There are 4 black, 4 red, and 4 white marbles in a box. How many marbles do you have to take out (without looking) to be sure you have at least two marbles of the same color
Answers
Answer:
6
Step-by-step explanation:
4 marbles we have to take out (without looking) to be sure that we have at least two marbles of the same color.
There are 4 black, 4 red, and 4 white marbles in a box.
So, in order to have atleast two marbles of the same color we must take out atleast four marbles.
That is 1 black, 1 red, and 1 white of each color and the fourth one may be of any color. So we have atleast two marbles of the same color.
Therefore we have to rake out atleast 4 marbles in order to have at least two marbles of the same color.
Learn more:https://brainly.com/question/16820454
Related Questions
Q1-) Consider a manufacturing system with two machines. Suppose that when both ma- chines are available, one is in use and the other is on standby. The probability that a machine in use fails during a day is p. When it fails its repair may start only the next day if the single repair facility is available. It takes two days to repair a failed machine. We can use a Markov Chain model to describe the evolution of this system. Let Xn = (i, j), n ≥ 0 denote the states of the Markov chain, where i is the number of machines in working condition and j is the number of elapsed repair days of a machine at the repair facility at the beginning of the n'th day. The corresponding transition probability matrix is (2,0) (1,0) (1,1) (0,1) (2,0) [1-p P 0 0 (1,0) 0 0 1-p Р P= (1,1) 1-p 0 0 P (0,1) 0 1 0 0 For parts (a)-(c) do not assume a specific value for p, leave your answer in terms of p. (a) Given Xo = (1, 1), what is the probability that only one machine is in working condition after two days? (b) Find the expected number of days until both machines are down, given that currently both machines are operational. (c) Find the steady state probabilities. (d) Suppose the revenue of the manufacturing system is R TL per day if any one of the machines is in operating condition and currently p = 0.3. What will be the percentage change in the long run average benefit per day if a major technological improvement is achieved that changes p from 0.3 to 0.2?
Answers
(a) To find the probability that only one machine is in working condition after two days, we need to determine the probability of transitioning from state (1, 1) to state (1, 0) after two days.
From the transition probability matrix, we see that to transition from (1, 1) to (1, 0) in one day, both machines need to remain operational, which has a probability of (1 - p) * (1 - p) = (1 - p)^2.
Therefore, the probability of transitioning from (1, 1) to (1, 0) after two days is ((1 - p) * (1 - p))^2 = (1 - p)^4.
(b) To find the expected number of days until both machines are down, given that currently both machines are operational, we need to consider the transition probabilities from state (2, 0) to state (0, 1).
From the transition probability matrix, we see that to transition from (2, 0) to (0, 1) in one day, both machines need to fail, which has a probability of p * p = p^2.
Therefore, the expected number of days until both machines are down, given that both machines are currently operational, is 1 / (p^2).
(c) To find the steady-state probabilities, we need to solve the equation πP = π, where π is the row vector of steady-state probabilities and P is the transition probability matrix.
Solving this equation will give us the steady-state probabilities for each state (i, j). Since the given matrix is not provided, it is not possible to calculate the exact steady-state probabilities without the specific values of the transition probabilities.
(d) To determine the percentage change in the long-run average benefit per day if p changes from 0.3 to 0.2, we would need to know how the revenue R TL is related to the probability p. Without this information, it is not possible to calculate the percentage change.
To learn more about probability : brainly.com/question/31828911
#SPJ11
A biologist uses a time machine to collect living material from 2 different time periods. Sample A is 3 billion years old and sample B is 1.5 billion years old. How would these samples differ?
Answers
The samples A and B, collected from different time periods, would differ in several aspects including the composition of living organisms, the environmental conditions, and the evolutionary stage of life forms. The differences between the samples can be attributed to the significant time gap between their existence, leading to evolutionary changes, species extinction, and the emergence of new organisms.
The age difference of 1.5 billion years between samples A and B represents a substantial period in Earth's history. During this time, various evolutionary processes, environmental changes, and natural selection would have influenced the development and diversity of life forms.
Sample A, being older at 3 billion years, would likely contain organisms that represent an early stage of life on Earth. This could include simple single-celled organisms or primitive multicellular organisms. Sample B, being 1.5 billion years younger, would reflect a more advanced stage of evolution, potentially containing more complex multicellular organisms and possibly even early forms of plants and animals.
Additionally, the environmental conditions during these two time periods would have differed. Factors such as atmospheric composition, temperature, availability of resources, and the presence of other species would have influenced the development and adaptation of organisms in each sample.
Overall, the differences between samples A and B would provide insights into the progression of life on Earth, the impact of environmental changes on organisms, and the evolutionary processes that have shaped the biodiversity we observe today.
To learn more about biodiversity : brainly.com/question/13073382
#SPJ11
help!! offering lots of points and brainliest!

Answers
Answer:
It would be C
Step-by-step explanation:
So, shows in the graph, you can see that the change in rise is 100, because to get to 150 from 50, you add 100
And the run is 1, because to go from 0 to 1, you add 1
Meaning the slope is 100/1
Hope this helped!
Consider the function f(x,y)=2x2−4x+y2−2xy subject to the constraints x+y≥1xy≤3x,y≥0 (a) Write down the Kuhn-Tucker conditions for the minimal value of f. (b) Show that the minimal point does not have x=0.
Answers
The minimal point does not have x = 0.
(a) Kuhn-Tucker conditions for the minimal value of fThe Kuhn-Tucker conditions are a set of necessary conditions for a point x* to be a minimum of a constrained optimization problem subject to inequality constraints. These conditions provide a way to find the optimal values of x1, x2, ..., xn that maximize or minimize a function f subject to a set of constraints. Let's first write down the Lagrangian: L(x, y, λ1, λ2, λ3) = f(x, y) - λ1(x+y-1) - λ2(xy-3) - λ3x - λ4y Where λ1, λ2, λ3, and λ4 are the Kuhn-Tucker multipliers associated with the constraints. Taking partial derivatives of L with respect to x, y, λ1, λ2, λ3, and λ4 and setting them equal to 0, we get the following set of equations: 4x - 2y - λ1 - λ2y - λ3 = 0 2y - 2x - λ1 - λ2x - λ4 = 0 x + y - 1 ≤ 0 xy - 3 ≤ 0 λ1 ≥ 0 λ2 ≥ 0 λ3 ≥ 0 λ4 ≥ 0 λ1(x + y - 1) = 0 λ2(xy - 3) = 0 From the complementary slackness condition, λ1(x + y - 1) = 0 and λ2(xy - 3) = 0. This implies that either λ1 = 0 or x + y - 1 = 0, and either λ2 = 0 or xy - 3 = 0. If λ1 > 0 and λ2 > 0, then x + y - 1 = 0 and xy - 3 = 0. If λ1 > 0 and λ2 = 0, then x + y - 1 = 0. If λ1 = 0 and λ2 > 0, then xy - 3 = 0. We now consider each case separately. Case 1: λ1 > 0 and λ2 > 0From λ1(x + y - 1) = 0 and λ2(xy - 3) = 0, we have the following possibilities: x + y - 1 = 0, xy - 3 ≤ 0 (i.e., xy = 3), λ1 > 0, λ2 > 0 x + y - 1 ≤ 0, xy - 3 = 0 (i.e., x = 3/y), λ1 > 0, λ2 > 0 x + y - 1 = 0, xy - 3 = 0 (i.e., x = y = √3), λ1 > 0, λ2 > 0 We can exclude the second case because it violates the constraint x, y ≥ 0. The first and third cases satisfy all the Kuhn-Tucker conditions, and we can check that they correspond to local minima of f subject to the constraints. For the first case, we have x = y = √3/2 and f(x, y) = -1/2. For the third case, we have x = y = √3 and f(x, y) = -2. Case 2: λ1 > 0 and λ2 = 0From λ1(x + y - 1) = 0, we have x + y - 1 = 0 (because λ1 > 0). From the first Kuhn-Tucker condition, we have 4x - 2y - λ1 = λ1y. Since λ1 > 0, we can solve for y to get y = (4x - λ1)/(2 + λ1). Substituting this into the constraint x + y - 1 = 0, we get x + (4x - λ1)/(2 + λ1) - 1 = 0. Solving for x, we get x = (1 + λ1 + √(λ1^2 + 10λ1 + 1))/4. We can check that this satisfies all the Kuhn-Tucker conditions for λ1 > 0, and we can also check that it corresponds to a local minimum of f subject to the constraints. For this value of x, we have y = (4x - λ1)/(2 + λ1), and we can compute f(x, y) = -3/4 + (5λ1^2 + 4λ1 + 1)/(2(2 + λ1)^2). Case 3: λ1 = 0 and λ2 > 0From λ2(xy - 3) = 0, we have xy - 3 = 0 (because λ2 > 0). Substituting this into the constraint x + y - 1 ≥ 0, we get x + (3/x) - 1 ≥ 0. This implies that x^2 + (3 - x) - x ≥ 0, or equivalently, x^2 - x + 3 ≥ 0. The discriminant of this quadratic is negative, so it has no real roots. Therefore, there are no feasible solutions in this case. Case 4: λ1 = 0 and λ2 = 0From λ1(x + y - 1) = 0 and λ2(xy - 3) = 0, we have x + y - 1 ≤ 0 and xy - 3 ≤ 0. This implies that x, y > 0, and we can use the first and second Kuhn-Tucker conditions to get 4x - 2y = 0 2y - 2x = 0 x + y - 1 = 0 xy - 3 = 0 Solving these equations, we get x = y = √3 and f(x, y) = -2. (b) Show that the minimal point does not have x=0.To show that the minimal point does not have x=0, we need to find the optimal value of x that minimizes f subject to the constraints and show that x > 0. From the Kuhn-Tucker conditions, we know that the optimal value of x satisfies one of the following conditions: x = y = √3/2 (λ1 > 0, λ2 > 0) x = √3 (λ1 > 0, λ2 > 0) x = (1 + λ1 + √(λ1^2 + 10λ1 + 1))/4 (λ1 > 0, λ2 = 0) If x = y = √3/2, then x > 0. If x = √3, then x > 0. If x = (1 + λ1 + √(λ1^2 + 10λ1 + 1))/4, then x > 0 because λ1 ≥ 0.
To know more about constraints, visit:
https://brainly.com/question/17156848
#SPJ11
PLS HELP ME $!!!!!!!
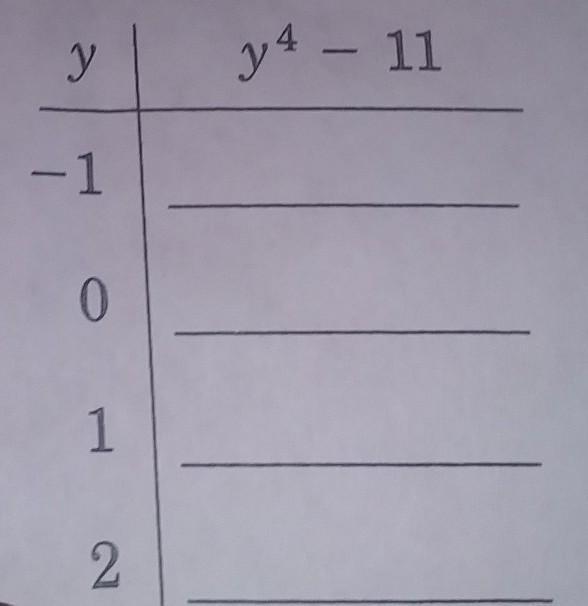
Answers
Step-by-step explanation:
(-1)⁴ - 11 = 1 - 11 = -10
0⁴ -11 = -11
1⁴ - 11 = -10
2⁴ -11 = -3
daniel earns extra money as a lifeguard he earns 37 dollars for 4 hours and 64.75 for 7 hours. the relationship between his earnings and the time worked is proportional true or false?
Answers
Answer: Yes, it is proportional.
Step-by-step explanation:
Find the amount Daniel earns each hour.
Divide the amount of money by the number of hours to find each earnings per hour.
Life guard: $37 for 4 hours.
37/4 = 9.25
64.75/ 7 = 9.25
Since Daniel receives the same amount of money per hour which is $9.25 per hour, then the relationship is proportional.
describe the value of 12x−4 when x=10
Answers
Answer:
Answer is 116
Step-by-step explanation:
12(10)-4 is 116
Answer:
=116
Step-by-step explanation:
12 x 10 = 120
120 - 4 = 116
if X =3, what is the value of 7x-2x?
Answers
Answer:
15
Step-by-step explanation:
x is equal to 3 so 7x - 2x = 7*3 - 2*3 = 21 - 6 = 15
How to solve y=2x-10 and 6x+7y=10 using substitution
Answers
Answer:
x=4
Step-by-step explanation:
y=2x-10 and 6x+7y=10
6x+7(2x-10)=10
6x+14x-70=10
20x=80
x=4
In one-half hour, a car traveled 20 km. Find the average velocity in km/min. (Round to the nearest
hundredth)
Answers
Step-by-step explanation:
\(s = 20km \\ t = 30min\)
\(v = \frac{s}{t} \\ v = \frac{2}{3} \)
\(v = 0.67\)
\(v = 0\)
b=1/4Af
im supposed to solve for A
Answers
/x=7
2=|3x|
10 is 32% of what number?
a. ; 32
b. ; 31.25
c. ; 3.2
d. ; 312.5
Answers
ANSWER:
31.25
STEP-BY-EXPLANATION:
you take 32 percent of a number and get 10, then what is that number?
you take 32 percent of a number and get 10, then what is that number?In other words, you know that 32 percent of a number is 10 and you want to know what that initial number is.
you take 32 percent of a number and get 10, then what is that number?In other words, you know that 32 percent of a number is 10 and you want to know what that initial number is.To solve this problem you multiply 10 by 100 and then divide the total by 32 as follows:
you take 32 percent of a number and get 10, then what is that number?In other words, you know that 32 percent of a number is 10 and you want to know what that initial number is.To solve this problem you multiply 10 by 100 and then divide the total by 32 as follows:(10 x 100) / 32
you take 32 percent of a number and get 10, then what is that number?In other words, you know that 32 percent of a number is 10 and you want to know what that initial number is.To solve this problem you multiply 10 by 100 and then divide the total by 32 as follows:(10 x 100) / 32When we put that into our calculator, we get the following answer:
you take 32 percent of a number and get 10, then what is that number?In other words, you know that 32 percent of a number is 10 and you want to know what that initial number is.To solve this problem you multiply 10 by 100 and then divide the total by 32 as follows:(10 x 100) / 32When we put that into our calculator, we get the following answer:31.25
GAVE ME THE BRAINLIEST IF MY ANSWER WAS HELPFUL...
Answer:
b. 31.25
Step-by-step explanation:
\(\frac{10}{y} :\frac{32}{100}\)
y × 32 = 10 × 100
32y = 1000
32y ÷ 32 = 1000 ÷ 32
y = 31.25
Determine whether the sequence converges or diverges. If it converges, find the limit. (If an answer does not exist, enter DNE.)
An= (4+3n^2)/(n+5n^2)
Lim n-> An =
Answers
To determine whether the sequence converges or diverges, we can use the Squeeze Theorem.
We can see that
\(4/(n + 5n^2) < = An < = (4 + 3n^2)/(n + 5n^2)\)
As n tends to infinity, \(4/(n + 5n^2)\) tends to 0 and\((4 + 3n^2)/(n + 5n^2)\) tends to\(4/(5n^2)\) which also tends to 0.
So by the Squeeze Theorem, we can say that An tends to 0 as n tends to infinity. Hence the limit of the sequence is Lim n-> An = 0
We can also see that the numerator of An is a constant and the denominator is a polynomial with degree 2. Since the denominator's degree is greater than the numerator, the limit will be zero as n -> infinity.
Therefore, the sequence converges to 0.
To learn more about Squeeze Theorem,
https://brainly.com/question/30077508
#SPJ4
2-53. a message is released at 1930 hours greenwich mean time on 2 january 1991. what is the correctly stated date-time group (dtg) assigned to the me
Answers
Step-by-step explanation:
. In Figure 5.144, of ΔABC, where
m(∠C) = 30, m(∠ABD) = 5x,
m(∠A) = 4x. Find m(∠ABC) in
degrees.
plz help solve this. i need the answer asap

Answers
Answer:
6 cups per month
Step-by-step explanation:
divide 72 by 12
What is the absolute value of -5
Answers
Answer:
5
Step-by-step explanation:
Find the value of x and y
3х
20
25
18
бу -2
Х=
ү=

Answers
Answer: first one =109360044xy−36453348x−2, 2nd,=3037778998,last one,=1968480790
Step-by-step explanation:Evaluate for x=3x,y=6y−2
33x(2025186)(6y−2)−2
33x(2025186)(6y−2)−2
=109360044xy−36453348x−2
Evaluate for x=20,y=25
(3)(20)(2025186)(25)−2
(3)(20)(2025186)(25)−2
=3037778998
because 18 is by itself i just did Evaluate for x=18,y=18
(3)(18)(2025186)(18)−2
(3)(18)(2025186)(18)−2
=1968480790
Which type of rigid transformation is the equivalent of two reflections across intersecting lines?
Answers
Rotation is the rigid type of transformation which is equivalent to the two reflections across intersecting lines.
Transformation of reflection gives us mirror image of the given geometrical shape or any object along the axis.Two reflections across the intersecting lines change the position of the shape or object in another coordinate plane .It represents the rotation of the given shape with center as the intersection of two given lines.Twice angle formed between the intersecting lines of the given shape.Therefore, the rigid type transformation which is equivalent to two reflection across the intersecting lines is called rotation.
Learn more about transformation here
brainly.com/question/11709244
#SPJ4
George was riding his bike downhill on a street in a Canadian town. The street- side speed sensor clocked him at 30 km per hour. His bike speedometer was set up in U.S. units of mph. What would the readout have been?b. A short-course meter pool is 25 meters long.
Answers
In order to find the readout in his bike speedometer, we need to know the approximate value for the conversion between miles and kilometers, then,
\(1\text{ }mi\Rightarrow1.609\text{ }km\)then, use conversion factors with the street side sensor,
\(\frac{30km}{h}\ast\frac{1mi}{1.609km}\approx\frac{18.64mi}{h}\)Answer:
The approximate value shown in his bike speedometer is 18.64 mph
A student analyzed the diagram and incorrectly concluded that AB = 2BC. Explain the student's error.
EB is the perpendicular bisector of AD,
so AB= BD.
angle BEC is congruent to angle DEC, so
BC= CD.
BC + CD = BD = AB, and
BC + CD = BC + BC = 2BC,
so AB= 2BC
Answers
Angle BEC is congruent to angle DEC. The student's error lies in assuming that BC + CD = 2BC means that AB = 2BC, which is incorrect. The student concluded that AB = 2BC by incorrectly analyzing the given diagram.
The error can be explained as follows: Since EB is the perpendicular bisector of AD, AB = BD is true.
Angle BEC is congruent to angle DEC, which makes BC = CD true.
If BC + CD is added, it equals BD, which is also equal to AB. Consequently, BC + CD = AB. Also, BC + CD can be written as BC + BC = 2BC.
However, this does not imply that AB = 2BC, as the student incorrectly concluded.
It is because BC and CD are two separate line segments, and just because they have the same length does not imply that they add up to double their length.
So, the student's error lies in assuming that BC + CD = 2BC means that AB = 2BC, which is incorrect.
To know more about congruent, refer
https://brainly.com/question/2938476
#SPJ11
-6.6 < 1.7 + u Solve the inequality for u.
Simplify your answer as much as possible.
Answers
Solving the inequality -6.6 < 1.7 + u for u, the solution is simplified as: u > -8.3 or -8.3 < u.
What is an Inequality?In maths, an inequality is defined as a statement that is used to compare two quantities that are unequal. For example, we can state that 5 is greater than 3 + 1, or 5x is less than 4x + 3x. We can equally state that a given value of a variable can be equal to or greater than a number, and so on.
Basically, we are comparing two unequal quantities when we state inequalities.
Given the inequality, -6.6 < 1.7 + u, we are asked to solve the inequality for u. That is, we need to find the possible value that u represents in the inequality or that would make the inequality true.
Therefore:
-6.6 < 1.7 + u
Subtract 1.7 from both sides
-6.6 - 1.7 < 1.7 + u - 1.7 [subtraction property of equality]
-8.3 < u
It can be rewritten as:
u > -8.3
Learn more about inequality on:
https://brainly.com/question/11613554
#SPJ1
the concept of hedonistic calculus is associated with
Answers
The concept of hedonistic calculus is associated with utilitarianism and the philosophy of maximizing pleasure and minimizing pain. It is a method for calculating the overall happiness or utility of actions based on the intensity, duration, certainty, propinquity, fecundity, purity, and extent of pleasure or pain they produce.
Hedonistic calculus is a term coined by the philosopher Jeremy Bentham, who was a proponent of utilitarianism. Utilitarianism is an ethical theory that states that the right action is the one that maximizes overall happiness or utility for the greatest number of people. The goal of hedonistic calculus is to measure and compare the happiness or pleasure derived from different actions or situations.
According to Bentham, pleasure and pain are the only relevant factors in determining the moral value of an action. Hedonistic calculus involves quantifying these pleasures and pains in order to assess their overall impact. Bentham proposed seven criteria to evaluate the intensity, duration, certainty, propinquity (nearness in time), fecundity (likelihood of leading to more pleasure or pain), purity (absence of pain mixed with pleasure), and extent of the pleasure or pain produced by an action.
By assigning values to each of these criteria, hedonistic calculus aims to determine the net amount of happiness or utility generated by a particular action or decision. The idea is to maximize pleasure and minimize pain, with the ultimate goal of promoting the greatest happiness for the greatest number of individuals.
Overall, hedonistic calculus provides a systematic approach to assess and compare the consequences of actions based on their impact on pleasure and pain. It serves as a framework for utilitarians to make ethical judgments and decisions by considering the net balance of happiness produced by different choices.
Learn more about Utilitarianism here: brainly.com/question/28148663
#SPJ11
Kelly needed to use 3 pounds 15 ounces of clay to make a bowl and twice as much to make a vase. If she had a 12-pound bag of clay available, did she have enough clay to make both items?
Answers
Answer:
yes
Step-by-step explanation:
so first you would convert pounds into ounces (It's easier for me)
and there are 16 ounces in one pound so for 3 pounds you would have 48 ounces then add the 15 ounces to get 63 ounces and if she needs twice as much to make a vase she would need 126 ounces for a vase then you would add the other 63 to that to get a total of 189 ounces of clay in order to create the bowl and vase, and in order to find out how many ounces are in a 12 pound bag you would just multiply 12 by 16 to get 192 ounces. So yes she does have enough clay to make a bowl and a vase.
14% of 81 is what number?
Answers
That’s the answer
Answer:
11.34
Step-by-step explanation:
14% of 81 = \(\frac{14}{100}\) × \(\frac{81}{1}\) \(\frac{14}{100}\) × \(\frac{81}{1} = \frac{1134}{100}\) 1134/100 = 11.34I hope this helps!
1100 square feet of sod for $1200 OR 1000 square feet of sod for $1100
Answers
Answer:
1100 for $1200
Step-by-step explanation: it is
1200/1100 is 1.09
1100/1000 is 1.1
Answer:
Sod installation in an average 1/5-acre, or 8,712 square foot, yard costs $8,715 to $17,430. ... Expect sod installation to cost $1,000 to $6,000 for small yards that are between 1,000 and 3,000 square feet. ... Tulsa, Oklahoma, $1,100-$2,300.
This is my answer i think its correct tell me if it is..........?
a certain statistic dˆ is being used to estimate a population parameter d. the expected value of dˆ is not equal to d. what property does dˆ exhibit?a. The sampling distribution of d hat is normal.b. The sampling distribution of d hat is binomial.c. The sampling distribution of d hat is uniform.d. d hat is unbiased.e. d hat is biased.
Answers
The right answer is: E, according to the Central Limit Theorem for proportionality. The statistic is inaccurate.
In probability theory, the central limit theorem establishes that, in many situations, when independent random variables are summed up, their properly normalized sum tends toward a normal distribution even if the original variables themselves are not normally distributed.
The Central Limit Theorem establishes that for a proportion p in a sample of size n:
The expected value is μ=р
The standard error is s=\(\sqrt{\frac{p(1-p)}{n} }\)
In this problem, the expected value is different of the expected of μ=р , hence, the statistic is biased, and the correct option is E.
To learn more about Central limit theorem visit: brainly.com/question/4086221
#SPJ4
Where v is the final velocity (in m/s), u is the initial velocity (in m/s), a is the acceleration (in m/s²) and t is the time (in seconds).
Find v when u is 19 m/s, a is 3 m/s², and t is 21 seconds.
Answers
The value of v, final velocity, is 82 m/s
Calculating velocityFrom the question, we are to calculate the final velocity, v
From one of the equations of linear motion, we have that
v = u + at
Where v is the final velocity
u is the initial velocity
a is the acceleration
and t is the time
From the given information
u = 19 m/s
a = 3 m/s²
t = 21 seconds
Putting the parameters into the equation,
v = u + at
v = 19 + 3(21)
v = 19 + 63
v = 82 m/s
Hence, the value of v, final velocity, is 82 m/s
Learn more on Calculating Velocity here: https://brainly.com/question/25905661
#SPJ1
use the formula for the sum of the first n integers to evaluate the sum given below. 3+6+9+12+....+150
Answers
The sum of the numbers 3+6+9+12+....+150 is 3825. To find the sum of an arithmetic series, you can use the formula:
Sum = (n * (a1 + an)) / 2
where n is the number of integers, a1 is the first integer, and an is the last integer.
In this case, the series is 3, 6, 9, ..., 150, and it's an arithmetic series with a common difference of 3. To find the number of integers (n) in the series, use the formula:
n = ((an - a1) / common difference) + 1
n = ((150 - 3) / 3) + 1 = (147 / 3) + 1 = 49 + 1 = 50
Now, use the sum formula:
Sum = (n * (a1 + an)) / 2
Sum = (50 * (3 + 150)) / 2
Sum = (50 * 153) / 2
Sum = 7650 / 2
Sum = 3825
So the sum of the given series is 3825.
Learn more about sum here:
https://brainly.com/question/13013054
#SPJ11
the ratio of dividends to the average number of common shares outstanding is:
Answers
The ratio of dividends to the average number of common shares outstanding is known as the dividend yield. It is a measure of the return on an investment in the form of dividends received relative to the number of shares held.
To calculate the dividend yield, you need to divide the annual dividends per share by the average number of common shares outstanding during a specific period. The annual dividends per share can be obtained by dividing the total dividends paid by the number of outstanding shares. The average number of common shares outstanding can be calculated by adding the beginning and ending shares outstanding and dividing by 2.
For example, let's say a company paid total dividends of $10,000 and had 1,000 common shares outstanding at the beginning of the year and 1,500 shares at the end. The average number of common shares outstanding would be (1,000 + 1,500) / 2 = 1,250. If the annual dividends per share is $2, the dividend yield would be $2 / 1,250 = 0.0016 or 0.16%.
In summary, the ratio of dividends to the average number of common shares outstanding is the dividend yield, which measures the return on an investment in terms of dividends received per share held.
To know more about dividend, here
brainly.com/question/3161471
#SPJ11
what is the missing blank?

Answers
Answer:
<1 and <8 are alternate exterior angles
Step-by-step explanation:
Alternate means on the opposite side of the transversal
Exterior means outside the parallel lines
<1 and <8 are alternate exterior angles