 0.500 M × 0.500 L
= 0.250 mol
Calculate the number of moles of HCl required.The balanced chemical equation shows that 2 moles of HCl react with 1 mole of Na2CO3. Hence, the number of moles of HCl required can be calculated as follows
:n(HCl) = 2 × n(Na2CO3)
= 2 × 0.250 mol
= 0.500 mol
Calculate the volume of 2.00 M HCl required.The number of moles of HCl required is 0.500 mol. Using the formula V = n/c, where V is the volume, n is the number of moles, and c is the concentration, we get:
V = n/c
= 0.500 mol ÷ 2.00 M
= 0.250 L
To know more about chemical equations visit:
https://brainly.com/question/28792948
#SPJ11
Spring compressed 10cm by 100N force and held in place with Pin. Pin is pulled and block is pushed Up the incline. Uk(coefficient of kinetic energy)=. 39
Determine the speed of block after the Spring extends forward 7cm,
Determine the height at which the block will stop moving
Determine the length of the incline such that the leading edge of the block is stopped when the block reaches the end of the incline.

Answers
The compression of 10 cm by a 100 N force on the plane that has a
coefficient of friction of 0.39 give the following values.
The velocity of the block after the Spring extends 7 cm is approximately 1.73 m/sThe height at which the block stops rising is approximately 1.1415 mThe length of the incline is approximately 1.536 mHow can the velocity and height of the block be calculated?Mass of the block, m = 3 kg
\(Spring \ constant, K = \dfrac{100 \, N}{0.1 \, m} = \mathbf{ 1000\, N/m}\)
Coefficient of kinetic friction, \(\mu_k\) = 0.39
Therefore, we have;
Friction force = \(\mathbf{\mu_k}\)·m·g·cos(θ)
Which gives;
Friction force = 0.39 × 3 × 9.81 × cos(48°) ≈ 7.68
Work done by the motion of the block, W ≈ 7.68 × d
The work done = The kinetic energy of the block, which gives;
\(\mathbf{\dfrac{1}{2} \times k \cdot x^2 }= 7.68 \cdot d\)
The initial kinetic energy in the spring is found as follows;
K.E. = 0.5 × 1000 N/m × (0.1 m)² = 5 J
The initial velocity of the block is therefore;
5 = 0.5·m·v²
v₁ = √(2 × 5 ÷ 3) ≈ 1.83
Work done by the motion of the block, W ≈ 7.68 N × 0.07 m ≈ 0.5376 J
Chane in kinetic energy, ΔK.E. = Work done
ΔK.E. = 0.5 × 3 × (v₁² - v₂²)
Which gives;
ΔK.E. = 0.5 × 3 × (1.83² - v₂²) = 0.5376
Which gives;
The velocity of the block after the Spring extends 7 cm, v₂ ≈ 1.73 m/sThe height at which the block will stop moving, h, is given as follows;
\(At \ the \ maximum \ height, \ h, \ we \ have ; \ \dfrac{1}{2} \times 1000 \times 0.1^2 = 7.68 \times x\)
Which gives;
\(Length \ of \ the \ incline \ at \ maximum \ height, \ x_{max} =\dfrac{ 7.68 }{ \dfrac{1}{2} \times 1000 \times 0.1^2 } \approx 1.536\)
The distance up the inclined, the block rises, at maximum height is therefore;
\(x_{max}\) ≈ 1.536 m
Therefore;
h = 1.536 × sin(48°) ≈ 1.1415
The height at which the block stops rising, h ≈ 1.1415 mFrom the above solution for the height, the length of the incline is he
distance along the incline at maximum height which is therefore;
Length of the incline, \(x_{max}\) = 1.536 mLearn more about conservation of energy here:
https://brainly.com/question/7538238
A runner completes a 400 meter race in 2.5 minutes. What is the runner's average speed?
Answers
Answer: I believe it’s 160 meters per minute. Hope this helps. Good luck :)
Explanation:
Types of resources include: a. expert, opinion leaders, support c. support, expert and technical b. material, support and expert d. technical, material and expert please select the best answer from the choices provided a b c d
Answers
Types of Resources can include: material, support and expert; option B.
What are resources?Resources refers to all the materials that are available in our environment which are used by man to satisfy his needs and wants.
Resources may either be:
renewable resources, ornon-renewable resourcesRenewable resources are replenished over a short time while non-renewable resources are not replenished within a short time.
Types of Resources can include:
material,support andexpertIn conclusion, resources are varied in nature and type.
Learn more about resources at: https://brainly.com/question/1290230
#SPJ1
Answer: B
Explanation:
took the eng test hope this helps :)
Time period of a charged particle undergoing a circular motion in a uniform magnetic field is independent of.
Answers
The time period of a charged particle in a uniform magnetic field is determined by the magnetic field strength and mass-to-charge ratio. The particle's velocity, radius, and charge do not affect its time period. The magnetic force determines the particle's circular motion, not its charge.
The time period of a charged particle undergoing circular motion in a uniform magnetic field is independent of three factors: the velocity of the charged particle, the radius of the circular path, and the charge of the particle.
Firstly, the velocity of the charged particle does not affect its time period. The time period is solely determined by the magnetic field and the mass-to-charge ratio of the particle. Regardless of how fast or slow the particle moves, the time taken to complete one full revolution remains the same.
Secondly, the radius of the circular path does not influence the time period either. As long as the magnetic field strength and the mass-to-charge ratio of the particle remain constant, the time period remains unchanged. This means that particles of different masses or charges can have the same time period if they have the same ratio of mass to charge.
Lastly, the charge of the particle does not impact the time period. Whether the particle has a positive or negative charge, the time taken to complete one revolution remains constant. The magnetic force acting on the charged particle determines the circular motion, not the charge itself.
To know more about time period Visit:
https://brainly.com/question/31824035
#SPJ11
A football of mass 1 kg is thrown at an initial velocity of 7 m/s at an angle of 33 degrees with respect to the horizontal. Please determine the maximum height the football can reach
Answers
The football can achieve a maximum height of 0.7415 m when thrown with a velocity of 7 m/s at an angle of 33 degrees with respect to the horizontal axis.
Let's find the initial velocity of the football on the vertical axis,
the velocity of football in the vertical axis, u = 7 sin(33)
u =7 (0.5446)
u = 3.8124
Now let's find the maximum height that can be achieved by the football.
The maximum velocity of the football will be zero, so the final velocity is zero.
Using equation,
\(v^2-u^2 = 2ah\)
we can find the height where h is the maximum height that can be achieved.
Substituting all the values in the above equation, we get
0 - 14.5343 = - 2(9.8)h
This negative depicts that acceleration is in the opposite direction of the initial velocity.
14.5343 = 19.6 h
h = 0.7415
Hence, the football can achieve a maximum height of 0.7415 m when thrown with a velocity of 7 m/s at an angle of 33 degrees with respect to the horizontal axis.
To learn more about maximum height :
https://brainly.com/question/11182480
a 3000 kg car with a full load of people, has a kinetic energy of 190,000 J. What would the kinetic energy of the car be if it was moving at the same speed but a different mass of 1500 kg?
Answers
Answer: 15.9 m/s
Explanation:
KE = 1/2(mv^2)
190,000J = 1/2(3000kg)*v^2
1 J = 1 kg*m^2/s^2
190,000 kg*m^2/s^2 = 1/2(3000kg)*v^2
v^2 = (190,000 kg*m^2/s^2)/(1/2(3000kg))
v^2 = (190,000 kg*m^2/s^2)/(1500kg))
v^2 = 126.6667 m^2/s^2
v = 11.25 mm/s velocity of 3000kg vehicle
With the same kinetic energy, a vehicle of 1500kg would have a different velocity:
190,000 kg*m^2/s^2 = 1/2(1500kg)*v^2
190,000 kg*m^2/s^2 =(750kg)*v^2
v^2 = 253.33 m^2/s^2
v = 15.9 m/s
John take measurements of position vs. time and plots the points on a graph. Find the slope of the line connecting the points (9, -8) and (-9, -7). Leave your answer as a decimal correct to three decimal places.
Answers
The slope of the line connecting the points (9, -8) and (-9, -7) will be
- 0.056
x1 = 9
y1 = -8
x2 = -9
y2 = -7
m = ( y2 - y1 ) / ( x2 - x1 )
= -7 + 8 / -9 - 9
= 1 / - 18 = - 0.056
The slope of the position vs. time graph will be - 0.056
To learn more about position vs. time graph here :
https://brainly.com/question/28610581
#SPJ1
Give Ideas to create hearing instruments to fix hearing problems in space, as you know sound waves can’t travel through empty space.