what is the vascular layer (of the ciliary body)?
Answers
The vascular layer of the ciliary body is a part of the eye that is located between the retina and the sclera.
It consists of a network of blood vessels that supply nutrients and oxygen to the structures of the eye, including the lens, iris, and retina.
The ciliary body also plays a role in the accommodation of the lens, which is responsible for adjusting the focus of the eye to see objects at different distances.
The vascular layer is made up of two parts: the ciliary muscle and the ciliary processes.
The ciliary muscle is responsible for controlling the shape of the lens, which changes its focus.
The ciliary processes produce aqueous humor, which is a fluid that fills the front of the eye and provides nourishment to the cornea and lens.
The vascular layer is important for maintaining the health and function of the eye. Diseases that affect this layer can lead to vision problems, including glaucoma and uveitis.
Regular eye exams are important for detecting and treating these conditions early.
For more such answers on Part of the eyes
https://brainly.com/question/30392658
#SPJ11
Related Questions
Referring to the illustration below, answer the following questions:
a. What process is represented here?
b. How do you know? (Give two reasons.)
c. Is the parent cell a somatic cell or a gamete? (Think before writing your answer!)
d. What is the end result of this process?
e. How similar or different are the daughter cells from one another? If they are different, explain why.
Answers
The genetic material in each daughter cell is identical to that in the parent cell, and the process of mitosis ensures that each daughter cell receives a copy of each chromosome.
a. The process represented here is cell division. b. The reasons why this process is cell division are:
1. The parent cell is dividing into two daughter cells.
2. The daughter cells are genetically identical to each other. c. The parent cell is a somatic cell. It is not a gamete because gametes are produced by meiosis, not mitosis. d. The end result of this process is two genetically identical daughter cells. e. The daughter cells are genetically identical to each other. They are the same because they are produced by mitosis, which involves only one round of cell division and results in two daughter cells that are genetically identical to each other. The genetic material in each daughter cell is identical to that in the parent cell, and the process of mitosis ensures that each daughter cell receives a copy of each chromosome.
To know more about mitosis visit: https://brainly.com/question/31626745
#SPJ11
Which scenario breaks the law of segregation?
Answers
Answer:
The answer is c a gamete has two of the same alleles after meiosis 2
Explanation:
A biologist spent many years researching the rate of evolutionary change in the finch populations of a group of islands. It was determined that the average beak size (both length and mass) of finches in a certain population increased dramatically during an intense drought between 1981 and 1987. During the drought, there was a reduction in the number of plants producing thin-walled seeds.
Answers
From 1981 to 1987, a significant number of finches had their beak sizes recorded The scientist spent several years studying the pace of evolutionary change. From 1981 to 1987, a significant number of finches had their beak sizes recorded annually.
Natural selection requires time and many generations to select for the desired character feature in evolutionary change development. Given that the researcher was interested in not only the incidence of evolutionary change but also its rate, extensive observation and data gathering were required over a lengthy period of generations. The beak size in a large number of finches was measured every year from 1981 to 1987 This is referred to as a longitudinal study. This would need extensive long-term study of a large sample of finches spanning several generations.
learn more about evolutionary change here:
https://brainly.com/question/4822518
#SPJ4
What is the structure labeled A?

Answers
non living martix . Lacunae . cartilage. onondrocyte
2. Economic systems
a. Do not depend on limited natural resources
b. Rarely balance the costs and benefits of every
action
c. Should not include the costs of pollution with the
costs of an action
d. Must operate within the environment
Answers
Economic systems must operate within the environment. Therefore, option D is correct.
What are economic systems?The system of economic activities including production, consumption, and investment that predominate in a given region is referred to as the economic system.
Every economy operates under a certain set of conditions and presumptions. Traditional economies, command economies, mixed economies, and market economies are the four primary types of economic systems.
Economic systems must operate within the environment. Therefore, option D is correct.
Learn more about economic systems, here:
https://brainly.com/question/27630988
#SPJ1
Which term describes the position (location) of a gene on a chromosome?
Answers
Answer:
B.
Explanation:
it is right
Locus is the term that describes the position (location) of a gene on a chromosome.
In biology, the specific site on a chromosome where a gene is found is called a locus (plural loci).
The locus, therefore, defines the position of the gene or other DNA sequence and the set of genes found on chromosomes is known as the genome.
A genetic map is an ordered listing of the loci that are known for a particular genome.
An allele, on the other hand, is a variant of a DNA sequence at a certain locus.
Therefore, we can conclude that locus is the term that describes the position (location) of a gene on a chromosome.
Learn more here: https://brainly.com/question/11636071
Does Planet Nine follow Kepler’s Second Law?
Answers
Can anyone tell the answer

Answers
it is an infunction of the lungs caused by bacteria virus fungi or protozoa in rare condition
Answers
Answer:
Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs caused by bacteria virus fungi or protozoa in rare condition.
A cell with a diploid number of 24 chromosomes undergoes meiosis. What will be the product at the end of meiosis? (quantity of cells and number of chromosomes in each cell)
Answers
Answer:
4 cells 6 chromosomes in each
Explanation:
What makes up a codon on an mRNA strand
Answers
Answer: The DNA serves as a pattern for making messenger RNA, and the messenger RNA then serves as a pattern for making a specific protein. DNA and the corresponding messenger RNA are made up of a series of bases. In RNA, these bases are often labeled with the letters A, U, C, and G. A set of three bases makes up a codon.
Explanation:
"Why is each part of the cell essential to survival?" please write and answer in CER form
Answers
Each part of the cell is essential to survival because they perform the necessary functions which help keep us alive.
What is a Cell?This is referred to as the simplest unit of life and becomes aggregated to for tissues which have similar structures and functions.
Let's take the eyes for example, if the cells are damaged then it will lead to the reduction in its function which in this scenario is a bad sight or having troubles seeing correctly. This in turn leads to not being able to work or move away from hazardous substances which is why each part of the cell is essential to survival.
Read more about Cell here https://brainly.com/question/13123319
#SPJ1
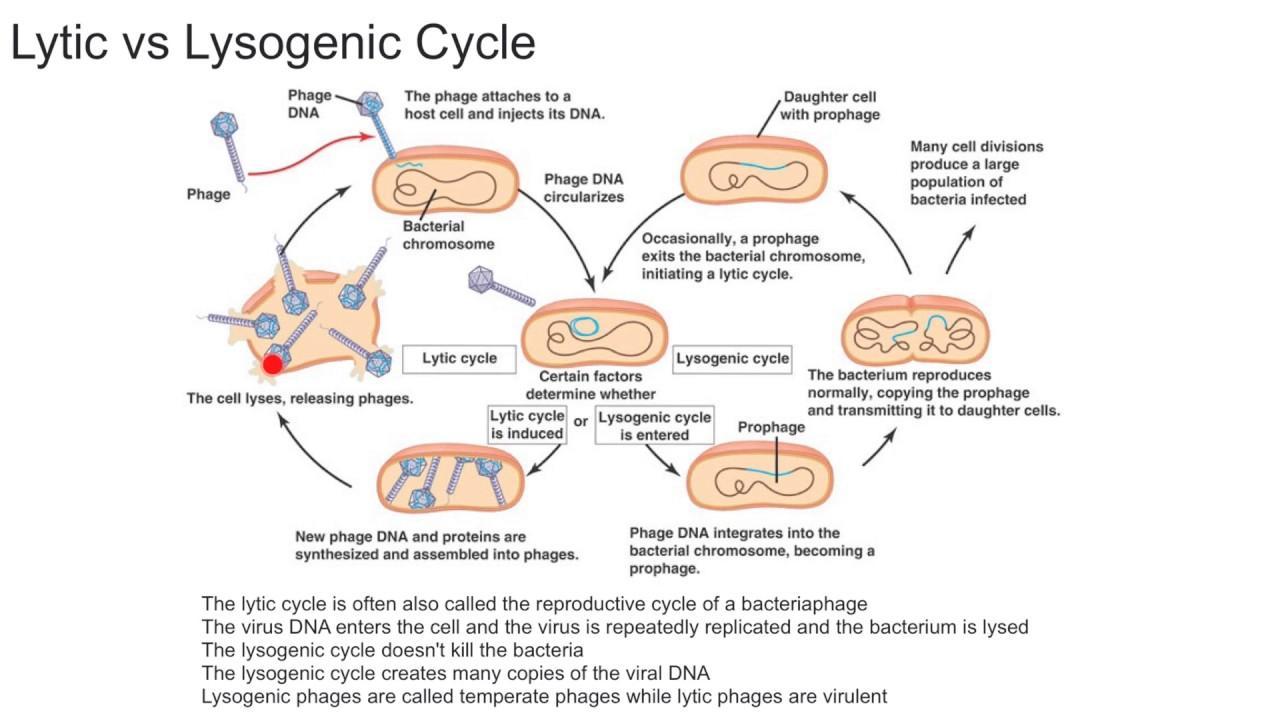
Lytic cycle or lysogenic cycle?: Infected cells have viral genes permanently.
Answers
Answer:
It is a lysogenic cycle.
Explanation:
In the lysogenic cycle, the viral DNA gets integrated into the host's DNA (see the picture attached).
Hope this will help :)
Hormones turn on, turn off, speed up, or slow down the
activities of organs and tissues.
true or false
Answers
Answer:
True
Explanation:
The answer is True.
Yellowstone National Park is located on top of a large active volcano. Heat rising from the underground magma chamber of the volcano fuels unique ecosystems within the park's geysers, hot
springs, and mud spots. If the volcano were to become inactive, the stability of ecosystems in the park's thermal features would
A decrease
B. increase.
С
decrease, then increase
D. increase, then decrease.
Answers
Answer: A
Explanation:
Decrease, Btw if I'm wrong I'm sry lol
But I think it's A
Which is the first checkpoint in the cell cycle that will cause a cell to exit the cycle if this point is not passed?.
Answers
'The Growth 1 (G1) phase is the first checkpoint in the cell cycle that may cause a cell to exit the cycle if this point is not passed.
What are the checkpoints in the cell cycle?The checkpoints in the cell cycle are stages during the cell cycle that need to fulfill certain requirements in order that the cell cycle can proceed. These sequential checkpoints in the cell cycle are found first at the G1 phase, then the S phase and finally the mitotic M phase.
Therefore, with this data, we can see that the checkpoints in the cell cycle control everything is fine in order to proceed with the cell cycle.
Learn more about the checkpoints in the cell cycle here:
https://brainly.com/question/2128300
#SPJ1
In the germinal period, about half of developing organisms do not survive. This can usually be explained by _____ failure.
Answers
In the germinal period, about half of developing organisms do not survive. This can usually be explained by chromosomal failure.What is chromosomal failure. Chromosomal failure is the loss or gain of chromosomes, resulting in aneuploidies, such as trisomy or monosomy.
The chromosomes in an individual's body control their development. The genetic material is made up of chromosomes. The zygote will be created when a sperm cell fertilizes an egg cell. This cell has two sets of 23 chromosomes, for a total of 46 chromosomes. In general, each of these chromosomes is well-defined.
There are occasions when chromosomes are missing or exist in greater than the typical quantity. This is referred to as aneuploidy. This typically leads to the death of the organism. Therefore, chromosomal failure explains why about half of developing organisms do not survive in the germinal period.
To know more about Chromosomal visit :
https://brainly.com/question/11087117
#SPJ11
Which of the following statements about water is NOT true?
A. It helps to maintain a normal body temperature.
B. It is a good source of energy.
C. It carries substances throughout the body in the bloodstream.
D. It is needed for all chemical reactions to occur.

Answers
What is the main function of glycolysis in cellular respiration?
O A. To make water molecules
B. To make glucose molecules
C. To breakdown water molecules
D. To breakdown glucose molecules
Answers
Answer:
The answer is B. To make glucose molecules
which of the following are represented by upper and lower case letters
A. proteins
B. chromosomes
C. genotypes
D. phenotypes
Answers
Answer: B. Chromosomes
Explanation:
a bird called the wandering albatross spends most of its life flying over the oceans of the southern hemisphere, stopping only to breed on storm-swept islands near antarctica. you would predict that the breast muscles of the wandering albatross:
Answers
The breast muscles of a bird is Pectoral muscles.
There are two pairs of large muscles that move the wings in flight that is the pectoralis, by which the bird lowers the wing, and the supracoracoideus, by which the bird raises the wings. The supracoracoideus lies in the between the angle of the keel and the plate of the sternum and along the coracoid. By this they creates a pulley like action by means of a tendon that passes through the canal at the junction which is formed by the coracoid, furcula, and scapula and then they attaches to the dorsal side of the head of the humerus. The pectoralis lies over the supracoracoideus and it attaches to the head of the humerus. Striated muscles of birds contain a respiratory pigment known as myoglobin. There are relatively few myoglobin-containing cells in white meat so their texture is white whereas the red meat contains a good amount of myoglobin. The white meat muscle is used in short, rapid bursts of activity, whereas the red meat muscle is characteristic of muscles used continuously for long periods and especially in muscles used during diving.
For for information on Pectoral muscles, visit:
https://brainly.com/question/29761732
#SPJ4
Consider an endangered tropical songbird from Indonesia and a city pigeon from San Francisco. How could you compare these two animals in terms of the Law of Tolerance? (Mention specific factors)
Answers
Answer:
Due to environmental factors.
Explanation:
The tropical songbird that is found in Indonesia has a very low tolerance against environmental factors as compared to city pigeon from San Francisco. Due to lack of tolerance the songbird decreases in population while on the other hand, the city pigeon maintains its population due to tolerance against the environmental factors such as climate, food and predators etc. If the climate is too harsh the survival of the organism is not possible and if there is a predator present in that environment, the organism also decreases in population.
EXPLAIN WHY CELL DIVISION IS AN IMPORTANT PROCESS FOR MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS.
Answers
Cell division is important because it helps the body to heal or repair in the case of an injury and helps in the formation of gametes which add up to aid reproduction in multicellular organisms
during the complete oxidation of glucose by aerobic respiration, a maximum of 4 atp molecules are made by substrate-level phosphorylation, compared to how many atp molecules made by oxidative phosphorylation?
Answers
The number of ATP molecules made by oxidative phosphorylation is 28 ATP.
Oxidative phosphorylation is the next step in aerobic energy metabolism after glycolysis and the Krebs cycle. This stage itself is a combination of the electron transport chain followed by a chemiosmosis process whose result is ATP.
1 NADH produces 2.5 ATP 1 FADH₂ generates 1.5 ATP.The process of aerobic respiration produces 10 NADH and 2 FADH2.
The amount of ATP produced from 10 NADH is 10 x 2.5 = 25 ATP2 FADH2 produces 2 x 1.5 = 3 ATP.So, the total ATP generated is 28 ATP.
Learn more about oxidative phosphorylation here https://brainly.com/question/8562250
#SPJ4
HELP! I'll give the brainliest!!

Answers
Answer:
In facilitated diffusion, molecules move down their concentration gradient.Explanation:
In facilitated diffusion, substances move into or out of cells down their concentration gradient through protein channels in the cell membrane. Simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion are similar in that both involve movement down the concentration gradient.
Osmosis refers specifically to the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane, with the solvent (water, for example) moving from an area of low solute (dissolved material) concentration to an area of high solute concentration.
Active transport is the movement of dissolved molecules into or out of a cell through the cell membrane, from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration. The particles move against the concentration gradient , using energy released during respiration .
Proteins embedded in the cell membrane may help molecules pass through that membrane without requiring any energy from the cell. Which type of passive transport would this be considered?
A) Osmosis
B) Diffusion
C) Exocytosis
D) Facilitated Diffusion
Answers
Answer:
Facilitated Diffusion
Explanation:
photosynthesis steps
Answers
Part 2: Internal Anatomy (cont.)
Complete the following statements.
1. The pharynx is located between segments
Answers
1. The pharynx is located between segments of the respiratory and digestive systems.
The pharynx is a muscular tube that serves as a common pathway for both air and food. It is located at the back of the throat and connects the nasal and oral cavities to the esophagus and larynx. The pharynx is divided into three regions: the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx.
The nasopharynx is located behind the nasal cavity and above the soft palate. It serves as a passageway for air, connecting the nasal cavity to the rest of the respiratory system. The oropharynx is located behind the oral cavity and extends from the soft palate to the epiglottis. It plays a role in both the respiratory and digestive systems, as it serves as a passage for both air and food. The laryngopharynx is the lowest part of the pharynx and is located behind the larynx. It leads to the esophagus for food passage and the larynx for air passage.
The pharynx plays a crucial role in the process of swallowing. When food is swallowed, it passes through the pharynx before entering the esophagus for digestion. The pharyngeal muscles contract in a coordinated manner, pushing the food bolus downward and preventing it from entering the airway.
In summary, the pharynx is located between segments of the respiratory and digestive systems. It acts as a common pathway for both air and food, playing a vital role in swallowing and directing the passage of substances into the appropriate pathways of the respiratory and digestive tracts.
For more such information on: pharynx
https://brainly.com/question/13554091
#SPJ8
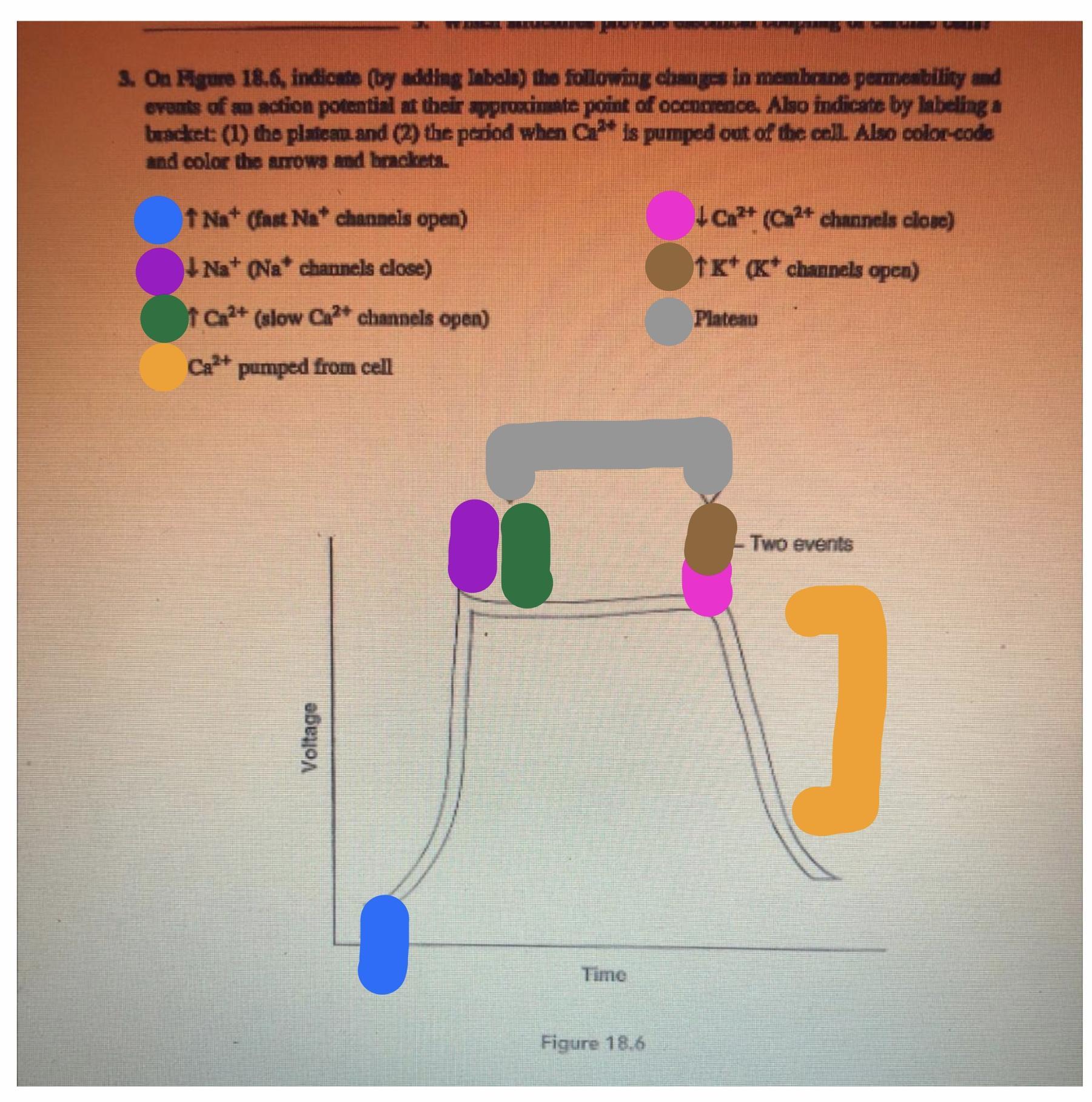
Can someone atleast tell me which line is which so I can color code please

Answers
Answer:
See attached image
Explanation:
Action potential can be split into 5 phases (0-4), where phase 4 leads from one action potential to the next. Phase 0 is the line up and is known as depolarization, it is here where the action potential is triggered and fast Na channels will open. Next, is phase 1 called early repolarization which is the little bit at the beginning of the plateau-here the Na channels will close. Then you have the plateau phase where Ca channels are open at the beginning and close at the end. Then is phase 3 called repolarization which is the big slope down and here is where the normal transmembrane ionic concentration gradients are restored. Finally, phase 4 which is the resting phase occurs. There are many resources online if you need more details, here is a pretty good one: http://www.pathophys.org/physiology-of-cardiac-conduction-and-contractility/
1. Lactose takes years to break down on its own. But if exposed to the protein lactase, the reaction proceeds very quickly, while lactase itself remains unchanged. Lactase is an example of a(n) . 2. A(n) is a molecule that can bind to an enzyme and prevent the enzyme from working. There are two types: a(n) binds to the active site of the enzyme; a(n) binds elsewhere on the enzyme. 3. Enzymes speed up chemical reactions by lowering the , which allows the reaction to proceed much more quickly. 4. During an enzymatic reaction, a molecule of binds to the enzyme and is broken down into one or more molecules of , which are released. 5. The specific location within an enzyme molecule where the substrate binds is called the .
Answers
Answer:
1.) Lactase is an example of ENZYME.
2.)An INHIBITOR is a molecule that can bind to an enzyme and prevent the enzyme from working.
3.)Enzymes speed up chemical reactions by lowering the ACTIVATION ENERGY,
4.) a molecule of SUBSTRATE binds to the enzyme and is broken down into one or more molecules of PRODUCT which are released.
5.) The specific location within an enzyme molecule where the substrate binds is called the ACTIVE SITE.
Explanation:
An enzyme is defined as the substances that aids in the breaking down of complex food substances, taken in by animals, into simple, soluble and diffusible substances before they can be absorbed into the body. In the enzymatic reactions, a molecule of SUBSTRATE binds to the ACTIVE SITE of an enzyme and is broken down into one or more molecules of PRODUCT which are released.
There are different types of enzymes which are named according to the type of good they digest, these include:
--> Lactase: breaks down Lactose
--> proteases: breaks down proteins
--> Amylases: breaks down carbohydrate
Enzymes have the following characteristics:
--> They are proteins
--> They are specific in action. For example Lactase can only act on lactose.
--> They can be inactivated by INHIBITORS.
--> They are sensitive to temperature
--> They speed up a reaction by lowering the ACTIVATION ENERGY