What is the word for a group of stars that’s not a constellation?.
Answers
Related Questions
Explain the physical meaning of each term in the following equations:
∂t
∂(rhou)
+div(rhouu)=−
∂x
∂p
+div(μgradu)+S
Mi
∂t
∂(rhoi)
+div(rhoiu)=−pdivu+div(kgradT)+Φ+S
i
Problem 2 (20 marks): Write the unsteady heat conduction equation for the case of constant specific heat c. Show that, with reference to the general equation
∂t
∂
(rhoϕ)+div(rhouϕ)=div(Γgradϕ)+S, this implies ϕ=T,u=0,Γ=k/c, and S=S
h
/c, where S
h
is the source term of the unsteady heat conduction equation.
Answers
We can derive the following relationships: ϕ=T (where ϕ represents the variable being solved for, which is temperature in this case), u=0 (no velocity in the heat conduction equation), Γ=k/c (thermal conductivity divided by specific heat), and S=S_h/c (where S_h is the source term in the unsteady heat conduction equation divided by specific heat).
These equations describe the physical quantities and their relationships involved in the conservation of momentum and energy, as well as the heat conduction equation for the case of constant specific heat.
In the given equations, let's break down the physical meaning of each term:
1. ∂t/∂(rhou) represents the rate of change of the momentum (rhou) with respect to time. It indicates how the momentum changes over time.
2. div(rhouu) is the divergence of the momentum flux (rhouu). It shows how the momentum is being distributed or spreading out in space.
3. ∂x/∂p signifies the rate of change of pressure (p) with respect to position (x). It tells us how the pressure changes as we move in space.
4. div(μgradu) represents the divergence of the viscous stress tensor (μgradu). It indicates how the viscous forces are distributed or spreading out in space.
5. S represents the source term, which includes any external forces or sources of momentum or energy.
6. ∂t/∂(rhoi) is the rate of change of the density of a particular species (rhoi) with respect to time. It tells us how the density of that species changes over time.
7. div(rhoiu) is the divergence of the mass flux of that particular species (rhoiu). It shows how the mass of that species is being distributed or spreading out in space.
8. −pdivu represents the negative divergence of the velocity field (u) multiplied by the pressure (p). It indicates the effect of pressure on the flow behavior.
9. div(kgradT) represents the divergence of the thermal flux (kgradT), where k is the thermal conductivity and gradT is the temperature gradient. It indicates how the heat is being distributed or spreading out in space.
10. Φ represents any additional heat sources or sinks in the system.
learn more about conservation of momentum
https://brainly.com/question/33316833
#SPJ11
Value analysis of (DEWA) Dubai Electricity & Water Authority ?
Answers
Value analysis is a method used to evaluate the worth and effectiveness of an organization or project.
In the case of DEWA (Dubai Electricity & Water Authority), conducting a value analysis can provide insights into the overall value created by the organization. Here are some key points to consider in a value analysis of DEWA:
1. Service Quality: Evaluate the quality and reliability of the electricity and water services provided by DEWA. Assess factors such as uptime, response time, customer satisfaction, and the overall impact on the daily lives of residents and businesses in Dubai.
2. Cost Efficiency: Analyze the cost-effectiveness of DEWA's operations, including the generation, transmission, and distribution of electricity, as well as water production and distribution. Assess the efficiency of resource utilization, cost management practices, and the impact on consumer tariffs.
3. Sustainability: Evaluate DEWA's commitment to sustainable practices, such as renewable energy integration, water conservation efforts, and environmental stewardship. Assess the organization's contributions to reducing carbon emissions and promoting a greener future.
4. Innovation and Technology: Assess DEWA's adoption of innovative technologies, such as smart grids, advanced metering systems, and digital solutions. Evaluate the impact of these technologies on service delivery, efficiency, and customer experience.
5. Stakeholder Engagement: Analyze DEWA's relationships with stakeholders, including customers, suppliers, government entities, and the community. Assess the effectiveness of communication, collaboration, and the organization's contribution to social and economic development in Dubai.
By conducting a comprehensive value analysis of DEWA, stakeholders can gain a holistic understanding of the organization's performance, impact, and value proposition. This analysis can guide decision-making, identify areas for improvement, and support DEWA's ongoing efforts to provide reliable, sustainable, and affordable electricity and water services to the residents and businesses of Dubai.
Learn more about Value analysis here:
brainly.com/question/30132218
#SPJ11
Question 55
Marks: 1
Long term effects of radiation on an individual are predictable.
Choose one answer.
a. True
b. False
Answers
False. While there are known long-term effects of radiation exposure, the specific effects on an individual can vary depending on factors such as the type and amount of radiation exposure, age, health status, and genetics.
Some known long-term effects of radiation exposure include an increased risk of cancer, genetic mutations, and damage to organs such as the thyroid and reproductive organs. However, the severity and timing of these effects can vary widely among individuals. Additionally, exposure to radiation can also have immediate effects such as skin burns and radiation sickness. It is important to note that the long-term effects of radiation exposure can be reduced through measures such as limiting exposure time, using protective equipment, and following proper safety protocols.
b. False
Long-term effects of radiation on an individual are not entirely predictable. While it is true that exposure to high levels of radiation can lead to an increased risk of certain health issues such as cancer and genetic mutations, the specific outcome for an individual depends on various factors. These factors include the type and amount of radiation, duration of exposure, age, and individual genetic makeup. Additionally, the latent period between radiation exposure and the onset of health issues can vary significantly, making it challenging to predict the exact long-term effects for a particular individual.
Learn more about health status here:-
https://brainly.com/question/14210656
#SPJ11
A silver cube with an edge length of 2. 28 cm2. 28 cm and a gold cube with an edge length of 2. 66 cm2. 66 cm are both heated to 89. 7 ∘C89. 7 ∘C and placed in 100. 5 mL 100. 5 mL of water at 19. 3 ∘C19. 3 ∘C. What is the final temperature of the water when thermal equilibrium is reached?
Answers
The final temperature of the water when thermal equilibrium is reached is approximately 30.7 °C. This is obtained by calculating the heat gained
final temperature of the water when thermal equilibrium is reached can be determined using the principle of heat transfer.
First, we need to calculate the heat gained or lost by each object. The amount of heat gained or lost can be calculated using the equation Q = mcΔT, where Q is the heat transferred, m is the mass, c is the specific heat capacity, and ΔT is the change in temperature.
Let's calculate the heat gained or lost by the silver cube. The mass of the silver cube can be calculated using the formula m = ρV, where ρ is the density and V is the volume. The density of silver is approximately 10.5 g/cm³. The volume of the cube can be calculated as V = (edge length)3.
Using the given edge length of 2.28 cm, we can calculate the volume of the silver cube as V = (2.28 cm)³ = 11.40 cm³.
The mass of the silver cube is then m = (10.5 g/cm³)(11.40 cm³) = 119.7 g.
Next, we calculate the heat gained or lost by the silver cube using Q = mcΔT. The specific heat capacity of silver is approximately 0.24 J/g·°C.
Given that the initial temperature of the silver cube is 89.7 °C and the final temperature of the water is unknown, we can write the equation as Qsilver = (119.7 g)(0.24 J/g·°C)(Tfinal - 89.7 °C).
Now, let's calculate the heat gained or lost by the gold cube. Using the same process as above, we find that the mass of the gold cube is 164.1 g.
The specific heat capacity of gold is approximately 0.13 J/g·°C.
Given that the initial temperature of the gold cube is 89.7 °C, we can write the equation as Qgold = (164.1 g)(0.13 J/g·°C)(Tfinal - 89.7 °C).
Since heat gained by the water equals the sum of the heat lost by the silver cube and the gold cube, we have Qwater = Qsilver + Qgold.
Now we can substitute the equations and solve for the final temperature of the water.
(100.5 mL)(1 g/mL)(4.18 J/g·°C)(Tfinal - 19.3 °C) = (119.7 g)(0.24 J/g·°C)(Tfinal - 89.7 °C) + (164.1 g)(0.13 J/g·°C)(Tfinal - 89.7 °C).
Simplifying and solving the equation, we find that the final temperature of the water when thermal equilibrium is reached is approximately 30.7 °C.
To know more about temperature visit;
brainly.com/question/7510619
#SPJ11
Sally has a mass of 50 kg and she is floating in space. She has 1000 balls each with a mass of 1 kg. If she starts from rest and starts continuously throwing each ball backwards at a relative speed of 60 m/s, then what would be her final speed after throwing the 1000th ball
Answers
Answer:
saxsccd
Explanation:
What happens to the gravity force if the mass of the planet is increased?
Answers
Answer:
The more mass an object has, the greater its gravitational field and gravity force will be.
Explanation:
gravity force = mass × gravitational field strength (g)
The more mass, the more g-force.
Newton's 3rd Law of Motion
For every__________ (or force), there is an ____________ and __________ action (or force).
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
For every action (or force), there is an equal and opposite action (or force).
Marsha and Wes are trying to create an amusement park on Mars. What dimensions do they need to create their first attraction, the Crater Craze Climber?
Answers
Assuming they have identified a suitable location on Mars with sufficient space, they will need to determine the height, width, and depth of the attraction. Here are some potential dimensions they could consider:
Height: Depending on the target age group, the height of the Crater Craze Climber could vary. If it's intended for younger children, the maximum height should be around 10-12 feet (3-3.6 meters). For older children or adults, it could be taller, up to 20-30 feet (6-9 meters).Width: The width of the attraction will depend on the number of climbers they want to accommodate at one time. A width of 20-30 feet (6-9 meters) would be suitable for a small to medium-sized attraction, while a larger attraction could be up to 50-60 feet (15-18 meters) wide.Depth: The depth of the attraction will depend on the level of difficulty they want to achieve. A shallow depth of 5-10 feet (1.5-3 meters) would be suitable for younger children or beginners, while a deeper depth of 20-30 feet (6-9 meters) would provide a greater challenge for older children or experienced climbers.These dimensions are just suggestions, and Marsha and Wes will need to consider their specific goals and constraints in creating the Crater Craze Climber. Additionally, they should consult with experts in engineering and safety to ensure the attraction is structurally sound and safe for visitors.
Learn more about mars here:
https://brainly.com/question/644043
#SPJ1
1. A kangaroo hops 84 m to the east in 7 seconds.
o What is the kangaroo's speed? 12 m/s
o What is the kangaroo's velocity?
Answers
Explanation:
Given parameters:
Distance hopped = 84m
Displacement = 84m due east
Time = 7s
Unknown:
Speed of kangaroo = ?
Velocity of kangaroo = ?
Solution:
To solve this problem,
Speed = \(\frac{distance}{time }\) = \(\frac{84}{7}\) = 12m/s
Velocity = \(\frac{displacement}{time}\) = \(\frac{84}{7}\) = 12m/s due east
State two sources of EMF cell other than the chemical cell
Answers
Answers
Explanation:
A photodiode or solar cell may be considered as a source of emf, similar to a battery, resulting in an electrical voltage generated by charge separation driven by light rather than chemical reaction. Other devices that produce emf are fuel cells, thermocouples, and thermopiles.
consider a case where the wave speed decreases from c to 0.71 c . by what factor does the wavelength change?
Answers
Answer: The wavelength must increase as well to maintain the same frequency.
Explanation: As a wave crosses a boundary into a new medium, its speed, and wavelength change while its frequency remains the same. If the speed increases, then the wavelength must increase as well to maintain the same frequency.
The wavelength will decrease by a factor of 1.4 if the wave speed decreases from c to 0.71c.
We know that the wavelength of a wave is given by the equation λ = v/f where λ is the wavelength, v is the wave speed and f is the frequency of the wave. If the wave speed decreases from c to 0.71 c, we can find the factor by which the wavelength changes by using the formula: λ1/λ2 = v2/v1 where λ1 and v1 are the original wavelength and wave speed respectively, and λ2 and v2 are the new values.
Substituting in the values, we get:λ1/λ2 = (0.71c)/c = 0.71Therefore, the wavelength will decrease by a factor of 1.4 (which is the reciprocal of 0.71) when the wave speed decreases from c to 0.71c.
Learn more about wavelength here:
https://brainly.com/question/29063816
#SPJ11
A sound wave traveling in water 144m/s has a wavelength of 0.5m determine the frequency of the wave
Answers
Heya!!
For calculate frequency, lets applicate formula:
\(\boxed{f=v/\lambda}\)
Δ Being Δ
f = Frequency = ?
v = Velocity = 144 m/s
\(\lambda\) = Wavelenght = 0,5 m
⇒ Let's replace according the formula:
\(\boxed{f = 144\ m/s / 0,5\ m }\)
⇒ Resolving
\(\boxed{f = 288\ Hz}\)
Result:
The frequency of that wave is 288 Hertz
Good Luck!!
Answer:
K Shut up bro
Explanation:
A boy shoots a .0025 kg rubber band up in the air. The rubber band gains 0.06615 J of energy. How high did the rubber band go, in meters?
Please explain.
Answers
Explanation:
Potential energy = m * g * h re-arrange to
PE/mg = h plug in the numbers
.06615 J / (9.81 m/s^2 * .0025 kg) = 2.7 m
1. What is the role of the battery in an electric circuit? a. Transformer b. Conductor c. Source d. switch
Answers
Answer:
Conductor
Explanation:
A battery holds all of the energy in itself. So without the battery, the circuit cannot work.
Hope this helped, and please mark as Brainliest <3
Use the vocabulary in the Word Bank to complete the following explanation.
Answers
asteroids that cross earth’s orbit may eventually collide with earth. if that were to happen, what could be the result?
Answers
If an asteroid that crosses Earth's orbit were to collide with our planet, it could have significant consequences depending on its size and impact location.
The effects of an asteroid impact can vary widely, ranging from localized destruction to global catastrophes. Here are some potential outcomes:
1. Localized Impact: If the asteroid is relatively small, it may result in a localized impact, causing damage over a limited area. This could lead to the destruction of buildings, infrastructure, and loss of life in the immediate vicinity of the impact site.
2. Regional Effects: Larger asteroids can cause more extensive damage, affecting larger regions. The impact could generate shockwaves, triggering earthquakes and tsunamis, particularly if it strikes an ocean. This could result in widespread destruction along coastlines and coastal communities.
3. Atmospheric Effects: A substantial asteroid impact can inject a large amount of dust and debris into the atmosphere. This debris can block sunlight, causing a temporary decrease in temperature on a global scale. The resulting change in climate can disrupt ecosystems, impact agriculture, and potentially lead to food shortages.
4. Global Catastrophe: In rare cases, a massive asteroid impact can have catastrophic consequences for the entire planet. It could trigger a significant release of energy, resulting in a fireball, massive shockwaves, and intense heat. The immediate effects would cause widespread devastation, with massive loss of life and destruction of infrastructure. Additionally, the dust and debris ejected into the atmosphere can lead to long-term climate effects, including a "nuclear winter" scenario, where the reduced sunlight and prolonged darkness disrupt ecosystems and seriously impact global food production.
It's important to note that while the potential consequences of an asteroid impact can be severe, the probability of a catastrophic collision with Earth from a known asteroid is relatively low. Scientists actively track and monitor near-Earth asteroids to identify potential threats and develop strategies for planetary defense if necessary.
To know more about nuclear visit:
brainly.com/question/13090058
#SPJ11
why are cepheid variables so important for measuring distances in astronomy?
Answers
Cepheid variables are crucial for measuring distances in astronomy.
Cepheid variables are a type of pulsating star that undergoes regular changes in brightness over time. The period of their brightness variations is directly related to their intrinsic luminosity, meaning that brighter Cepheids have longer periods.
This relationship, known as the period-luminosity relationship, allows astronomers to use Cepheids as "standard candles" for distance measurements. By measuring the period of a Cepheid and comparing it to its observed brightness, astronomers can determine its intrinsic luminosity and then calculate its distance using the inverse square law.
Since Cepheids are observable in distant galaxies, they serve as reliable distance indicators and have played a vital role in determining the scale of the universe and studying cosmic expansion.
For more questions like Cepheid variables click the link below:
https://brainly.com/question/28707403
#SPJ11
Cepheid variables are important in astronomy due to their unique period-luminosity relationship allowing astronomers to measure stellar distances. This relation has helped in the discovery of the universe's expansion and breaking the distance confines of parallax, aiding exploration into more distant parts of our Galaxy and others.
Explanation:Cepheid variables are important for measuring distances in astronomy due to their unique period-luminosity relationship. The
period-luminosity relation
states that the longer the period (the time it takes for the star to vary), the greater the luminosity (brightness) of the Cepheid variable star is. This relationship is essential as it allows astronomers to measure the distance of these stars once the period has been determined.
To initially define this relationship with actual numbers, astronomers had to measure distances to a few nearby Cepheids in a different way, typically by finding Cepheids in clusters with stars whose distances could be estimated using spectral analysis. Once this period-luminosity relation was calibrated, it could be used to estimate the distance of any Cepheid, regardless of its location.
Cepheids have become crucial markers in space, acting as cosmic signposts. For instance, in the 1920s, Edwin Hubble used Cepheid variables to discover the expansion of the universe. They have been instrumental in breaking the distance confines of parallax, allowing astronomers to explore more distant parts of our Galaxy and others.
Today, the search continues with modern instruments including the Hubble Space Telescope, identifying and measuring individual Cepheids in galaxies farther and farther away. Some Cepheids are known to be about 60 million light-years away.
Learn more about Cepheid variables here:https://brainly.com/question/32130830
#SPJ11
I need help with these questions ASAP .. I have to get them done tonight because it is due tomorrow

Answers
Answer:
22. A: 4000m C: 3200
23: The feature at point D is a mid ocean ridge
24. cold and dark
25. E is far closer sitting just on the edge of the ridge
an experiment involving the scientific method begins with a/an:
Answers
Answer:
Step 1. Make observations.
Step 2. Form a hypothesis.
Step 3. Make a prediction.
Step 4. Perform an experiment.
Step 5. Analyze the results of the experiment.
Step 6. Draw a conclusion.
Step 7. Report your results.
Explanation:
The first step in the Scientific Method is to make objective observations. These observations are based on specific events that have already happened and can be verified by others as true or false. Step 2. Form a hypothesis.
Our observations tell us about the past or the present. As scientists, we want to be able to predict future events. We must therefore use our ability to reason.
Scientists use their knowledge of past events to develop a general principle or explanation to help predict future events. The general principle is called a hypothesis. The type of reasoning involved is called inductive reasoning (deriving a generalization from specific details).
A hypothesis should have the following characteristics:
• It should be a general principle that holds across space and time
• It should be a tentative idea
• It should agree with available observations
• It should be kept as simple as possible.
• It should be testable and potentially falsifiable. In other words, there should be a
way to show the hypothesis is false; a way to disprove the hypothesis.
Some mammals have two hind limbs would be a useless hypothesis. There is no observation that would not fit this hypothesis!
All mammals have two hind limbs is a good hypothesis. We would look throughout the world at mammals. When we find whales, which have no hind limbs, we would have shown our hypothesis to be false; we have falsified the hypothesis.
When a hypothesis involves a cause-and-effect relationship, we state our hypothesis to indicate there is no effect. A hypothesis, which asserts no effect, is called a null hypothesis. For instance, the drug Celebra does not help relieve rheumatoid arthritis.
a downwind point of sailing about 100 degrees to 140 degrees from the wind, with the sails approximately three-quarters of the way out is which point of sail?
Answers
The point of sail described in your question is called a broad reach. When sailing a broad reach, the wind is coming from the side of the boat at an angle of about 100 to 140 degrees, making it a downwind point of sailing.
The sails are positioned approximately three-quarters of the way out, allowing them to catch as much wind as possible and propel the boat forward.
This is a popular point of sail for many sailors because it allows for faster speeds compared to sailing directly downwind (known as a run). It also provides a more comfortable ride than sailing close hauled (the point of sail where the boat is sailing as close to the wind as possible), as the boat is not heeled over as much.
When sailing a broad reach, it is important to keep an eye on the wind and adjust the sails as necessary to maintain optimal speed and control. If the wind shifts or gusts, the sails may need to be adjusted or the boat's course may need to be altered to maintain the desired point of sail.The point of sail described in your question is called a broad reach. When sailing a broad reach, the wind is coming from the side of the boat at an angle of about 100 to 140 degrees, making it a downwind point of sailing.
learn more about angle
https://brainly.com/question/31813650
#SPJ11
Use the particle model of matter to explain how a gas exerts pressure on the surfaces of its container.
Answers
The moving particles in a gas collide with each other and also with the walls of the container and as the collision increases, gases exert more pressure on the walls of the container.
What is kinetic theory of matter?Kinetic theory of matter states that “Matter is made up of those substances or particles which are constantly moving.” The energy level of the particles depends upon the temperature possessed by the matter. This helps us to determine whether that matter is in a solid, liquid, or gas state.
Thus, using the particle model of matter, we can how a gas exerts pressure on the surfaces of its container, and this occurs when the gas particles collides with one another. This collision of gas particles exert pressure on the surface of the container.
Learn more about kinetic theory here: https://brainly.com/question/8101588
#SPJ1
the weight of a body of certain mass becomes zero in space.why?write with reasons
Answers
Answer:
Weight is what you get when a certain amount of gravity is acting on that mass, and something, like the surface of a planet, is resisting that action. In space, when falling freely, there's nothing resisting the pull of gravity so weight disappears. Mass however stays.
hope this helps u
Explanation:
what obstacles faced scientists in breaking the sound barrier
Answers
Breaking the sound barrier, which is the transition from subsonic to supersonic speed, presented several challenges and obstacles for scientists and engineers. Some of the obstacles faced were:
1. Aerodynamic forces: As an aircraft approaches the speed of sound, it encounters a range of aerodynamic forces that can cause instability and vibrations. These forces include shock waves, which can create areas of high pressure and drag on the aircraft, making it difficult to maintain control.
2. Engine power: Breaking the sound barrier requires a significant amount of engine power to overcome the drag and other aerodynamic forces. Developing engines that were powerful enough to achieve supersonic speeds was a major challenge for scientists and engineers.
3. Structural integrity: The shock waves and other forces encountered during supersonic flight can place significant stress on an aircraft's structure, potentially leading to failure or damage. Designing and building aircraft that could withstand these forces was a major challenge.
4. Instrumentation: To safely break the sound barrier, pilots need accurate and reliable instrumentation to monitor the aircraft's speed, altitude, and other critical parameters.
Developing instrumentation that could function reliably at supersonic speeds was another obstacle that scientists and engineers had to overcome.
In summary, breaking the sound barrier presented several challenges and obstacles, including aerodynamic forces, engine power, structural integrity, and instrumentation. Overcoming these obstacles required significant advances in technology and engineering.
To know more about sound barrier refer here
https://brainly.com/question/31029109#
#SPJ11
An electric pole casts a shadow of 24 m long . If the tip of the shadow is 25m far from the top of the pole , how high is the pole?????
Answers
Answer:
7 m
Explanation:
a^ + b^=c^
a^ + 24^=25^
a^+576=625
a^=625-576
a^=49
a=7
Which statements best describe X-rays?
Answers
Answer:x rays are electromagnetic waves.
x rays are transverse waves
x rays travel at the speed of light
Explanation:
A pendulum is swinging next to a wall. The distance from the bob of the pendulum to the wall varies in a periodic way that can be modeled by a trigonometric function.
Answers
The formula of the trigonometric function that models the distance HHH from the pendulum's bob to the wall after t seconds is
H(t) = 15 -6sin(2.5π(t -0.5))
Detailed explanation:
The function can be expressed as the following for the midline M, amplitude A, period T, and time t0 at which the function deviates from the midline:
H(t) = M -Asin(2π/T(t -t0))
The equation is based on the parameters M=15, A=6, T=0.8, and t0 = 0.5.
H(t) is equal to 15 -6sin(2.5π(t -0.5))
What is function?The trigonometric functions in mathematics are real functions that connect the right-angled triangle's angle to the ratios of its two side lengths .In all areas of study that involve geometry, such as geodesy, solid mechanics, celestial mechanics, and many others, they are widely used.
To learn more about functions visit:
https://brainly.com/question/15607563
#SPJ4
The correct question is:
A pendulum is swinging next to a wall. The distance from the bob of the swinging pendulum to the wall varies in a periodic way that can be modeled by a trigonometric function.
The function has period 0.80.80, point, 8 seconds, amplitude 6 \text{ cm}6 cm6, start text, space, c, m, end text, and midline H = 15 \text{ cm}H=15 cmH, equals, 15, start text, space, c, m, end text. At time t = 0.5t=0.5t, equals, 0, point, 5 seconds, the bob is at its midline, moving towards the wall.
Find the formula of the trigonometric function that models the distance HHH from the pendulum's bob to the wall after t seconds. Define the function using radians.
A heavy truck and a light car travel at the same velocity side-by-side on the highway. Both drivers apply the same braking force at the same moment. What will happen to the two vehicles
Answers
A heavy truck and a light car travel at the same velocity side-by-side on the highway. Both drivers apply the same braking force at the same moment Maintaining the minimum pressure of 90 psi in the system providies the necessary stopping power for the vehicle
Before driving a truck or bus with a dual air brake system, the pressure in the entire system should be at least 90 psi. The dual air brake system is a safety mechanism used in larger vehicles like trucks and buses. It consists of two separate air brake systems, each with its own air reservoirs, brake chambers, and control valves. This redundancy provides added safety in case one of the systems fails. To ensure effective braking, it is necessary to have a sufficient amount of compressed air in the system. The minimum required pressure for the entire dual air brake system is typically set at 90 psi (pounds per square inch). This pressure level is considered adequate to ensure reliable and responsive braking performance. Maintaining the minimum pressure of 90 psi in the system ensures that there is enough force to engage the brake chambers and apply the brakes effectively when needed. It allows for proper air distribution to the brakes and ensures that the braking system functions optimally, providing the necessary stopping power for the vehicle. Adhering to the minimum pressure requirement helps maintain the safety standards and operational reliability of the air brake system, which is crucial for the safe operation of trucks and buses on the road.
Learn more about pressure here:
https://brainly.com/question/32771988
#SPJ11
Use the information from the graph to answer the question. A graph titled Velocity versus Time shows time in seconds on the x axis, numbered 0 to 25, velocity in meters per second on the y axis, numbered 0 to 40. A line starts at (0, 10) and ends at (25, 35). What is the total displacement of the object? m
Answers
Answer:
its -2.5 on edge 2020
Explanation:
i just took the quiz answer above is the next part of the quiz, answer is 562.5
Answer:
What is the acceleration of the object?
-2.5 m/s2
Students raced each other in the gym while the teacher recorded each student's speed. Jeremy ran 14 miles per hour, Isaiah ran 10 miles per hour, Jonah ran 13 miles per hour, and Alexis ran 16 miles per hour. Which of the bar graphs should the teacher use to compare the students' speeds? (pictures re the choices)




Answers
In a gym the students raced with each other and teacher is recording everyone's speed than the second graph is representing correctly.
What is a graph?A graph is a visual depiction of statistical data or a logical relationship between variables. Graphs serve a predictive purpose because they have the virtue of displaying broad trends in the mathematical behavior of data. However, as just approximations, they may be incorrect and occasionally deceptive.
Most graphs have two axes, with the axis denoting a set of independent variables and the vertical axis denoting a set of dependent variables. The most typical graph is indeed a broken-line chart, where the regression coefficient is typically a factor of duration.
In the second graph the speed of every student is represented accurately, therefore the second graph is correct.
To know more about Graph :
https://brainly.com/question/17267403
#SPJ2
I need help please pleaseee
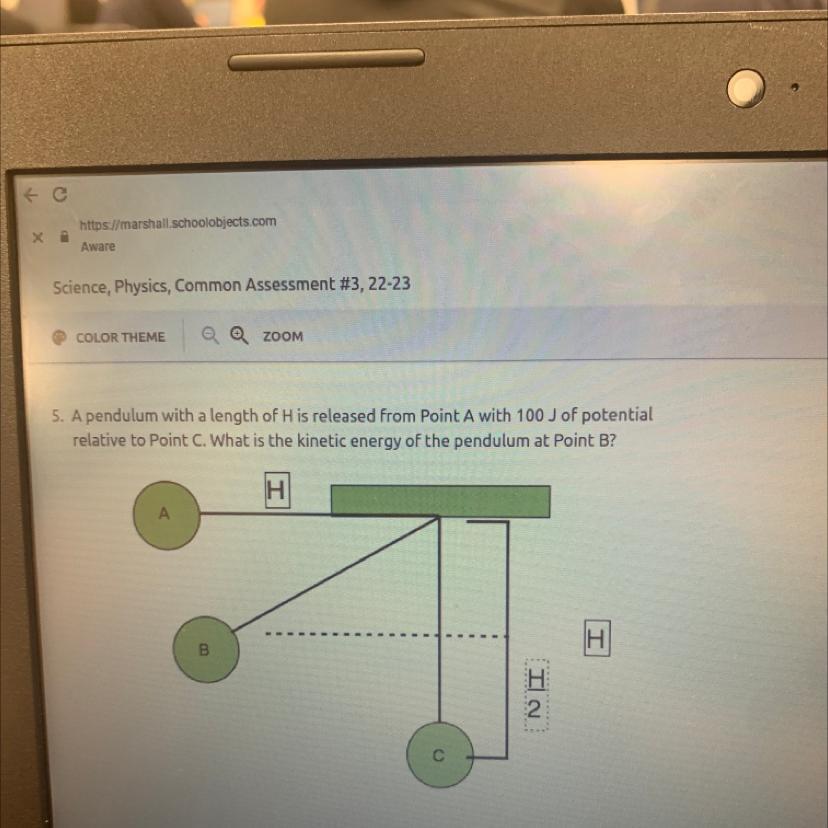
Answers
The kinetic energy of the simple pendulum at point B is 50 J
What are kinetic energy and potential energy?The kinetic energy of a body is the energy possessed by the body by virtue of its motion.
Kinetic energy is the product of the mass and the velocity of the moving body.
The potential energy of a body is the energy possessed by a body by virtue of its state or position.
Considering the simple pendulum, its energy alternates between kinetic energy and potential energy from point A to C.
At point B, midway through the motion of the pendulum, its energy is a mixture of potential and kinetic energy,
The kinetic energy of the body = 1/2 * 100 J
The kinetic energy of the body = 50 J
Learn more about kinetic energy at: https://brainly.com/question/8101588
#SPJ1